mirror of
https://github.com/Luzifer/staticmap.git
synced 2024-12-20 04:41:18 +00:00
Remove old vendoring
Signed-off-by: Knut Ahlers <knut@ahlers.me>
This commit is contained in:
parent
b480398d1c
commit
bfc88cb04e
534 changed files with 0 additions and 229356 deletions
173
Gopkg.lock
generated
173
Gopkg.lock
generated
|
|
@ -1,173 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# This file is autogenerated, do not edit; changes may be undone by the next 'dep ensure'.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "320790ed53294a789e715b3d0d5da8110efea1a2"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers"
|
||||
packages = [
|
||||
"accessLogger",
|
||||
"http",
|
||||
"str"
|
||||
]
|
||||
revision = "b0da2aa67ecc05ee4c8848d679b4a11a2fa578b2"
|
||||
version = "v2.6.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/Luzifer/rconfig"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "7aef1d393c1e2d0758901853b59981c7adc67c7e"
|
||||
version = "v1.2.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/Wessie/appdirs"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "6573e894f8e294cbae0c4e45c25ff9f2e2918a4e"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/didip/tollbooth"
|
||||
packages = [
|
||||
".",
|
||||
"errors",
|
||||
"libstring",
|
||||
"limiter"
|
||||
]
|
||||
revision = "c95eaa3ddc98f635a91e218b48727fb2e06613ea"
|
||||
version = "v4.0.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "845bca739e263e1cd38de25024a47b4d6acbfc1f"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "6166aa3c1afaee416f384645a81636267aee6d25"
|
||||
version = "v1.0.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/golang/freetype"
|
||||
packages = [
|
||||
"raster",
|
||||
"truetype"
|
||||
]
|
||||
revision = "e2365dfdc4a05e4b8299a783240d4a7d5a65d4e4"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/golang/geo"
|
||||
packages = [
|
||||
"r1",
|
||||
"r2",
|
||||
"r3",
|
||||
"s1",
|
||||
"s2"
|
||||
]
|
||||
revision = "e41ca803f92c4c1770133cfa5b4fc8249a7dbe82"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/gorilla/context"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "08b5f424b9271eedf6f9f0ce86cb9396ed337a42"
|
||||
version = "v1.1.1"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/gorilla/mux"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "e3702bed27f0d39777b0b37b664b6280e8ef8fbf"
|
||||
version = "v1.6.2"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/lucasb-eyer/go-colorful"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "d9cec903b20cbeda6062366e460c2c1bdc717e4d"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/patrickmn/go-cache"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "a3647f8e31d79543b2d0f0ae2fe5c379d72cedc0"
|
||||
version = "v2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "c155da19408a8799da419ed3eeb0cb5db0ad5dbc"
|
||||
version = "v1.0.5"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/spf13/pflag"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "583c0c0531f06d5278b7d917446061adc344b5cd"
|
||||
version = "v1.0.1"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/tkrajina/gpxgo"
|
||||
packages = ["gpx"]
|
||||
revision = "7848cf26f5a58b4a4e23b89a4b67cfc3d52dd042"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "golang.org/x/crypto"
|
||||
packages = ["ssh/terminal"]
|
||||
revision = "027cca12c2d63e3d62b670d901e8a2c95854feec"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "golang.org/x/image"
|
||||
packages = [
|
||||
"font",
|
||||
"font/basicfont",
|
||||
"font/plan9font",
|
||||
"math/fixed"
|
||||
]
|
||||
revision = "af66defab954cb421ca110193eed9477c8541e2a"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "golang.org/x/net"
|
||||
packages = ["context"]
|
||||
revision = "db08ff08e8622530d9ed3a0e8ac279f6d4c02196"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "golang.org/x/sys"
|
||||
packages = [
|
||||
"unix",
|
||||
"windows"
|
||||
]
|
||||
revision = "6c888cc515d3ed83fc103cf1d84468aad274b0a7"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "golang.org/x/time"
|
||||
packages = ["rate"]
|
||||
revision = "fbb02b2291d28baffd63558aa44b4b56f178d650"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
branch = "v2"
|
||||
name = "gopkg.in/validator.v2"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "135c24b11c19e52befcae2ec3fca5d9b78c4e98e"
|
||||
|
||||
[[projects]]
|
||||
name = "gopkg.in/yaml.v2"
|
||||
packages = ["."]
|
||||
revision = "5420a8b6744d3b0345ab293f6fcba19c978f1183"
|
||||
version = "v2.2.1"
|
||||
|
||||
[solve-meta]
|
||||
analyzer-name = "dep"
|
||||
analyzer-version = 1
|
||||
inputs-digest = "c59f72846eca4898dab7e7c3fc9a28b340f42aafbe4ac4866ad1ae33c382ea76"
|
||||
solver-name = "gps-cdcl"
|
||||
solver-version = 1
|
||||
66
Gopkg.toml
66
Gopkg.toml
|
|
@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Gopkg.toml example
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Refer to https://golang.github.io/dep/docs/Gopkg.toml.html
|
||||
# for detailed Gopkg.toml documentation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# required = ["github.com/user/thing/cmd/thing"]
|
||||
# ignored = ["github.com/user/project/pkgX", "bitbucket.org/user/project/pkgA/pkgY"]
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [[constraint]]
|
||||
# name = "github.com/user/project"
|
||||
# version = "1.0.0"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [[constraint]]
|
||||
# name = "github.com/user/project2"
|
||||
# branch = "dev"
|
||||
# source = "github.com/myfork/project2"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [[override]]
|
||||
# name = "github.com/x/y"
|
||||
# version = "2.4.0"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# [prune]
|
||||
# non-go = false
|
||||
# go-tests = true
|
||||
# unused-packages = true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers"
|
||||
version = "2.3.1"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/Luzifer/rconfig"
|
||||
version = "1.2.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
|
||||
version = "1.0.5"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/didip/tollbooth"
|
||||
version = "4.0.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
version = "1.0.0"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/golang/geo"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
name = "github.com/gorilla/mux"
|
||||
version = "1.6.1"
|
||||
|
||||
[[constraint]]
|
||||
branch = "master"
|
||||
name = "github.com/lucasb-eyer/go-colorful"
|
||||
|
||||
[prune]
|
||||
go-tests = true
|
||||
unused-packages = true
|
||||
1
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/.gitignore
generated
vendored
1
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/.gitignore
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
|||
*.png
|
||||
36
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
36
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
|||
language: go
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.9
|
||||
- master
|
||||
|
||||
install:
|
||||
- go get -t ./...
|
||||
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
allow_failures:
|
||||
- go: master
|
||||
# Don't wait for tip tests to finish. Mark the test run green if the
|
||||
# tests pass on the stable versions of Go.
|
||||
fast_finish: true
|
||||
|
||||
notifications:
|
||||
email: false
|
||||
|
||||
# Anything in before_script that returns a nonzero exit code will
|
||||
# flunk the build and immediately stop. It's sorta like having
|
||||
# set -e enabled in bash.
|
||||
before_script:
|
||||
- GO_FILES=$(find . -iname '*.go' -type f) # All the .go files
|
||||
- go get github.com/golang/lint/golint # Linter
|
||||
- go get honnef.co/go/tools/cmd/megacheck # Badass static analyzer/linter
|
||||
- go get github.com/fzipp/gocyclo
|
||||
|
||||
# script always run to completion (set +e). All of these code checks are must haves
|
||||
# in a modern Go project.
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- test -z $(gofmt -s -l $GO_FILES) # Fail if a .go file hasn't been formatted with gofmt
|
||||
- go vet ./... # go vet is the official Go static analyzer
|
||||
- megacheck ./... # "go vet on steroids" + linter
|
||||
- gocyclo -over 19 $GO_FILES # forbid code with huge functions
|
||||
- golint -set_exit_status $(go list ./...) # one last linter
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/LICENSE
generated
vendored
21
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||
The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2016 Florian Pigorsch
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
249
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/README.md
generated
vendored
249
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/README.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,249 +0,0 @@
|
|||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps)
|
||||
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/flopp/go-staticmaps)
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/flopp/go-staticmaps)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps/)
|
||||
|
||||
# go-staticmaps
|
||||
A go (golang) library and command line tool to render static map images using OpenStreetMap tiles.
|
||||
|
||||
## What?
|
||||
go-staticmaps is a golang library that allows you to create nice static map images from OpenStreetMap tiles, along with markers of different size and color, as well as paths and colored areas.
|
||||
|
||||
go-staticmaps comes with a command line tool called `create-static-map` for use in shell scripts, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## How?
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Installing go-staticmaps is as easy as
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
go get -u github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the command line tool, use
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
go get -u github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps/create-static-map
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, your local Go installation must be setup up properly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Library Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Create a 400x300 pixel map with a red marker:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps"
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
ctx := sm.NewContext()
|
||||
ctx.SetSize(400, 300)
|
||||
ctx.AddMarker(sm.NewMarker(s2.LatLngFromDegrees(52.514536, 13.350151), color.RGBA{0xff, 0, 0, 0xff}, 16.0))
|
||||
|
||||
img, err := ctx.Render()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := gg.SavePNG("my-map.png", img); err != nil {
|
||||
panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
See [GoDoc](https://godoc.org/github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps) for a complete documentation and the source code of the [command line tool](https://github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps/blob/master/create-static-map/create-static-map.go) for an example how to use the package.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Command Line Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
create-static-map [OPTIONS]
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a static map
|
||||
|
||||
Application Options:
|
||||
--width=PIXELS Width of the generated static map image (default: 512)
|
||||
--height=PIXELS Height of the generated static map image (default: 512)
|
||||
-o, --output=FILENAME Output file name (default: map.png)
|
||||
-t, --type=MAPTYPE Select the map type; list possible map types with '--type list'
|
||||
-c, --center=LATLNG Center coordinates (lat,lng) of the static map
|
||||
-z, --zoom=ZOOMLEVEL Zoom factor
|
||||
-b, --bbox=NW_LATLNG|SE_LATLNG
|
||||
Set the bounding box (NW_LATLNG = north-western point of the
|
||||
bounding box, SW_LATLNG = southe-western point of the bounding
|
||||
box)
|
||||
--background=COLOR Background color (default: transparent)
|
||||
-u, --useragent=USERAGENT
|
||||
Overwrite the default HTTP user agent string
|
||||
-m, --marker=MARKER Add a marker to the static map
|
||||
-p, --path=PATH Add a path to the static map
|
||||
-a, --area=AREA Add an area to the static map
|
||||
-C, --circle=CIRCLE Add a circle to the static map
|
||||
|
||||
Help Options:
|
||||
-h, --help Show this help message
|
||||
|
||||
### General
|
||||
The command line interface tries to resemble [Google's Static Maps API](https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/static-maps/intro).
|
||||
If neither `--bbox`, `--center`, nor `--zoom` are given, the map extent is determined from the specified markers, paths and areas.
|
||||
|
||||
`--background` lets you specify a color used for map areas that are not covered by map tiles (areas north of 85°/south of -85°).
|
||||
|
||||
### Markers
|
||||
The `--marker` option defines one or more map markers of the same style. Use multiple `--marker` options to add markers of different styles.
|
||||
|
||||
--marker MARKER_STYLES|LATLNG|LATLNG|...
|
||||
|
||||
`LATLNG` is a comma separated pair of latitude and longitude, e.g. `52.5153,13.3564`.
|
||||
|
||||
`MARKER_STYLES` consists of a set of style descriptors separated by the pipe character `|`:
|
||||
|
||||
- `color:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: `red`)
|
||||
- `size:SIZE` - where `SIZE` is one of `mid`, `small`, `tiny`, or some number > 0 (default: `mid`)
|
||||
- `label:LABEL` - where `LABEL` is an alpha numeric character, i.e. `A`-`Z`, `a`-`z`, `0`-`9`; (default: no label)
|
||||
- `labelcolor:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: `black` or `white`, depending on the marker color)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Paths
|
||||
The `--path` option defines a path on the map. Use multiple `--path` options to add multiple paths to the map.
|
||||
|
||||
--path PATH_STYLES|LATLNG|LATLNG|...
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
--path PATH_STYLES|gpx:my_gpx_file.gpx
|
||||
|
||||
`PATH_STYLES` consists of a set of style descriptors separated by the pipe character `|`:
|
||||
|
||||
- `color:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: `red`)
|
||||
- `weight:WEIGHT` - where `WEIGHT` is the line width in pixels (defaut: `5`)
|
||||
|
||||
### Areas
|
||||
The `--area` option defines a closed area on the map. Use multiple `--area` options to add multiple areas to the map.
|
||||
|
||||
--area AREA_STYLES|LATLNG|LATLNG|...
|
||||
|
||||
`AREA_STYLES` consists of a set of style descriptors separated by the pipe character `|`:
|
||||
|
||||
- `color:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: `red`)
|
||||
- `weight:WEIGHT` - where `WEIGHT` is the line width in pixels (defaut: `5`)
|
||||
- `fill:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: none)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Circles
|
||||
The `--circles` option defines one or more circles of the same style. Use multiple `--circle` options to add circles of different styles.
|
||||
|
||||
--circle CIRCLE_STYLES|LATLNG|LATLNG|...
|
||||
|
||||
`LATLNG` is a comma separated pair of latitude and longitude, e.g. `52.5153,13.3564`.
|
||||
|
||||
`CIRCLE_STYLES` consists of a set of style descriptors separated by the pipe character `|`:
|
||||
|
||||
- `color:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: `red`)
|
||||
- `fill:COLOR` - where `COLOR` is either of the form `0xRRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, or one of `black`, `blue`, `brown`, `green`, `orange`, `purple`, `red`, `yellow`, `white` (default: no fill color)
|
||||
- `radius:RADIUS` - where `RADIUS` is te circle radius in meters (default: `100.0`)
|
||||
- `weight:WEIGHT` - where `WEIGHT` is the line width in pixels (defaut: `5`)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Maps
|
||||
|
||||
Centered at "N 52.514536 E 13.350151" with zoom level 10:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ create-static-map --width 600 --height 400 -o map1.png -c "52.514536,13.350151" -z 10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
A map with a marker at "N 52.514536 E 13.350151" with zoom level 14 (no need to specify the map's center - it is automatically computed from the marker(s)):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ create-static-map --width 600 --height 400 -o map2.png -z 14 -m "52.514536,13.350151"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
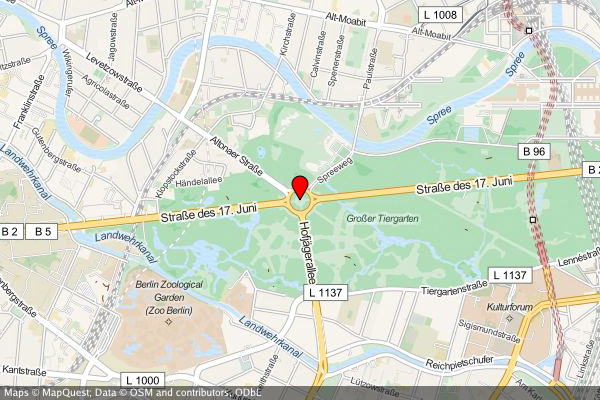
|
||||
|
||||
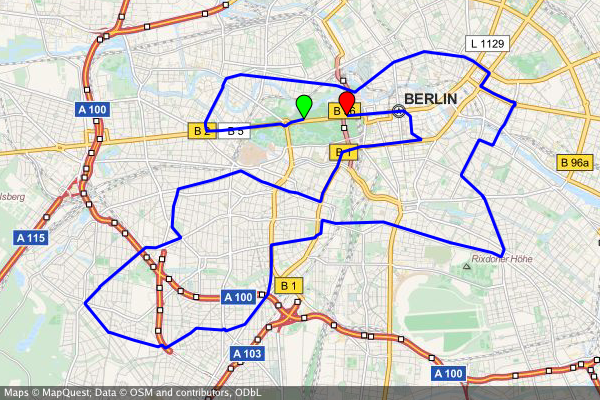
A map with two markers (red and green). If there are more than two markers in the map, a *good* zoom level can be determined automatically:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ create-static-map --width 600 --height 400 -o map3.png -m "color:red|52.514536,13.350151" -m "color:green|52.516285,13.377746"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a map of the Berlin Marathon
|
||||
|
||||
create-static-map --width 800 --height 600 \
|
||||
--marker "color:green|52.5153,13.3564" \
|
||||
--marker "color:red|52.5160,13.3711" \
|
||||
--output "berlin-marathon.png" \
|
||||
--path "color:blue|weight:2|gpx:berlin-marathon.gpx"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Create a map of the US capitals
|
||||
|
||||
create-static-map --width 800 --height 400 \
|
||||
--output "us-capitals.png" \
|
||||
--marker "color:blue|size:tiny|32.3754,-86.2996|58.3637,-134.5721|33.4483,-112.0738|34.7244,-92.2789|\
|
||||
38.5737,-121.4871|39.7551,-104.9881|41.7665,-72.6732|39.1615,-75.5136|30.4382,-84.2806|33.7545,-84.3897|\
|
||||
21.2920,-157.8219|43.6021,-116.2125|39.8018,-89.6533|39.7670,-86.1563|41.5888,-93.6203|39.0474,-95.6815|\
|
||||
38.1894,-84.8715|30.4493,-91.1882|44.3294,-69.7323|38.9693,-76.5197|42.3589,-71.0568|42.7336,-84.5466|\
|
||||
44.9446,-93.1027|32.3122,-90.1780|38.5698,-92.1941|46.5911,-112.0205|40.8136,-96.7026|39.1501,-119.7519|\
|
||||
43.2314,-71.5597|40.2202,-74.7642|35.6816,-105.9381|42.6517,-73.7551|35.7797,-78.6434|46.8084,-100.7694|\
|
||||
39.9622,-83.0007|35.4931,-97.4591|44.9370,-123.0272|40.2740,-76.8849|41.8270,-71.4087|34.0007,-81.0353|\
|
||||
44.3776,-100.3177|36.1589,-86.7821|30.2687,-97.7452|40.7716,-111.8882|44.2627,-72.5716|37.5408,-77.4339|\
|
||||
47.0449,-122.9016|38.3533,-81.6354|43.0632,-89.4007|41.1389,-104.8165"
|
||||
|
||||
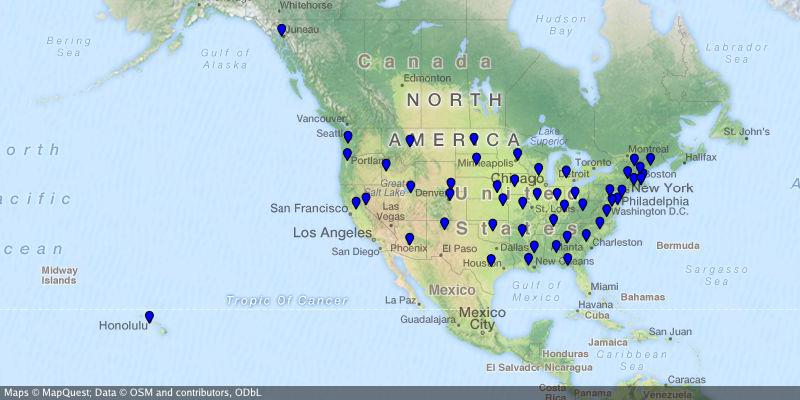
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a map of Australia
|
||||
...where the Northern Territory is highlighted and the capital Canberra is marked.
|
||||
|
||||
create-static-map --width 800 --height 600 \
|
||||
--center="-26.284973,134.303764" \
|
||||
--output "australia.png" \
|
||||
--marker "color:blue|-35.305200,149.121574" \
|
||||
--area "color:0x00FF00|fill:0x00FF007F|weight:2|-25.994024,129.013847|-25.994024,137.989677|-16.537670,138.011649|\
|
||||
-14.834820,135.385917|-12.293236,137.033866|-11.174554,130.398124|-12.925791,130.167411|-14.866678,129.002860"
|
||||
|
||||
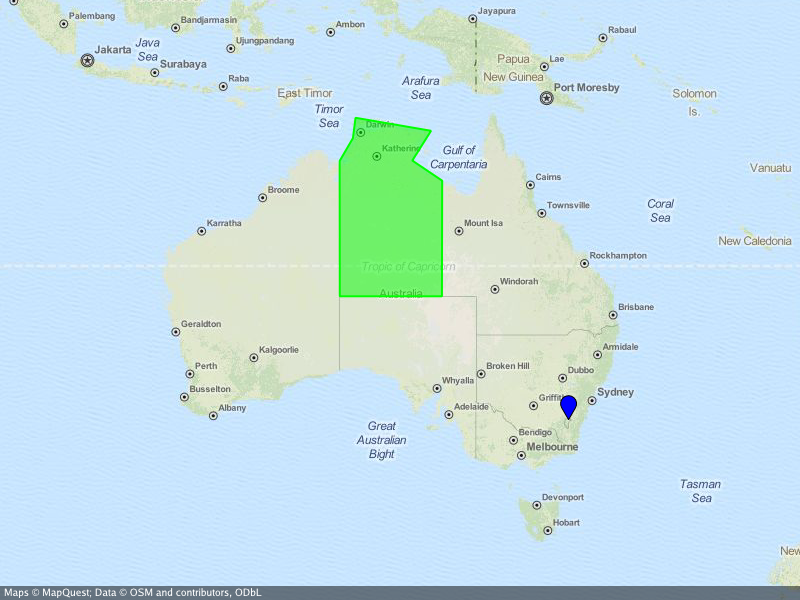
|
||||
|
||||
## Acknowledgements
|
||||
Besides the go standard library, go-staticmaps uses
|
||||
|
||||
- [OpenStreetMap](http://openstreetmap.org/), [Thunderforest](http://www.thunderforest.com/), [OpenTopoMap](http://www.opentopomap.org/), [Stamen](http://maps.stamen.com/) and [Carto](http://carto.com) as map tile providers
|
||||
- [Go Graphics](https://github.com/fogleman/gg) for 2D drawing
|
||||
- [S2 geometry library](https://github.com/golang/geo) for spherical geometry calculations
|
||||
- [appdirs](https://github.com/Wessie/appdirs) for platform specific system directories
|
||||
- [gpxgo](github.com/tkrajina/gpxgo) for loading GPX files
|
||||
- [go-coordsparser](https://github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser) for parsing geo coordinates
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributors
|
||||
- [Kooper](https://github.com/Kooper): fixed *library usage examples*
|
||||
- [felix](https://github.com/felix): added *more tile servers*
|
||||
- [wiless](https://github.com/wiless): suggested to add user definable *marker label colors*
|
||||
- [noki](https://github.com/Noki): suggested to add a user definable *bounding box*
|
||||
- [digitocero](https://github.com/digitocero): reported and fixed *type mismatch error*
|
||||
- [bcicen](https://github.com/bcicen): reported and fixed *syntax error in examples*
|
||||
- [pshevtsov](https://github.com/pshevtsov): fixed *drawing of empty attribution strings*
|
||||
- [Luzifer](https://github.com/Luzifer): added *overwritable user agent strings* to comply with the OSM tile usage policy
|
||||
- [Jason Fox](https://github.com/jasonpfox): added `RenderWithBounds` function
|
||||
- [Alexander A. Kapralov](https://github.com/alnkapa): initial *circles* implementation
|
||||
- [tsukumaru](https://github.com/tsukumaru): added `NewArea` and `NewPath` functions
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch & Contributors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
104
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/area.go
generated
vendored
104
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/area.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser"
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Area represents a area or area on the map
|
||||
type Area struct {
|
||||
MapObject
|
||||
Positions []s2.LatLng
|
||||
Color color.Color
|
||||
Fill color.Color
|
||||
Weight float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewArea creates a new Area
|
||||
func NewArea(positions []s2.LatLng, col color.Color, fill color.Color, weight float64) *Area {
|
||||
a := new(Area)
|
||||
a.Positions = positions
|
||||
a.Color = col
|
||||
a.Fill = fill
|
||||
a.Weight = weight
|
||||
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseAreaString parses a string and returns an area
|
||||
func ParseAreaString(s string) (*Area, error) {
|
||||
area := new(Area)
|
||||
area.Color = color.RGBA{0xff, 0, 0, 0xff}
|
||||
area.Fill = color.Transparent
|
||||
area.Weight = 5.0
|
||||
|
||||
for _, ss := range strings.Split(s, "|") {
|
||||
if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "color:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
area.Color, err = ParseColorString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "fill:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
area.Fill, err = ParseColorString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "weight:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
area.Weight, err = strconv.ParseFloat(suffix, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lat, lng, err := coordsparser.Parse(ss)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
area.Positions = append(area.Positions, s2.LatLngFromDegrees(lat, lng))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return area, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Area) extraMarginPixels() float64 {
|
||||
return 0.5 * p.Weight
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Area) bounds() s2.Rect {
|
||||
r := s2.EmptyRect()
|
||||
for _, ll := range p.Positions {
|
||||
r = r.AddPoint(ll)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Area) draw(gc *gg.Context, trans *transformer) {
|
||||
if len(p.Positions) <= 1 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gc.ClearPath()
|
||||
gc.SetLineWidth(p.Weight)
|
||||
gc.SetLineCap(gg.LineCapRound)
|
||||
gc.SetLineJoin(gg.LineJoinRound)
|
||||
for _, ll := range p.Positions {
|
||||
gc.LineTo(trans.ll2p(ll))
|
||||
}
|
||||
gc.ClosePath()
|
||||
gc.SetColor(p.Fill)
|
||||
gc.FillPreserve()
|
||||
gc.SetColor(p.Color)
|
||||
gc.Stroke()
|
||||
}
|
||||
53
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/bbox.go
generated
vendored
53
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/bbox.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CreateBBox creates a bounding box from a north-western point
|
||||
// (lat/lng in degrees) and a south-eastern point (lat/lng in degrees).
|
||||
// Note that you can create a bounding box wrapping over the antimeridian at
|
||||
// lng=+-/180° by nwlng > selng.
|
||||
func CreateBBox(nwlat float64, nwlng float64, selat float64, selng float64) (*s2.Rect, error) {
|
||||
if nwlat < -90 || nwlat > 90 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Out of range nwlat (%f) must be in [-90, 90]", nwlat)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if nwlng < -180 || nwlng > 180 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Out of range nwlng (%f) must be in [-180, 180]", nwlng)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if selat < -90 || selat > 90 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Out of range selat (%f) must be in [-90, 90]", selat)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if selng < -180 || selng > 180 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Out of range selng (%f) must be in [-180, 180]", selng)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if nwlat == selat {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("nwlat and selat must not be equal")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if nwlng == selng {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("nwlng and selng must not be equal")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bbox := new(s2.Rect)
|
||||
if selat < nwlat {
|
||||
bbox.Lat.Lo = selat * math.Pi / 180.0
|
||||
bbox.Lat.Hi = nwlat * math.Pi / 180.0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
bbox.Lat.Lo = nwlat * math.Pi / 180.0
|
||||
bbox.Lat.Hi = selat * math.Pi / 180.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
bbox.Lng = s1.IntervalFromEndpoints(nwlng*math.Pi/180.0, selng*math.Pi/180.0)
|
||||
|
||||
return bbox, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
128
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/circle.go
generated
vendored
128
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/circle.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,128 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser"
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Circle represents a circle on the map
|
||||
type Circle struct {
|
||||
MapObject
|
||||
Position s2.LatLng
|
||||
Color color.Color
|
||||
Fill color.Color
|
||||
Weight float64
|
||||
Radius float64 // in m.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewCircle creates a new circle
|
||||
func NewCircle(pos s2.LatLng, col, fill color.Color, radius, weight float64) *Circle {
|
||||
return &Circle{
|
||||
Position: pos,
|
||||
Color: col,
|
||||
Fill: fill,
|
||||
Weight: weight,
|
||||
Radius: radius,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseCircleString parses a string and returns an array of circles
|
||||
func ParseCircleString(s string) (circles []*Circle, err error) {
|
||||
circles = make([]*Circle, 0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
var col color.Color = color.RGBA{0xff, 0, 0, 0xff}
|
||||
var fill color.Color = color.Transparent
|
||||
radius := 100.0
|
||||
weight := 5.0
|
||||
|
||||
for _, ss := range strings.Split(s, "|") {
|
||||
if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "color:"); ok {
|
||||
col, err = ParseColorString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "fill:"); ok {
|
||||
fill, err = ParseColorString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "radius:"); ok {
|
||||
if radius, err = strconv.ParseFloat(suffix, 64); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "weight:"); ok {
|
||||
if weight, err = strconv.ParseFloat(suffix, 64); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lat, lng, err := coordsparser.Parse(ss)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
c := NewCircle(s2.LatLngFromDegrees(lat, lng), col, fill, radius, weight)
|
||||
circles = append(circles, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return circles, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Circle) getLatLng(plus bool) s2.LatLng {
|
||||
const (
|
||||
R = 6371000.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
th := m.Radius / R
|
||||
br := 0 / float64(s1.Degree)
|
||||
if !plus {
|
||||
th *= -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
lat := m.Position.Lat.Radians()
|
||||
lat1 := math.Asin(math.Sin(lat)*math.Cos(th) + math.Cos(lat)*math.Sin(th)*math.Cos(br))
|
||||
lng1 := m.Position.Lng.Radians() +
|
||||
math.Atan2(math.Sin(br)*math.Sin(th)*math.Cos(lat),
|
||||
math.Cos(th)-math.Sin(lat)*math.Sin(lat1))
|
||||
return s2.LatLng{
|
||||
Lat: s1.Angle(lat1),
|
||||
Lng: s1.Angle(lng1),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Circle) extraMarginPixels() float64 {
|
||||
return 0.5 * m.Weight
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Circle) bounds() s2.Rect {
|
||||
r := s2.EmptyRect()
|
||||
r = r.AddPoint(m.getLatLng(false))
|
||||
r = r.AddPoint(m.getLatLng(true))
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Circle) draw(gc *gg.Context, trans *transformer) {
|
||||
if !CanDisplay(m.Position) {
|
||||
log.Printf("Circle coordinates not displayable: %f/%f", m.Position.Lat.Degrees(), m.Position.Lng.Degrees())
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ll := m.getLatLng(true)
|
||||
x, y := trans.ll2p(m.Position)
|
||||
x1, y1 := trans.ll2p(ll)
|
||||
radius := math.Sqrt(math.Pow(x1-x, 2) + math.Pow(y1-y, 2))
|
||||
gc.ClearPath()
|
||||
gc.SetLineWidth(m.Weight)
|
||||
gc.SetLineCap(gg.LineCapRound)
|
||||
gc.SetLineJoin(gg.LineJoinRound)
|
||||
gc.DrawCircle(x, y, radius)
|
||||
gc.SetColor(m.Fill)
|
||||
gc.FillPreserve()
|
||||
gc.SetColor(m.Color)
|
||||
gc.Stroke()
|
||||
}
|
||||
67
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/color.go
generated
vendored
67
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/color.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseColorString parses hex color strings (i.e. `0xRRGGBB`, `#RRGGBB`, `0xRRGGBBAA`, `#RRGGBBAA`), and names colors (e.g. 'black', 'blue', ...)
|
||||
func ParseColorString(s string) (color.Color, error) {
|
||||
s = strings.ToLower(strings.TrimSpace(s))
|
||||
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`^(0x|#)([A-Fa-f0-9]{6})$`)
|
||||
matches := re.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if matches != nil {
|
||||
var r, g, b int
|
||||
fmt.Sscanf(matches[2], "%2x%2x%2x", &r, &g, &b)
|
||||
return color.RGBA{uint8(r), uint8(g), uint8(b), 0xff}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
re = regexp.MustCompile(`^(0x|#)([A-Fa-f0-9]{8})$`)
|
||||
matches = re.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if matches != nil {
|
||||
var r, g, b, a int
|
||||
fmt.Sscanf(matches[2], "%2x%2x%2x%2x", &r, &g, &b, &a)
|
||||
rr := float64(r) * float64(a) / 256.0
|
||||
gg := float64(g) * float64(a) / 256.0
|
||||
bb := float64(b) * float64(a) / 256.0
|
||||
return color.RGBA{uint8(rr), uint8(gg), uint8(bb), uint8(a)}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch s {
|
||||
case "black":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "blue":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0x00, 0x00, 0xff, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "brown":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0x96, 0x4b, 0x00, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "green":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0x00, 0xff, 0x00, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "orange":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0xff, 0x7f, 0x00, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "purple":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0x7f, 0x00, 0x7f, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "red":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0xff, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "yellow":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0xff, 0xff, 0x00, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "white":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff}, nil
|
||||
case "transparent":
|
||||
return color.RGBA{0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return color.Transparent, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse color string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Luminance computes the luminance (~ brightness) of the given color. Range: 0.0 for black to 1.0 for white.
|
||||
func Luminance(col color.Color) float64 {
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := col.RGBA()
|
||||
return (float64(r)*0.299 + float64(g)*0.587 + float64(b)*0.114) / float64(0xffff)
|
||||
}
|
||||
503
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/context.go
generated
vendored
503
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/context.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,503 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package sm (~ static maps) renders static map images from OSM tiles with markers, paths, and filled areas.
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"image/draw"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Context holds all information about the map image that is to be rendered
|
||||
type Context struct {
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
|
||||
hasZoom bool
|
||||
zoom int
|
||||
|
||||
hasCenter bool
|
||||
center s2.LatLng
|
||||
|
||||
hasBoundingBox bool
|
||||
boundingBox s2.Rect
|
||||
|
||||
background color.Color
|
||||
|
||||
markers []*Marker
|
||||
paths []*Path
|
||||
areas []*Area
|
||||
circles []*Circle
|
||||
overlays []*TileProvider
|
||||
|
||||
userAgent string
|
||||
tileProvider *TileProvider
|
||||
|
||||
overrideAttribution *string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContext creates a new instance of Context
|
||||
func NewContext() *Context {
|
||||
t := new(Context)
|
||||
t.width = 512
|
||||
t.height = 512
|
||||
t.hasZoom = false
|
||||
t.hasCenter = false
|
||||
t.hasBoundingBox = false
|
||||
t.background = nil
|
||||
t.userAgent = ""
|
||||
t.tileProvider = NewTileProviderOpenStreetMaps()
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTileProvider sets the TileProvider to be used
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetTileProvider(t *TileProvider) {
|
||||
m.tileProvider = t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetUserAgent sets the HTTP user agent string used when downloading map tiles
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetUserAgent(a string) {
|
||||
m.userAgent = a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetSize sets the size of the generated image
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetSize(width, height int) {
|
||||
m.width = width
|
||||
m.height = height
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetZoom sets the zoom level
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetZoom(zoom int) {
|
||||
m.zoom = zoom
|
||||
m.hasZoom = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCenter sets the center coordinates
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetCenter(center s2.LatLng) {
|
||||
m.center = center
|
||||
m.hasCenter = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBoundingBox sets the bounding box
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetBoundingBox(bbox s2.Rect) {
|
||||
m.boundingBox = bbox
|
||||
m.hasBoundingBox = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBackground sets the background color (used as a fallback for areas without map tiles)
|
||||
func (m *Context) SetBackground(col color.Color) {
|
||||
m.background = col
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddMarker adds a marker to the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) AddMarker(marker *Marker) {
|
||||
m.markers = append(m.markers, marker)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearMarkers removes all markers from the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) ClearMarkers() {
|
||||
m.markers = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPath adds a path to the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) AddPath(path *Path) {
|
||||
m.paths = append(m.paths, path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearPaths removes all paths from the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) ClearPaths() {
|
||||
m.paths = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddArea adds an area to the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) AddArea(area *Area) {
|
||||
m.areas = append(m.areas, area)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearAreas removes all areas from the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) ClearAreas() {
|
||||
m.areas = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddCircle adds an circle to the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) AddCircle(circle *Circle) {
|
||||
m.circles = append(m.circles, circle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearCircles removes all circles from the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) ClearCircles() {
|
||||
m.circles = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddOverlay adds an overlay to the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) AddOverlay(overlay *TileProvider) {
|
||||
m.overlays = append(m.overlays, overlay)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearOverlays removes all overlays from the Context
|
||||
func (m *Context) ClearOverlays() {
|
||||
m.overlays = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OverrideAttribution sets a custom attribution string (or none if empty)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Pay attention you might be violating the terms of usage for the
|
||||
// selected map provider - only use the function if you are aware of this!
|
||||
func (m *Context) OverrideAttribution(attribution string) {
|
||||
m.overrideAttribution = &attribution
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Context) determineBounds() s2.Rect {
|
||||
r := s2.EmptyRect()
|
||||
for _, marker := range m.markers {
|
||||
r = r.Union(marker.bounds())
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, path := range m.paths {
|
||||
r = r.Union(path.bounds())
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, area := range m.areas {
|
||||
r = r.Union(area.bounds())
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, circle := range m.circles {
|
||||
r = r.Union(circle.bounds())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Context) determineExtraMarginPixels() float64 {
|
||||
p := 0.0
|
||||
for _, marker := range m.markers {
|
||||
if pp := marker.extraMarginPixels(); pp > p {
|
||||
p = pp
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, path := range m.paths {
|
||||
if pp := path.extraMarginPixels(); pp > p {
|
||||
p = pp
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, area := range m.areas {
|
||||
if pp := area.extraMarginPixels(); pp > p {
|
||||
p = pp
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, circle := range m.circles {
|
||||
if pp := circle.extraMarginPixels(); pp > p {
|
||||
p = pp
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Context) determineZoom(bounds s2.Rect, center s2.LatLng) int {
|
||||
b := bounds.AddPoint(center)
|
||||
if b.IsEmpty() || b.IsPoint() {
|
||||
return 15
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tileSize := m.tileProvider.TileSize
|
||||
margin := 4.0 + m.determineExtraMarginPixels()
|
||||
w := (float64(m.width) - 2.0*margin) / float64(tileSize)
|
||||
h := (float64(m.height) - 2.0*margin) / float64(tileSize)
|
||||
minX := (b.Lo().Lng.Degrees() + 180.0) / 360.0
|
||||
maxX := (b.Hi().Lng.Degrees() + 180.0) / 360.0
|
||||
minY := (1.0 - math.Log(math.Tan(b.Lo().Lat.Radians())+(1.0/math.Cos(b.Lo().Lat.Radians())))/math.Pi) / 2.0
|
||||
maxY := (1.0 - math.Log(math.Tan(b.Hi().Lat.Radians())+(1.0/math.Cos(b.Hi().Lat.Radians())))/math.Pi) / 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
dx := maxX - minX
|
||||
for dx < 0 {
|
||||
dx = dx + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
for dx > 1 {
|
||||
dx = dx - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
dy := math.Abs(maxY - minY)
|
||||
|
||||
zoom := 1
|
||||
for zoom < 30 {
|
||||
tiles := float64(uint(1) << uint(zoom))
|
||||
if dx*tiles > w || dy*tiles > h {
|
||||
return zoom - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
zoom = zoom + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 15
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Context) determineZoomCenter() (int, s2.LatLng, error) {
|
||||
bounds := m.determineBounds()
|
||||
if m.hasBoundingBox && !m.boundingBox.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
center := m.boundingBox.Center()
|
||||
return m.determineZoom(m.boundingBox, center), center, nil
|
||||
} else if m.hasCenter {
|
||||
if m.hasZoom {
|
||||
return m.zoom, m.center, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m.determineZoom(bounds, m.center), m.center, nil
|
||||
} else if !bounds.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
center := bounds.Center()
|
||||
if m.hasZoom {
|
||||
return m.zoom, center, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m.determineZoom(bounds, center), center, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 0, s2.LatLngFromDegrees(0, 0), errors.New("Cannot determine map extent: no center coordinates given, no bounding box given, no content (markers, paths, areas) given")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type transformer struct {
|
||||
zoom int
|
||||
numTiles float64 // number of tiles per dimension at this zoom level
|
||||
tileSize int // tile size in pixels from this provider
|
||||
pWidth, pHeight int // pixel size of returned set of tiles
|
||||
pCenterX, pCenterY int // pixel location of requested center in set of tiles
|
||||
tCountX, tCountY int // download area in tile units
|
||||
tCenterX, tCenterY float64 // tile index to requested center
|
||||
tOriginX, tOriginY int // bottom left tile to download
|
||||
pMinX, pMaxX int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newTransformer(width int, height int, zoom int, llCenter s2.LatLng, tileSize int) *transformer {
|
||||
t := new(transformer)
|
||||
|
||||
t.zoom = zoom
|
||||
t.numTiles = math.Exp2(float64(t.zoom))
|
||||
t.tileSize = tileSize
|
||||
|
||||
// fractional tile index to center of requested area
|
||||
t.tCenterX, t.tCenterY = t.ll2t(llCenter)
|
||||
|
||||
ww := float64(width) / float64(tileSize)
|
||||
hh := float64(height) / float64(tileSize)
|
||||
|
||||
// origin tile to fulfill request
|
||||
t.tOriginX = int(math.Floor(t.tCenterX - 0.5*ww))
|
||||
t.tOriginY = int(math.Floor(t.tCenterY - 0.5*hh))
|
||||
|
||||
// tiles in each axis to fulfill request
|
||||
t.tCountX = 1 + int(math.Floor(t.tCenterX+0.5*ww)) - t.tOriginX
|
||||
t.tCountY = 1 + int(math.Floor(t.tCenterY+0.5*hh)) - t.tOriginY
|
||||
|
||||
// final pixel dimensions of area returned
|
||||
t.pWidth = t.tCountX * tileSize
|
||||
t.pHeight = t.tCountY * tileSize
|
||||
|
||||
// Pixel location in returned image for center of requested area
|
||||
t.pCenterX = int((t.tCenterX - float64(t.tOriginX)) * float64(tileSize))
|
||||
t.pCenterY = int((t.tCenterY - float64(t.tOriginY)) * float64(tileSize))
|
||||
|
||||
t.pMinX = t.pCenterX - width/2
|
||||
t.pMaxX = t.pMinX + width
|
||||
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ll2t returns fractional tile index for a lat/lng points
|
||||
func (t *transformer) ll2t(ll s2.LatLng) (float64, float64) {
|
||||
x := t.numTiles * (ll.Lng.Degrees() + 180.0) / 360.0
|
||||
y := t.numTiles * (1 - math.Log(math.Tan(ll.Lat.Radians())+(1.0/math.Cos(ll.Lat.Radians())))/math.Pi) / 2.0
|
||||
return x, y
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *transformer) ll2p(ll s2.LatLng) (float64, float64) {
|
||||
x, y := t.ll2t(ll)
|
||||
x = float64(t.pCenterX) + (x-t.tCenterX)*float64(t.tileSize)
|
||||
y = float64(t.pCenterY) + (y-t.tCenterY)*float64(t.tileSize)
|
||||
|
||||
offset := t.numTiles * float64(t.tileSize)
|
||||
if x < float64(t.pMinX) {
|
||||
for x < float64(t.pMinX) {
|
||||
x = x + offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if x >= float64(t.pMaxX) {
|
||||
for x >= float64(t.pMaxX) {
|
||||
x = x - offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return x, y
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rect returns an s2.Rect bounding box around the set of tiles described by transformer
|
||||
func (t *transformer) Rect() (bbox s2.Rect) {
|
||||
// transform from https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Slippy_map_tilenames#Go
|
||||
invNumTiles := 1.0 / t.numTiles
|
||||
// Get latitude bounds
|
||||
n := math.Pi - 2.0*math.Pi*float64(t.tOriginY)*invNumTiles
|
||||
bbox.Lat.Hi = math.Atan(0.5 * (math.Exp(n) - math.Exp(-n)))
|
||||
n = math.Pi - 2.0*math.Pi*float64(t.tOriginY+t.tCountY)*invNumTiles
|
||||
bbox.Lat.Lo = math.Atan(0.5 * (math.Exp(n) - math.Exp(-n)))
|
||||
// Get longtitude bounds, much easier
|
||||
bbox.Lng.Lo = float64(t.tOriginX)*invNumTiles*2.0*math.Pi - math.Pi
|
||||
bbox.Lng.Hi = float64(t.tOriginX+t.tCountX)*invNumTiles*2.0*math.Pi - math.Pi
|
||||
return bbox
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render actually renders the map image including all map objects (markers, paths, areas)
|
||||
func (m *Context) Render() (image.Image, error) {
|
||||
zoom, center, err := m.determineZoomCenter()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tileSize := m.tileProvider.TileSize
|
||||
trans := newTransformer(m.width, m.height, zoom, center, tileSize)
|
||||
img := image.NewRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, trans.pWidth, trans.pHeight))
|
||||
gc := gg.NewContextForRGBA(img)
|
||||
if m.background != nil {
|
||||
draw.Draw(img, img.Bounds(), &image.Uniform{m.background}, image.ZP, draw.Src)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fetch and draw tiles to img
|
||||
layers := []*TileProvider{m.tileProvider}
|
||||
if m.overlays != nil {
|
||||
layers = append(layers, m.overlays...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, layer := range layers {
|
||||
if err := m.renderLayer(gc, zoom, trans, tileSize, layer); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// draw map objects
|
||||
for _, area := range m.areas {
|
||||
area.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, path := range m.paths {
|
||||
path.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, marker := range m.markers {
|
||||
marker.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, circle := range m.circles {
|
||||
circle.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// crop image
|
||||
croppedImg := image.NewRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, int(m.width), int(m.height)))
|
||||
draw.Draw(croppedImg, image.Rect(0, 0, int(m.width), int(m.height)),
|
||||
img, image.Point{trans.pCenterX - int(m.width)/2, trans.pCenterY - int(m.height)/2},
|
||||
draw.Src)
|
||||
|
||||
attribution := m.tileProvider.Attribution
|
||||
if m.overrideAttribution != nil {
|
||||
attribution = *m.overrideAttribution
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// draw attribution
|
||||
if attribution == "" {
|
||||
return croppedImg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, textHeight := gc.MeasureString(attribution)
|
||||
boxHeight := textHeight + 4.0
|
||||
gc = gg.NewContextForRGBA(croppedImg)
|
||||
gc.SetRGBA(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5)
|
||||
gc.DrawRectangle(0.0, float64(m.height)-boxHeight, float64(m.width), boxHeight)
|
||||
gc.Fill()
|
||||
gc.SetRGBA(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.75)
|
||||
gc.DrawString(attribution, 4.0, float64(m.height)-4.0)
|
||||
|
||||
return croppedImg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RenderWithBounds actually renders the map image including all map objects (markers, paths, areas).
|
||||
// The returned image covers requested area as well as any tiles necessary to cover that area, which may
|
||||
// be larger than the request.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Specific bounding box of returned image is provided to support image registration with other data
|
||||
func (m *Context) RenderWithBounds() (image.Image, s2.Rect, error) {
|
||||
zoom, center, err := m.determineZoomCenter()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, s2.Rect{}, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tileSize := m.tileProvider.TileSize
|
||||
trans := newTransformer(m.width, m.height, zoom, center, tileSize)
|
||||
img := image.NewRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, trans.pWidth, trans.pHeight))
|
||||
gc := gg.NewContextForRGBA(img)
|
||||
if m.background != nil {
|
||||
draw.Draw(img, img.Bounds(), &image.Uniform{m.background}, image.ZP, draw.Src)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fetch and draw tiles to img
|
||||
layers := []*TileProvider{m.tileProvider}
|
||||
if m.overlays != nil {
|
||||
layers = append(layers, m.overlays...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, layer := range layers {
|
||||
if err := m.renderLayer(gc, zoom, trans, tileSize, layer); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, s2.Rect{}, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// draw map objects
|
||||
for _, area := range m.areas {
|
||||
area.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, path := range m.paths {
|
||||
path.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, circle := range m.circles {
|
||||
circle.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, marker := range m.markers {
|
||||
marker.draw(gc, trans)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// draw attribution
|
||||
if m.tileProvider.Attribution == "" {
|
||||
return img, trans.Rect(), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, textHeight := gc.MeasureString(m.tileProvider.Attribution)
|
||||
boxHeight := textHeight + 4.0
|
||||
gc.SetRGBA(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5)
|
||||
gc.DrawRectangle(0.0, float64(trans.pHeight)-boxHeight, float64(trans.pWidth), boxHeight)
|
||||
gc.Fill()
|
||||
gc.SetRGBA(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.75)
|
||||
gc.DrawString(m.tileProvider.Attribution, 4.0, float64(m.height)-4.0)
|
||||
|
||||
return img, trans.Rect(), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Context) renderLayer(gc *gg.Context, zoom int, trans *transformer, tileSize int, provider *TileProvider) error {
|
||||
t := NewTileFetcher(provider)
|
||||
if m.userAgent != "" {
|
||||
t.SetUserAgent(m.userAgent)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tiles := (1 << uint(zoom))
|
||||
for xx := 0; xx < trans.tCountX; xx++ {
|
||||
x := trans.tOriginX + xx
|
||||
if x < 0 {
|
||||
x = x + tiles
|
||||
} else if x >= tiles {
|
||||
x = x - tiles
|
||||
}
|
||||
for yy := 0; yy < trans.tCountY; yy++ {
|
||||
y := trans.tOriginY + yy
|
||||
if y < 0 || y >= tiles {
|
||||
log.Printf("Skipping out of bounds tile %d/%d", x, y)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if tileImg, err := t.Fetch(zoom, x, y); err == nil {
|
||||
gc.DrawImage(tileImg, xx*tileSize, yy*tileSize)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
log.Printf("Error downloading tile file: %s", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
25
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/map_object.go
generated
vendored
25
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/map_object.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// MapObject is the interface for all objects on the map
|
||||
type MapObject interface {
|
||||
bounds() s2.Rect
|
||||
extraMarginPixels() float64
|
||||
draw(dc *gg.Context, trans *transformer)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CanDisplay checks if pos is generally displayable (i.e. its latitude is in [-85,85])
|
||||
func CanDisplay(pos s2.LatLng) bool {
|
||||
const minLatitude float64 = -85.0
|
||||
const maxLatitude float64 = 85.0
|
||||
return (minLatitude <= pos.Lat.Degrees()) && (pos.Lat.Degrees() <= maxLatitude)
|
||||
}
|
||||
149
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/marker.go
generated
vendored
149
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/marker.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser"
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker represents a marker on the map
|
||||
type Marker struct {
|
||||
MapObject
|
||||
Position s2.LatLng
|
||||
Color color.Color
|
||||
Size float64
|
||||
Label string
|
||||
LabelColor color.Color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMarker creates a new Marker
|
||||
func NewMarker(pos s2.LatLng, col color.Color, size float64) *Marker {
|
||||
m := new(Marker)
|
||||
m.Position = pos
|
||||
m.Color = col
|
||||
m.Size = size
|
||||
m.Label = ""
|
||||
if Luminance(m.Color) >= 0.5 {
|
||||
m.LabelColor = color.RGBA{0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0xff}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
m.LabelColor = color.RGBA{0xff, 0xff, 0xff, 0xff}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseSizeString(s string) (float64, error) {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case s == "mid":
|
||||
return 16.0, nil
|
||||
case s == "small":
|
||||
return 12.0, nil
|
||||
case s == "tiny":
|
||||
return 8.0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if ss, err := strconv.ParseFloat(s, 64); err != nil && ss > 0 {
|
||||
return ss, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 0.0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse size string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseMarkerString parses a string and returns an array of markers
|
||||
func ParseMarkerString(s string) ([]*Marker, error) {
|
||||
markers := make([]*Marker, 0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
var markerColor color.Color = color.RGBA{0xff, 0, 0, 0xff}
|
||||
size := 16.0
|
||||
label := ""
|
||||
var labelColor color.Color
|
||||
|
||||
for _, ss := range strings.Split(s, "|") {
|
||||
if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "color:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
markerColor, err = ParseColorString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "label:"); ok {
|
||||
label = suffix
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "size:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
size, err = parseSizeString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "labelcolor:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
labelColor, err = ParseColorString(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lat, lng, err := coordsparser.Parse(ss)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
m := NewMarker(s2.LatLngFromDegrees(lat, lng), markerColor, size)
|
||||
m.Label = label
|
||||
if labelColor != nil {
|
||||
m.SetLabelColor(labelColor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
markers = append(markers, m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return markers, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetLabelColor sets the color of the marker's text label
|
||||
func (m *Marker) SetLabelColor(col color.Color) {
|
||||
m.LabelColor = col
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Marker) extraMarginPixels() float64 {
|
||||
return 1.0 + 1.5*m.Size
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Marker) bounds() s2.Rect {
|
||||
r := s2.EmptyRect()
|
||||
r = r.AddPoint(m.Position)
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *Marker) draw(gc *gg.Context, trans *transformer) {
|
||||
if !CanDisplay(m.Position) {
|
||||
log.Printf("Marker coordinates not displayable: %f/%f", m.Position.Lat.Degrees(), m.Position.Lng.Degrees())
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gc.ClearPath()
|
||||
gc.SetLineJoin(gg.LineJoinRound)
|
||||
gc.SetLineWidth(1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
radius := 0.5 * m.Size
|
||||
x, y := trans.ll2p(m.Position)
|
||||
gc.DrawArc(x, y-m.Size, radius, (90.0+60.0)*math.Pi/180.0, (360.0+90.0-60.0)*math.Pi/180.0)
|
||||
gc.LineTo(x, y)
|
||||
gc.ClosePath()
|
||||
gc.SetColor(m.Color)
|
||||
gc.FillPreserve()
|
||||
gc.SetRGB(0, 0, 0)
|
||||
gc.Stroke()
|
||||
|
||||
if m.Label != "" {
|
||||
gc.SetColor(m.LabelColor)
|
||||
gc.DrawStringAnchored(m.Label, x, y-m.Size, 0.5, 0.5)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
113
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/path.go
generated
vendored
113
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/path.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser"
|
||||
"github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s2"
|
||||
"github.com/tkrajina/gpxgo/gpx"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Path represents a path or area on the map
|
||||
type Path struct {
|
||||
MapObject
|
||||
Positions []s2.LatLng
|
||||
Color color.Color
|
||||
Weight float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewPath creates a new Path
|
||||
func NewPath(positions []s2.LatLng, col color.Color, weight float64) *Path {
|
||||
p := new(Path)
|
||||
p.Positions = positions
|
||||
p.Color = col
|
||||
p.Weight = weight
|
||||
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParsePathString parses a string and returns a path
|
||||
func ParsePathString(s string) ([]*Path, error) {
|
||||
paths := make([]*Path, 0, 0)
|
||||
currentPath := new(Path)
|
||||
currentPath.Color = color.RGBA{0xff, 0, 0, 0xff}
|
||||
currentPath.Weight = 5.0
|
||||
|
||||
for _, ss := range strings.Split(s, "|") {
|
||||
if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "color:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
if currentPath.Color, err = ParseColorString(suffix); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "weight:"); ok {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
if currentPath.Weight, err = strconv.ParseFloat(suffix, 64); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if ok, suffix := hasPrefix(ss, "gpx:"); ok {
|
||||
gpxData, err := gpx.ParseFile(suffix)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, trk := range gpxData.Tracks {
|
||||
for _, seg := range trk.Segments {
|
||||
p := new(Path)
|
||||
p.Color = currentPath.Color
|
||||
p.Weight = currentPath.Weight
|
||||
for _, pt := range seg.Points {
|
||||
p.Positions = append(p.Positions, s2.LatLngFromDegrees(pt.GetLatitude(), pt.GetLongitude()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(p.Positions) > 0 {
|
||||
paths = append(paths, p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lat, lng, err := coordsparser.Parse(ss)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
currentPath.Positions = append(currentPath.Positions, s2.LatLngFromDegrees(lat, lng))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(currentPath.Positions) > 0 {
|
||||
paths = append(paths, currentPath)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return paths, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Path) extraMarginPixels() float64 {
|
||||
return 0.5 * p.Weight
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Path) bounds() s2.Rect {
|
||||
r := s2.EmptyRect()
|
||||
for _, ll := range p.Positions {
|
||||
r = r.AddPoint(ll)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Path) draw(gc *gg.Context, trans *transformer) {
|
||||
if len(p.Positions) <= 1 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gc.ClearPath()
|
||||
gc.SetLineWidth(p.Weight)
|
||||
gc.SetLineCap(gg.LineCapRound)
|
||||
gc.SetLineJoin(gg.LineJoinRound)
|
||||
for _, ll := range p.Positions {
|
||||
gc.LineTo(trans.ll2p(ll))
|
||||
}
|
||||
gc.SetColor(p.Color)
|
||||
gc.Stroke()
|
||||
}
|
||||
167
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/tile_fetcher.go
generated
vendored
167
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/tile_fetcher.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,167 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
_ "image/jpeg" // to be able to decode jpegs
|
||||
_ "image/png" // to be able to decode pngs
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/Wessie/appdirs"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TileFetcher downloads map tile images from a TileProvider
|
||||
type TileFetcher struct {
|
||||
tileProvider *TileProvider
|
||||
cacheDir string
|
||||
useCaching bool
|
||||
userAgent string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileFetcher creates a new Tilefetcher struct
|
||||
func NewTileFetcher(tileProvider *TileProvider) *TileFetcher {
|
||||
t := new(TileFetcher)
|
||||
t.tileProvider = tileProvider
|
||||
app := appdirs.New("go-staticmaps", "flopp.net", "0.1")
|
||||
t.cacheDir = fmt.Sprintf("%s/%s", app.UserCache(), tileProvider.Name)
|
||||
t.useCaching = true
|
||||
t.userAgent = "Mozilla/5.0+(compatible; go-staticmaps/0.1; https://github.com/flopp/go-staticmaps)"
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetUserAgent sets the HTTP user agent string used when downloading map tiles
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) SetUserAgent(a string) {
|
||||
t.userAgent = a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) url(zoom, x, y int) string {
|
||||
shard := ""
|
||||
ss := len(t.tileProvider.Shards)
|
||||
if len(t.tileProvider.Shards) > 0 {
|
||||
shard = t.tileProvider.Shards[(x+y)%ss]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.tileProvider.getURL(shard, zoom, x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) cacheFileName(zoom int, x, y int) string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s/%d/%d/%d", t.cacheDir, zoom, x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ToggleCaching enables/disables caching
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) ToggleCaching(enabled bool) {
|
||||
t.useCaching = enabled
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fetch download (or retrieves from the cache) a tile image for the specified zoom level and tile coordinates
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) Fetch(zoom, x, y int) (image.Image, error) {
|
||||
if t.useCaching {
|
||||
fileName := t.cacheFileName(zoom, x, y)
|
||||
cachedImg, err := t.loadCache(fileName)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return cachedImg, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
url := t.url(zoom, x, y)
|
||||
data, err := t.download(url)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
img, _, err := image.Decode(bytes.NewBuffer(data))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if t.useCaching {
|
||||
fileName := t.cacheFileName(zoom, x, y)
|
||||
if err := t.storeCache(fileName, data); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Printf("Failed to store map tile as '%s': %s", fileName, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return img, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) download(url string) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
req, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", url, nil)
|
||||
req.Header.Set("User-Agent", t.userAgent)
|
||||
|
||||
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if resp.StatusCode != 200 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("GET %s: %s", url, resp.Status)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
defer resp.Body.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
contents, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return contents, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) loadCache(fileName string) (image.Image, error) {
|
||||
file, err := os.Open(fileName)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
img, _, err := image.Decode(file)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return img, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) createCacheDir(path string) error {
|
||||
src, err := os.Stat(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return os.MkdirAll(path, 0777)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if src.IsDir() {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("File exists but is not a directory: %s", path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileFetcher) storeCache(fileName string, data []byte) error {
|
||||
dir, _ := filepath.Split(fileName)
|
||||
|
||||
if err := t.createCacheDir(dir); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
file, err := os.Create(fileName)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err = io.Copy(file, bytes.NewBuffer(data)); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
158
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/tile_provider.go
generated
vendored
158
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/tile_provider.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,158 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import "fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
// TileProvider encapsulates all infos about a map tile provider service (name, url scheme, attribution, etc.)
|
||||
type TileProvider struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Attribution string
|
||||
TileSize int
|
||||
URLPattern string // "%[1]s" => shard, "%[2]d" => zoom, "%[3]d" => x, "%[4]d" => y
|
||||
Shards []string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TileProvider) getURL(shard string, zoom, x, y int) string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(t.URLPattern, shard, zoom, x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderOpenStreetMaps creates a TileProvider struct for OSM's tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderOpenStreetMaps() *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = "osm"
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Maps and Data (c) openstreetmap.org and contributors, ODbL"
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "http://%[1]s.tile.openstreetmap.org/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b", "c"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newTileProviderThunderforest(name string) *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = fmt.Sprintf("thunderforest-%s", name)
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Maps (c) Thundeforest; Data (c) OSM and contributors, ODbL"
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "https://%[1]s.tile.thunderforest.com/" + name + "/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b", "c"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderThunderforestLandscape creates a TileProvider struct for thundeforests's 'landscape' tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderThunderforestLandscape() *TileProvider {
|
||||
return newTileProviderThunderforest("landscape")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderThunderforestOutdoors creates a TileProvider struct for thundeforests's 'outdoors' tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderThunderforestOutdoors() *TileProvider {
|
||||
return newTileProviderThunderforest("outdoors")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderThunderforestTransport creates a TileProvider struct for thundeforests's 'transport' tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderThunderforestTransport() *TileProvider {
|
||||
return newTileProviderThunderforest("transport")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderStamenToner creates a TileProvider struct for stamens' 'toner' tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderStamenToner() *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = "stamen-toner"
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Maps (c) Stamen; Data (c) OSM and contributors, ODbL"
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "http://%[1]s.tile.stamen.com/toner/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b", "c", "d"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderStamenTerrain creates a TileProvider struct for stamens' 'terrain' tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderStamenTerrain() *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = "stamen-terrain"
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Maps (c) Stamen; Data (c) OSM and contributors, ODbL"
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "http://%[1]s.tile.stamen.com/terrain/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b", "c", "d"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderOpenTopoMap creates a TileProvider struct for opentopomap's tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderOpenTopoMap() *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = "opentopomap"
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Maps (c) OpenTopoMap [CC-BY-SA]; Data (c) OSM and contributors [ODbL]; Data (c) SRTM"
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "http://%[1]s.tile.opentopomap.org/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b", "c"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderWikimedia creates a TileProvider struct for Wikimedia's tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderWikimedia() *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = "wikimedia"
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Map (c) Wikimedia; Data (c) OSM and contributors, ODbL."
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "https://maps.wikimedia.org/osm-intl/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderOpenCycleMap creates a TileProvider struct for OpenCycleMap's tile service
|
||||
func NewTileProviderOpenCycleMap() *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = "cycle"
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Maps and Data (c) openstreetmaps.org and contributors, ODbL"
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "http://%[1]s.tile.opencyclemap.org/cycle/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newTileProviderCarto(name string) *TileProvider {
|
||||
t := new(TileProvider)
|
||||
t.Name = fmt.Sprintf("carto-%s", name)
|
||||
t.Attribution = "Map (c) Carto [CC BY 3.0] Data (c) OSM and contributors, ODbL."
|
||||
t.TileSize = 256
|
||||
t.URLPattern = "https://cartodb-basemaps-%[1]s.global.ssl.fastly.net/" + name + "_all/%[2]d/%[3]d/%[4]d.png"
|
||||
t.Shards = []string{"a", "b", "c", "d"}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderCartoLight creates a TileProvider struct for Carto's tile service (light variant)
|
||||
func NewTileProviderCartoLight() *TileProvider {
|
||||
return newTileProviderCarto("light")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTileProviderCartoDark creates a TileProvider struct for Carto's tile service (dark variant)
|
||||
func NewTileProviderCartoDark() *TileProvider {
|
||||
return newTileProviderCarto("dark")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTileProviders returns a map of all available TileProviders
|
||||
func GetTileProviders() map[string]*TileProvider {
|
||||
m := make(map[string]*TileProvider)
|
||||
|
||||
list := []*TileProvider{
|
||||
NewTileProviderOpenStreetMaps(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderOpenCycleMap(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderThunderforestLandscape(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderThunderforestOutdoors(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderThunderforestTransport(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderStamenToner(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderStamenTerrain(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderOpenTopoMap(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderOpenStreetMaps(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderOpenCycleMap(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderCartoLight(),
|
||||
NewTileProviderCartoDark(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, tp := range list {
|
||||
m[tp.Name] = tp
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
18
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/util.go
generated
vendored
18
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go-staticmaps/util.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016, 2017 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package sm
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// hasPrefix checks if 's' has prefix 'prefix'; returns 'true' and the remainder on success, and 'false', 's' otherwise.
|
||||
func hasPrefix(s string, prefix string) (bool, string) {
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(s, prefix) {
|
||||
return true, strings.TrimPrefix(s, prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false, s
|
||||
}
|
||||
37
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/accessLogger/accessLogger.go
generated
vendored
37
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/accessLogger/accessLogger.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package accessLogger
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type AccessLogResponseWriter struct {
|
||||
StatusCode int
|
||||
Size int
|
||||
|
||||
http.ResponseWriter
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func New(res http.ResponseWriter) *AccessLogResponseWriter {
|
||||
return &AccessLogResponseWriter{
|
||||
StatusCode: 200,
|
||||
Size: 0,
|
||||
ResponseWriter: res,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *AccessLogResponseWriter) Write(out []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
s, err := a.ResponseWriter.Write(out)
|
||||
a.Size += s
|
||||
return s, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *AccessLogResponseWriter) WriteHeader(code int) {
|
||||
a.StatusCode = code
|
||||
a.ResponseWriter.WriteHeader(code)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *AccessLogResponseWriter) HTTPResponseType() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%cxx", strconv.FormatInt(int64(a.StatusCode), 10)[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
55
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/http/digest.go
generated
vendored
55
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/http/digest.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package http
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"crypto/md5"
|
||||
"crypto/rand"
|
||||
"encoding/hex"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/str"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func GetDigestAuth(resp *http.Response, method, requestPath, user, password string) string {
|
||||
params := map[string]string{}
|
||||
for _, part := range strings.Split(resp.Header.Get("Www-Authenticate"), " ") {
|
||||
if !strings.Contains(part, `="`) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
spl := strings.Split(strings.Trim(part, " ,"), "=")
|
||||
if !str.StringInSlice(spl[0], []string{"nonce", "realm", "qop"}) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
params[spl[0]] = strings.Trim(spl[1], `"`)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := make([]byte, 8)
|
||||
io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, b)
|
||||
|
||||
params["cnonce"] = fmt.Sprintf("%x", b)
|
||||
params["nc"] = "1"
|
||||
params["uri"] = requestPath
|
||||
params["username"] = user
|
||||
params["response"] = getMD5([]string{
|
||||
getMD5([]string{params["username"], params["realm"], password}),
|
||||
params["nonce"],
|
||||
params["nc"],
|
||||
params["cnonce"],
|
||||
params["qop"],
|
||||
getMD5([]string{method, requestPath}),
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
authParts := []string{}
|
||||
for k, v := range params {
|
||||
authParts = append(authParts, fmt.Sprintf("%s=%q", k, v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "Digest " + strings.Join(authParts, ", ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getMD5(in []string) string {
|
||||
h := md5.New()
|
||||
h.Write([]byte(strings.Join(in, ":")))
|
||||
return hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
|
||||
}
|
||||
52
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/http/logHandler.go
generated
vendored
52
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/http/logHandler.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package http
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/accessLogger"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type HTTPLogHandler struct {
|
||||
Handler http.Handler
|
||||
TrustedIPHeaders []string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewHTTPLogHandler(h http.Handler) http.Handler {
|
||||
return HTTPLogHandler{
|
||||
Handler: h,
|
||||
TrustedIPHeaders: []string{"X-Forwarded-For", "RemoteAddr", "X-Real-IP"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l HTTPLogHandler) ServeHTTP(res http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
start := time.Now()
|
||||
ares := accessLogger.New(res)
|
||||
|
||||
l.Handler.ServeHTTP(ares, r)
|
||||
|
||||
log.Printf("%s - \"%s %s\" %d %d \"%s\" \"%s\" %s",
|
||||
l.findIP(r),
|
||||
r.Method,
|
||||
r.URL.Path,
|
||||
ares.StatusCode,
|
||||
ares.Size,
|
||||
r.Header.Get("Referer"),
|
||||
r.Header.Get("User-Agent"),
|
||||
time.Since(start),
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l HTTPLogHandler) findIP(r *http.Request) string {
|
||||
remoteAddr := strings.SplitN(r.RemoteAddr, ":", 2)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
for _, hdr := range l.TrustedIPHeaders {
|
||||
if value := r.Header.Get(hdr); value != "" {
|
||||
return strings.SplitN(value, ",", 2)[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return remoteAddr
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/str/slice.go
generated
vendored
21
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/go_helpers/str/slice.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package str
|
||||
|
||||
// AppendIfMissing adds a string to a slice when it's not present yet
|
||||
func AppendIfMissing(slice []string, s string) []string {
|
||||
for _, e := range slice {
|
||||
if e == s {
|
||||
return slice
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return append(slice, s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringInSlice checks for the existence of a string in the slice
|
||||
func StringInSlice(a string, list []string) bool {
|
||||
for _, b := range list {
|
||||
if b == a {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
8
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
8
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
|||
language: go
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.6
|
||||
- 1.7
|
||||
- tip
|
||||
|
||||
script: go test -v -race -cover ./...
|
||||
9
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/History.md
generated
vendored
9
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/History.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# 1.2.0 / 2017-06-19
|
||||
|
||||
* Add ParseAndValidate method
|
||||
|
||||
# 1.1.0 / 2016-06-28
|
||||
|
||||
* Support time.Duration config parameters
|
||||
* Added goreportcard badge
|
||||
* Added testcase for using bool with ENV and default
|
||||
13
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/LICENSE
generated
vendored
13
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Copyright 2015 Knut Ahlers <knut@ahlers.me>
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
87
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/README.md
generated
vendored
87
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/README.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
|||
[](https://travis-ci.org/Luzifer/rconfig)
|
||||
[](http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
|
||||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig)
|
||||
[](http://goreportcard.com/report/Luzifer/rconfig)
|
||||
|
||||
## Description
|
||||
|
||||
> Package rconfig implements a CLI configuration reader with struct-embedded defaults, environment variables and posix compatible flag parsing using the [pflag](https://github.com/spf13/pflag) library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install by running:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
go get -u github.com/Luzifer/rconfig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
OR fetch a specific version:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
go get -u gopkg.in/luzifer/rconfig.v1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run tests by running:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
go test -v -race -cover github.com/Luzifer/rconfig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
A very simple usecase is to just configure a struct inside the vars section of your `main.go` and to parse the commandline flags from the `main()` function:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"github.com/Luzifer/rconfig"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
cfg = struct {
|
||||
Username string `default:"unknown" flag:"user" description:"Your name"`
|
||||
Details struct {
|
||||
Age int `default:"25" flag:"age" env:"age" description:"Your age"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
}{}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
rconfig.Parse(&cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Printf("Hello %s, happy birthday for your %dth birthday.",
|
||||
cfg.Username,
|
||||
cfg.Details.Age)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Provide variable defaults by using a file
|
||||
|
||||
Given you have a file `~/.myapp.yml` containing some secrets or usernames (for the example below username is assumed to be "luzifer") as a default configuration for your application you can use this source code to load the defaults from that file using the `vardefault` tag in your configuration struct.
|
||||
|
||||
The order of the directives (lower number = higher precedence):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Flags provided in command line
|
||||
1. Environment variables
|
||||
1. Variable defaults (`vardefault` tag in the struct)
|
||||
1. `default` tag in the struct
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var cfg = struct {
|
||||
Username string `vardefault:"username" flag:"username" description:"Your username"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
rconfig.SetVariableDefaults(rconfig.VarDefaultsFromYAMLFile("~/.myapp.yml"))
|
||||
rconfig.Parse(&cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Printf("Username = %s", cfg.Username)
|
||||
// Output: Username = luzifer
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## More info
|
||||
|
||||
You can see the full reference documentation of the rconfig package [at godoc.org](https://godoc.org/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig), or through go's standard documentation system by running `godoc -http=:6060` and browsing to [http://localhost:6060/pkg/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig](http://localhost:6060/pkg/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig) after installation.
|
||||
356
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/config.go
generated
vendored
356
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/config.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,356 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package rconfig implements a CLI configuration reader with struct-embedded
|
||||
// defaults, environment variables and posix compatible flag parsing using
|
||||
// the pflag library.
|
||||
package rconfig
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/spf13/pflag"
|
||||
validator "gopkg.in/validator.v2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
fs *pflag.FlagSet
|
||||
variableDefaults map[string]string
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
variableDefaults = make(map[string]string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse takes the pointer to a struct filled with variables which should be read
|
||||
// from ENV, default or flag. The precedence in this is flag > ENV > default. So
|
||||
// if a flag is specified on the CLI it will overwrite the ENV and otherwise ENV
|
||||
// overwrites the default specified.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For your configuration struct you can use the following struct-tags to control
|
||||
// the behavior of rconfig:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// default: Set a default value
|
||||
// vardefault: Read the default value from the variable defaults
|
||||
// env: Read the value from this environment variable
|
||||
// flag: Flag to read in format "long,short" (for example "listen,l")
|
||||
// description: A help text for Usage output to guide your users
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The format you need to specify those values you can see in the example to this
|
||||
// function.
|
||||
//
|
||||
func Parse(config interface{}) error {
|
||||
return parse(config, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseAndValidate works exactly like Parse but implements an additional run of
|
||||
// the go-validator package on the configuration struct. Therefore additonal struct
|
||||
// tags are supported like described in the readme file of the go-validator package:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// https://github.com/go-validator/validator/tree/v2#usage
|
||||
func ParseAndValidate(config interface{}) error {
|
||||
return parseAndValidate(config, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Args returns the non-flag command-line arguments.
|
||||
func Args() []string {
|
||||
return fs.Args()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Usage prints a basic usage with the corresponding defaults for the flags to
|
||||
// os.Stdout. The defaults are derived from the `default` struct-tag and the ENV.
|
||||
func Usage() {
|
||||
if fs != nil && fs.Parsed() {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Usage of %s:\n", os.Args[0])
|
||||
fs.PrintDefaults()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetVariableDefaults presets the parser with a map of default values to be used
|
||||
// when specifying the vardefault tag
|
||||
func SetVariableDefaults(defaults map[string]string) {
|
||||
variableDefaults = defaults
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseAndValidate(in interface{}, args []string) error {
|
||||
if err := parse(in, args); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return validator.Validate(in)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parse(in interface{}, args []string) error {
|
||||
if args == nil {
|
||||
args = os.Args
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fs = pflag.NewFlagSet(os.Args[0], pflag.ExitOnError)
|
||||
if err := execTags(in, fs); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return fs.Parse(args)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func execTags(in interface{}, fs *pflag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if reflect.TypeOf(in).Kind() != reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
return errors.New("Calling parser with non-pointer")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if reflect.ValueOf(in).Elem().Kind() != reflect.Struct {
|
||||
return errors.New("Calling parser with pointer to non-struct")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
st := reflect.ValueOf(in).Elem()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < st.NumField(); i++ {
|
||||
valField := st.Field(i)
|
||||
typeField := st.Type().Field(i)
|
||||
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("default") == "" && typeField.Tag.Get("env") == "" && typeField.Tag.Get("flag") == "" && typeField.Type.Kind() != reflect.Struct {
|
||||
// None of our supported tags is present and it's not a sub-struct
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
value := varDefault(typeField.Tag.Get("vardefault"), typeField.Tag.Get("default"))
|
||||
value = envDefault(typeField.Tag.Get("env"), value)
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(typeField.Tag.Get("flag"), ",")
|
||||
|
||||
switch typeField.Type {
|
||||
case reflect.TypeOf(time.Duration(0)):
|
||||
v, err := time.ParseDuration(value)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if value == "" {
|
||||
v = time.Duration(0)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("flag") != "" {
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.DurationVar(valField.Addr().Interface().(*time.Duration), parts[0], v, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.DurationVarP(valField.Addr().Interface().(*time.Duration), parts[0], parts[1], v, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
valField.Set(reflect.ValueOf(v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch typeField.Type.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("flag") != "" {
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.StringVar(valField.Addr().Interface().(*string), parts[0], value, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.StringVarP(valField.Addr().Interface().(*string), parts[0], parts[1], value, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
valField.SetString(value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Bool:
|
||||
v := value == "true"
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("flag") != "" {
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.BoolVar(valField.Addr().Interface().(*bool), parts[0], v, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.BoolVarP(valField.Addr().Interface().(*bool), parts[0], parts[1], v, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
valField.SetBool(v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
vt, err := strconv.ParseInt(value, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if value == "" {
|
||||
vt = 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("flag") != "" {
|
||||
registerFlagInt(typeField.Type.Kind(), fs, valField.Addr().Interface(), parts, vt, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
valField.SetInt(vt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64:
|
||||
vt, err := strconv.ParseUint(value, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if value == "" {
|
||||
vt = 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("flag") != "" {
|
||||
registerFlagUint(typeField.Type.Kind(), fs, valField.Addr().Interface(), parts, vt, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
valField.SetUint(vt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64:
|
||||
vt, err := strconv.ParseFloat(value, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if value == "" {
|
||||
vt = 0.0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typeField.Tag.Get("flag") != "" {
|
||||
registerFlagFloat(typeField.Type.Kind(), fs, valField.Addr().Interface(), parts, vt, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
valField.SetFloat(vt)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Struct:
|
||||
if err := execTags(valField.Addr().Interface(), fs); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Slice:
|
||||
switch typeField.Type.Elem().Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Int:
|
||||
def := []int{}
|
||||
for _, v := range strings.Split(value, ",") {
|
||||
it, err := strconv.ParseInt(strings.TrimSpace(v), 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
def = append(def, int(it))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.IntSliceVar(valField.Addr().Interface().(*[]int), parts[0], def, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.IntSliceVarP(valField.Addr().Interface().(*[]int), parts[0], parts[1], def, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
del := typeField.Tag.Get("delimiter")
|
||||
if len(del) == 0 {
|
||||
del = ","
|
||||
}
|
||||
def := strings.Split(value, del)
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.StringSliceVar(valField.Addr().Interface().(*[]string), parts[0], def, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.StringSliceVarP(valField.Addr().Interface().(*[]string), parts[0], parts[1], def, typeField.Tag.Get("description"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func registerFlagFloat(t reflect.Kind, fs *pflag.FlagSet, field interface{}, parts []string, vt float64, desc string) {
|
||||
switch t {
|
||||
case reflect.Float32:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Float32Var(field.(*float32), parts[0], float32(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Float32VarP(field.(*float32), parts[0], parts[1], float32(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Float64:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Float64Var(field.(*float64), parts[0], float64(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Float64VarP(field.(*float64), parts[0], parts[1], float64(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func registerFlagInt(t reflect.Kind, fs *pflag.FlagSet, field interface{}, parts []string, vt int64, desc string) {
|
||||
switch t {
|
||||
case reflect.Int:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.IntVar(field.(*int), parts[0], int(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.IntVarP(field.(*int), parts[0], parts[1], int(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Int8:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Int8Var(field.(*int8), parts[0], int8(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Int8VarP(field.(*int8), parts[0], parts[1], int8(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Int32:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Int32Var(field.(*int32), parts[0], int32(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Int32VarP(field.(*int32), parts[0], parts[1], int32(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Int64:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Int64Var(field.(*int64), parts[0], int64(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Int64VarP(field.(*int64), parts[0], parts[1], int64(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func registerFlagUint(t reflect.Kind, fs *pflag.FlagSet, field interface{}, parts []string, vt uint64, desc string) {
|
||||
switch t {
|
||||
case reflect.Uint:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.UintVar(field.(*uint), parts[0], uint(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.UintVarP(field.(*uint), parts[0], parts[1], uint(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Uint8:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Uint8Var(field.(*uint8), parts[0], uint8(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Uint8VarP(field.(*uint8), parts[0], parts[1], uint8(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Uint16:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Uint16Var(field.(*uint16), parts[0], uint16(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Uint16VarP(field.(*uint16), parts[0], parts[1], uint16(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Uint32:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Uint32Var(field.(*uint32), parts[0], uint32(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Uint32VarP(field.(*uint32), parts[0], parts[1], uint32(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.Uint64:
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
fs.Uint64Var(field.(*uint64), parts[0], uint64(vt), desc)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fs.Uint64VarP(field.(*uint64), parts[0], parts[1], uint64(vt), desc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func envDefault(env, def string) string {
|
||||
value := def
|
||||
|
||||
if env != "" {
|
||||
if e := os.Getenv(env); e != "" {
|
||||
value = e
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func varDefault(name, def string) string {
|
||||
value := def
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
if v, ok := variableDefaults[name]; ok {
|
||||
value = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
27
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/vardefault_providers.go
generated
vendored
27
vendor/github.com/Luzifer/rconfig/vardefault_providers.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package rconfig
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
|
||||
"gopkg.in/yaml.v2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VarDefaultsFromYAMLFile reads contents of a file and calls VarDefaultsFromYAML
|
||||
func VarDefaultsFromYAMLFile(filename string) map[string]string {
|
||||
data, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filename)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return make(map[string]string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return VarDefaultsFromYAML(data)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VarDefaultsFromYAML creates a vardefaults map from YAML raw data
|
||||
func VarDefaultsFromYAML(in []byte) map[string]string {
|
||||
out := make(map[string]string)
|
||||
err := yaml.Unmarshal(in, &out)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return make(map[string]string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return out
|
||||
}
|
||||
0
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/.gitignore
generated
vendored
0
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/.gitignore
generated
vendored
18
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/LICENSE
generated
vendored
18
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2013 Wesley Bitter
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of
|
||||
this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in
|
||||
the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to
|
||||
use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of
|
||||
the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so,
|
||||
subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
|
||||
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR
|
||||
COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER
|
||||
IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN
|
||||
CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
3
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/README.md
generated
vendored
3
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/README.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
This is a port of the excellent python module named the same, which can be found here [appdirs](https://github.com/ActiveState/appdirs).
|
||||
|
||||
The README and documentation in the original should be a good starting point. Documentation is currently lacking on the port itself, but the API is very similar to the python version.
|
||||
80
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs.go
generated
vendored
80
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// A port of the excellent python module `appdirs`.
|
||||
// See https://github.com/ActiveState/appdirs for the python version.
|
||||
package appdirs
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os/user"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// App is a helper type to create easy access across your program to the appdirs
|
||||
// functions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The *App type has 6 methods that map to the 6 functions exported by `appdirs`.
|
||||
// All methods take no arguments, and supply the function it wraps with arguments
|
||||
// pre-set in the struct on creation.
|
||||
type App struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Author string
|
||||
Version string
|
||||
Roaming bool
|
||||
Opinion bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New returns a new App helper that has various methods for receiving
|
||||
// relevant directories for your application.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The following defaults are used for the two fields not settable by New:
|
||||
// Roaming: false, Opinion: true
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you want to set these, create your own App struct by the usual means.
|
||||
func New(name, author, version string) *App {
|
||||
return &App{
|
||||
Name: name,
|
||||
Author: author,
|
||||
Version: version,
|
||||
Roaming: false,
|
||||
Opinion: true,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserData returns the full path to the user-specific data directory
|
||||
func (app *App) UserData() string {
|
||||
return UserDataDir(app.Name, app.Author, app.Version, app.Roaming)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SiteData returns the full path to the user-shared data directory
|
||||
func (app *App) SiteData() string {
|
||||
return SiteDataDir(app.Name, app.Author, app.Version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SiteConfig returns the full path to the user-shared configuration directory
|
||||
func (app *App) SiteConfig() string {
|
||||
return SiteConfigDir(app.Name, app.Author, app.Version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserConfig returns the full path to the user-specific configuration directory
|
||||
func (app *App) UserConfig() string {
|
||||
return UserConfigDir(app.Name, app.Author, app.Version, app.Roaming)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserCache returns the full path to the user-specific cache directory
|
||||
func (app *App) UserCache() string {
|
||||
return UserCacheDir(app.Name, app.Author, app.Version, app.Opinion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserLog returns the full path to the user-specific log directory
|
||||
func (app *App) UserLog() string {
|
||||
return UserLogDir(app.Name, app.Author, app.Version, app.Opinion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExpandUser is a helper function that expands the first '~' it finds in the
|
||||
// passed path with the home directory of the current user.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: This only works on environments similar to bash.
|
||||
func ExpandUser(path string) string {
|
||||
if u, err := user.Current(); err == nil {
|
||||
return strings.Replace(path, "~", u.HomeDir, -1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
63
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs_darwin.go
generated
vendored
63
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs_darwin.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package appdirs
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func userDataDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) (path string) {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("~/Library/Application Support")
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func siteDataDir(name, author, version string) (path string) {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("/Library/Application Support")
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userConfigDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) (path string) {
|
||||
return UserDataDir(name, author, version, roaming)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func siteConfigDir(name, author, version string) (path string) {
|
||||
return SiteDataDir(name, author, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userCacheDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) (path string) {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("~/Library/Caches")
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userLogDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) (path string) {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("~/Library/Logs")
|
||||
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name)
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
102
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs_unix.go
generated
vendored
102
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs_unix.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// +build linux freebsd netbsd openbsd
|
||||
|
||||
package appdirs
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func userDataDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) (path string) {
|
||||
if path = os.Getenv("XDG_DATA_HOME"); path == "" {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("~/.local/share")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func SiteDataDirs(name, author, version string) (paths []string) {
|
||||
var path string
|
||||
|
||||
if path = os.Getenv("XDG_DATA_DIRS"); path == "" {
|
||||
paths = []string{"/usr/local/share", "/usr/share"}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
paths = filepath.SplitList(path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, path := range paths {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser(path)
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
paths[i] = path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return paths
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func siteDataDir(name, author, version string) (path string) {
|
||||
return SiteDataDirs(name, author, version)[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userConfigDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) (path string) {
|
||||
if path = os.Getenv("XDG_CONFIG_HOME"); path == "" {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("~/.config")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func SiteConfigDirs(name, author, version string) (paths []string) {
|
||||
var path string
|
||||
|
||||
if path = os.Getenv("XDG_CONFIG_DIRS"); path == "" {
|
||||
paths = []string{"/etc/xdg"}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
paths = filepath.SplitList(path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, path := range paths {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser(path)
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
paths[i] = path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return paths
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func siteConfigDir(name, author, version string) (path string) {
|
||||
return SiteConfigDirs(name, author, version)[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userCacheDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) (path string) {
|
||||
if path = os.Getenv("XDG_CACHE_HOME"); path == "" {
|
||||
path = ExpandUser("~/.cache")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, name, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userLogDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) (path string) {
|
||||
path = UserCacheDir(name, author, version, opinion)
|
||||
|
||||
return filepath.Join(path, "log")
|
||||
}
|
||||
171
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs_windows.go
generated
vendored
171
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/appdirs_windows.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,171 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package appdirs
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
"unsafe"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
shell32, _ = syscall.LoadLibrary("shell32.dll")
|
||||
getKnownFolderPath, _ = syscall.GetProcAddress(shell32, "SHGetKnownFolderPath")
|
||||
|
||||
ole32, _ = syscall.LoadLibrary("Ole32.dll")
|
||||
coTaskMemFree, _ = syscall.GetProcAddress(ole32, "CoTaskMemFree")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// These are KNOWNFOLDERID constants that are passed to GetKnownFolderPath
|
||||
var (
|
||||
rfidLocalAppData = syscall.GUID{
|
||||
0xf1b32785,
|
||||
0x6fba,
|
||||
0x4fcf,
|
||||
[8]byte{0x9d, 0x55, 0x7b, 0x8e, 0x7f, 0x15, 0x70, 0x91},
|
||||
}
|
||||
rfidRoamingAppData = syscall.GUID{
|
||||
0x3eb685db,
|
||||
0x65f9,
|
||||
0x4cf6,
|
||||
[8]byte{0xa0, 0x3a, 0xe3, 0xef, 0x65, 0x72, 0x9f, 0x3d},
|
||||
}
|
||||
rfidProgramData = syscall.GUID{
|
||||
0x62ab5d82,
|
||||
0xfdc1,
|
||||
0x4dc3,
|
||||
[8]byte{0xa9, 0xdd, 0x07, 0x0d, 0x1d, 0x49, 0x5d, 0x97},
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func userDataDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) (path string) {
|
||||
if author == "" {
|
||||
author = name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var rfid syscall.GUID
|
||||
if roaming {
|
||||
rfid = rfidRoamingAppData
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
rfid = rfidLocalAppData
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
path, err := getFolderPath(rfid)
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if path, err = filepath.Abs(path); err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, author, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func siteDataDir(name, author, version string) (path string) {
|
||||
path, err := getFolderPath(rfidProgramData)
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if path, err = filepath.Abs(path); err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if author == "" {
|
||||
author = name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, author, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userConfigDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) string {
|
||||
return UserDataDir(name, author, version, roaming)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func siteConfigDir(name, author, version string) (path string) {
|
||||
return SiteDataDir(name, author, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userCacheDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) (path string) {
|
||||
if author == "" {
|
||||
author = name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
path, err := getFolderPath(rfidLocalAppData)
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if path, err = filepath.Abs(path); err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, author, name)
|
||||
if opinion {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, "Cache")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if name != "" && version != "" {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func userLogDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) (path string) {
|
||||
path = UserDataDir(name, author, version, false)
|
||||
|
||||
if opinion {
|
||||
path = filepath.Join(path, "Logs")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getFolderPath(rfid syscall.GUID) (string, error) {
|
||||
var res uintptr
|
||||
|
||||
ret, _, callErr := syscall.Syscall6(
|
||||
uintptr(getKnownFolderPath),
|
||||
4,
|
||||
uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&rfid)),
|
||||
0,
|
||||
0,
|
||||
uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&res)),
|
||||
0,
|
||||
0,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if callErr != 0 && ret != 0 {
|
||||
return "", callErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
defer syscall.Syscall(uintptr(coTaskMemFree), 1, res, 0, 0)
|
||||
return ucs2PtrToString(res), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func ucs2PtrToString(p uintptr) string {
|
||||
ptr := (*[4096]uint16)(unsafe.Pointer(p))
|
||||
|
||||
return syscall.UTF16ToString((*ptr)[:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
108
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/doc.go
generated
vendored
108
vendor/github.com/Wessie/appdirs/doc.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// appdirs project doc.go
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
This is a port of a python module used for finding what directory you 'should'
|
||||
be using for saving your application data such as configuration, cache files or
|
||||
other files.
|
||||
|
||||
The location of these directories is often hard to get right. The original python
|
||||
module set out to change this into a simple API that returns you the exact
|
||||
directory you need. This is a port of it to Go.
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on platform, this package exports you at the least 6 functions that
|
||||
return various system directories. And one helper struct type that combines the
|
||||
functions into methods for less arguments in your code.
|
||||
|
||||
Each function defined accepts a number of arguments, each argument is optional
|
||||
and can be left to the types default value if omitted. Often the function will
|
||||
ignore arguments if the name given is empty.
|
||||
|
||||
Passing in all default values into any of the functions will return you the base
|
||||
directory without any of the arguments appended to it.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package appdirs
|
||||
|
||||
// UserDataDir returns the full path to the user-specific data directory.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function uses XDG_DATA_HOME as defined by the XDG spec on *nix like systems.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples of return values:
|
||||
// Mac OS X: ~/Library/Application Support/<AppName>
|
||||
// Unix: ~/.local/share/<AppName> # or in $XDG_DATA_HOME, if defined
|
||||
// Win XP (not roaming): C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
// Win XP (roaming): C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
// Win 7 (not roaming): C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
// Win 7 (roaming): C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
func UserDataDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) string {
|
||||
return userDataDir(name, author, version, roaming)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SiteDataDir returns the full path to the user-shared data directory.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function uses XDG_DATA_DIRS[0] as by the XDG spec on *nix like systems.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples of return values:
|
||||
// Mac OS X: /Library/Application Support/<AppName>
|
||||
// Unix: /usr/local/share/<AppName> or /usr/share/<AppName>
|
||||
// Win XP: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
// Vista: (Fail! "C:\ProgramData" is a hidden *system* directory on Vista.)
|
||||
// Win 7: C:\ProgramData\<AppAuthor>\<AppName> # Hidden, but writeable on Win 7.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// WARNING: Do not use this on Windows Vista, See the note above.
|
||||
func SiteDataDir(name, author, version string) string {
|
||||
return siteDataDir(name, author, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserConfigDir returns the full path to the user-specific configuration directory
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function uses XDG_CONFIG_HOME as by the XDG spec on *nix like systems.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples of return values:
|
||||
// Mac OS X: same as UserDataDir
|
||||
// Unix: ~/.config/<AppName> # or in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME, if defined
|
||||
// Win *: same as UserDataDir
|
||||
func UserConfigDir(name, author, version string, roaming bool) string {
|
||||
return userConfigDir(name, author, version, roaming)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SiteConfigDir returns the full path to the user-shared data directory.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function uses XDG_CONFIG_DIRS[0] as by the XDG spec on *nix like systems.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples of return values:
|
||||
// Mac OS X: same as SiteDataDir
|
||||
// Unix: /etc/xdg/<AppName> or $XDG_CONFIG_DIRS[i]/<AppName> for each value in $XDG_CONFIG_DIRS
|
||||
// Win *: same as SiteDataDir
|
||||
// Vista: (Fail! "C:\ProgramData" is a hidden *system* directory on Vista.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// WARNING: Do not use this on Windows Vista, see the note above.
|
||||
func SiteConfigDir(name, author, version string) string {
|
||||
return siteConfigDir(name, author, version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserCacheDir returns the full path to the user-specific cache directory.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The opinion argument will append 'Cache' to the base directory if set to true.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples of return values:
|
||||
// Mac OS X: ~/Library/Caches/<AppName>
|
||||
// Unix: ~/.cache/<AppName> (XDG default)
|
||||
// Win XP: C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Cache
|
||||
// Vista: C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Cache
|
||||
func UserCacheDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) string {
|
||||
return userCacheDir(name, author, version, opinion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UserLogDir returns the full path to the user-specific log directory.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The opinion argument will append either 'Logs' (windows) or 'log' (unix) to
|
||||
// the base directory when set to true.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples of return values:
|
||||
// Mac OS X: ~/Library/Logs/<AppName>
|
||||
// Unix: ~/.cache/<AppName>/log # or under $XDG_CACHE_HOME if defined
|
||||
// Win XP: C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Logs
|
||||
// Vista: C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Logs
|
||||
func UserLogDir(name, author, version string, opinion bool) string {
|
||||
return userLogDir(name, author, version, opinion)
|
||||
}
|
||||
2
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/.gitignore
generated
vendored
2
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/.gitignore
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
|||
/debug
|
||||
/.vscode
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/LICENSE
generated
vendored
21
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||
The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2015 Didip Kerabat
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
|
||||
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
164
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/README.md
generated
vendored
164
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/README.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,164 +0,0 @@
|
|||
[](http://godoc.org/github.com/didip/tollbooth)
|
||||
[](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/didip/tollbooth/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
## Tollbooth
|
||||
|
||||
This is a generic middleware to rate-limit HTTP requests.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE 1:** This library is considered finished.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE 2:** In the coming weeks, I will be removing thirdparty modules and moving them to their own dedicated repos.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE 3:** Major version changes are backward-incompatible. `v2.0.0` streamlines the ugliness of the old API.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Versions
|
||||
|
||||
**v1.0.0:** This version maintains the old API but all of the thirdparty modules are moved to their own repo.
|
||||
|
||||
**v2.x.x:** Brand new API for the sake of code cleanup, thread safety, & auto-expiring data structures.
|
||||
|
||||
**v3.x.x:** Apparently we have been using golang.org/x/time/rate incorrectly. See issue #48. It always limit X number per 1 second. The time duration is not changeable, so it does not make sense to pass TTL to tollbooth.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Five Minutes Tutorial
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/didip/tollbooth"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func HelloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
|
||||
w.Write([]byte("Hello, World!"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
// Create a request limiter per handler.
|
||||
http.Handle("/", tollbooth.LimitFuncHandler(tollbooth.NewLimiter(1, nil), HelloHandler))
|
||||
http.ListenAndServe(":12345", nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
1. Rate-limit by request's remote IP, path, methods, custom headers, & basic auth usernames.
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
"github.com/didip/tollbooth/limiter"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
lmt := tollbooth.NewLimiter(1, nil)
|
||||
|
||||
// or create a limiter with expirable token buckets
|
||||
// This setting means:
|
||||
// create a 1 request/second limiter and
|
||||
// every token bucket in it will expire 1 hour after it was initially set.
|
||||
lmt = tollbooth.NewLimiter(1, &limiter.ExpirableOptions{DefaultExpirationTTL: time.Hour})
|
||||
|
||||
// Configure list of places to look for IP address.
|
||||
// By default it's: "RemoteAddr", "X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"
|
||||
// If your application is behind a proxy, set "X-Forwarded-For" first.
|
||||
lmt.SetIPLookups([]string{"RemoteAddr", "X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"})
|
||||
|
||||
// Limit only GET and POST requests.
|
||||
lmt.SetMethods([]string{"GET", "POST"})
|
||||
|
||||
// Limit based on basic auth usernames.
|
||||
// You add them on-load, or later as you handle requests.
|
||||
lmt.SetBasicAuthUsers([]string{"bob", "jane", "didip", "vip"})
|
||||
// You can remove them later as well.
|
||||
lmt.RemoveBasicAuthUsers([]string{"vip"})
|
||||
|
||||
// Limit request headers containing certain values.
|
||||
// You add them on-load, or later as you handle requests.
|
||||
lmt.SetHeader("X-Access-Token", []string{"abc123", "xyz098"})
|
||||
// You can remove all entries at once.
|
||||
lmt.RemoveHeader("X-Access-Token")
|
||||
// Or remove specific ones.
|
||||
lmt.RemoveHeaderEntries("X-Access-Token", []string{"limitless-token"})
|
||||
|
||||
// By the way, the setters are chainable. Example:
|
||||
lmt.SetIPLookups([]string{"RemoteAddr", "X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"}).
|
||||
SetMethods([]string{"GET", "POST"}).
|
||||
SetBasicAuthUsers([]string{"sansa"}).
|
||||
SetBasicAuthUsers([]string{"tyrion"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Compose your own middleware by using `LimitByKeys()`.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Header entries and basic auth users can expire over time (to conserve memory).
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "time"
|
||||
|
||||
lmt := tollbooth.NewLimiter(1, nil)
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a custom expiration TTL for token bucket.
|
||||
lmt.SetTokenBucketExpirationTTL(time.Hour)
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a custom expiration TTL for basic auth users.
|
||||
lmt.SetBasicAuthExpirationTTL(time.Hour)
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a custom expiration TTL for header entries.
|
||||
lmt.SetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL(time.Hour)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Upon rejection, the following HTTP response headers are available to users:
|
||||
|
||||
* `X-Rate-Limit-Limit` The maximum request limit.
|
||||
|
||||
* `X-Rate-Limit-Duration` The rate-limiter duration.
|
||||
|
||||
* `X-Rate-Limit-Request-Forwarded-For` The rejected request `X-Forwarded-For`.
|
||||
|
||||
* `X-Rate-Limit-Request-Remote-Addr` The rejected request `RemoteAddr`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
5. Customize your own message or function when limit is reached.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lmt := tollbooth.NewLimiter(1, nil)
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a custom message.
|
||||
lmt.SetMessage("You have reached maximum request limit.")
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a custom content-type.
|
||||
lmt.SetMessageContentType("text/plain; charset=utf-8")
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a custom function for rejection.
|
||||
lmt.SetOnLimitReached(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { fmt.Println("A request was rejected") })
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Tollbooth does not require external storage since it uses an algorithm called [Token Bucket](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Token_bucket) [(Go library: golang.org/x/time/rate)](//godoc.org/golang.org/x/time/rate).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Other Web Frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes, other frameworks require a little bit of shim to use Tollbooth. These shims below are contributed by the community, so I make no promises on how well they work. The one I am familiar with are: Chi, Gin, and Negroni.
|
||||
|
||||
* [Chi](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_chi)
|
||||
|
||||
* [Echo](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_echo)
|
||||
|
||||
* [FastHTTP](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_fasthttp)
|
||||
|
||||
* [Gin](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_gin)
|
||||
|
||||
* [GoRestful](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_gorestful)
|
||||
|
||||
* [HTTPRouter](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_httprouter)
|
||||
|
||||
* [Iris](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_iris)
|
||||
|
||||
* [Negroni](https://github.com/didip/tollbooth_negroni)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## My other Go libraries
|
||||
|
||||
* [Stopwatch](https://github.com/didip/stopwatch): A small library to measure latency of things. Useful if you want to report latency data to Graphite.
|
||||
|
||||
* [Gomet](https://github.com/didip/gomet): Simple HTTP client & server long poll library for Go. Useful for receiving live updates without needing Websocket.
|
||||
15
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/errors/errors.go
generated
vendored
15
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/errors/errors.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package errors provide data structure for errors.
|
||||
package errors
|
||||
|
||||
import "fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
// HTTPError is an error struct that returns both message and status code.
|
||||
type HTTPError struct {
|
||||
Message string
|
||||
StatusCode int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Error returns error message.
|
||||
func (httperror *HTTPError) Error() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%v: %v", httperror.StatusCode, httperror.Message)
|
||||
}
|
||||
55
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/libstring/libstring.go
generated
vendored
55
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/libstring/libstring.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package libstring provides various string related functions.
|
||||
package libstring
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"net"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// StringInSlice finds needle in a slice of strings.
|
||||
func StringInSlice(sliceString []string, needle string) bool {
|
||||
for _, b := range sliceString {
|
||||
if b == needle {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RemoteIP finds IP Address given http.Request struct.
|
||||
func RemoteIP(ipLookups []string, forwardedForIndexFromBehind int, r *http.Request) string {
|
||||
realIP := r.Header.Get("X-Real-IP")
|
||||
forwardedFor := r.Header.Get("X-Forwarded-For")
|
||||
|
||||
for _, lookup := range ipLookups {
|
||||
if lookup == "RemoteAddr" {
|
||||
// 1. Cover the basic use cases for both ipv4 and ipv6
|
||||
ip, _, err := net.SplitHostPort(r.RemoteAddr)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
// 2. Upon error, just return the remote addr.
|
||||
return r.RemoteAddr
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ip
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lookup == "X-Forwarded-For" && forwardedFor != "" {
|
||||
// X-Forwarded-For is potentially a list of addresses separated with ","
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(forwardedFor, ",")
|
||||
for i, p := range parts {
|
||||
parts[i] = strings.TrimSpace(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
partIndex := len(parts) - 1 - forwardedForIndexFromBehind
|
||||
if partIndex < 0 {
|
||||
partIndex = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return parts[partIndex]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if lookup == "X-Real-IP" && realIP != "" {
|
||||
return realIP
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
474
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/limiter/limiter.go
generated
vendored
474
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/limiter/limiter.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,474 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package limiter provides data structure to configure rate-limiter.
|
||||
package limiter
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
gocache "github.com/patrickmn/go-cache"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/time/rate"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// New is a constructor for Limiter.
|
||||
func New(generalExpirableOptions *ExpirableOptions) *Limiter {
|
||||
lmt := &Limiter{}
|
||||
|
||||
lmt.SetMessageContentType("text/plain; charset=utf-8").
|
||||
SetMessage("You have reached maximum request limit.").
|
||||
SetStatusCode(429).
|
||||
SetOnLimitReached(nil).
|
||||
SetIPLookups([]string{"RemoteAddr", "X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP"}).
|
||||
SetForwardedForIndexFromBehind(0).
|
||||
SetHeaders(make(map[string][]string))
|
||||
|
||||
if generalExpirableOptions != nil {
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions = generalExpirableOptions
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions = &ExpirableOptions{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Default for ExpireJobInterval is every minute.
|
||||
if lmt.generalExpirableOptions.ExpireJobInterval <= 0 {
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions.ExpireJobInterval = time.Minute
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Default for DefaultExpirationTTL is 10 years.
|
||||
if lmt.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL <= 0 {
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL = 87600 * time.Hour
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lmt.tokenBuckets = gocache.New(
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL,
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions.ExpireJobInterval,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
lmt.basicAuthUsers = gocache.New(
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL,
|
||||
lmt.generalExpirableOptions.ExpireJobInterval,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return lmt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Limiter is a config struct to limit a particular request handler.
|
||||
type Limiter struct {
|
||||
// Maximum number of requests to limit per second.
|
||||
max float64
|
||||
|
||||
// Limiter burst size
|
||||
burst int
|
||||
|
||||
// HTTP message when limit is reached.
|
||||
message string
|
||||
|
||||
// Content-Type for Message
|
||||
messageContentType string
|
||||
|
||||
// HTTP status code when limit is reached.
|
||||
statusCode int
|
||||
|
||||
// A function to call when a request is rejected.
|
||||
onLimitReached func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)
|
||||
|
||||
// List of places to look up IP address.
|
||||
// Default is "RemoteAddr", "X-Forwarded-For", "X-Real-IP".
|
||||
// You can rearrange the order as you like.
|
||||
ipLookups []string
|
||||
|
||||
forwardedForIndex int
|
||||
|
||||
// List of HTTP Methods to limit (GET, POST, PUT, etc.).
|
||||
// Empty means limit all methods.
|
||||
methods []string
|
||||
|
||||
// Able to configure token bucket expirations.
|
||||
generalExpirableOptions *ExpirableOptions
|
||||
|
||||
// List of basic auth usernames to limit.
|
||||
basicAuthUsers *gocache.Cache
|
||||
|
||||
// Map of HTTP headers to limit.
|
||||
// Empty means skip headers checking.
|
||||
headers map[string]*gocache.Cache
|
||||
|
||||
// Map of limiters with TTL
|
||||
tokenBuckets *gocache.Cache
|
||||
|
||||
tokenBucketExpirationTTL time.Duration
|
||||
basicAuthExpirationTTL time.Duration
|
||||
headerEntryExpirationTTL time.Duration
|
||||
|
||||
sync.RWMutex
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTokenBucketExpirationTTL is thread-safe way of setting custom token bucket expiration TTL.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetTokenBucketExpirationTTL(ttl time.Duration) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.tokenBucketExpirationTTL = ttl
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GettokenBucketExpirationTTL is thread-safe way of getting custom token bucket expiration TTL.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetTokenBucketExpirationTTL() time.Duration {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.tokenBucketExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBasicAuthExpirationTTL is thread-safe way of setting custom basic auth expiration TTL.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetBasicAuthExpirationTTL(ttl time.Duration) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.basicAuthExpirationTTL = ttl
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBasicAuthExpirationTTL is thread-safe way of getting custom basic auth expiration TTL.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetBasicAuthExpirationTTL() time.Duration {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.basicAuthExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL is thread-safe way of setting custom basic auth expiration TTL.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL(ttl time.Duration) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.headerEntryExpirationTTL = ttl
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL is thread-safe way of getting custom basic auth expiration TTL.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL() time.Duration {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.headerEntryExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetMax is thread-safe way of setting maximum number of requests to limit per duration.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetMax(max float64) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.max = max
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMax is thread-safe way of getting maximum number of requests to limit per duration.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetMax() float64 {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.max
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBurst is thread-safe way of setting maximum burst size.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetBurst(burst int) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.burst = burst
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBurst is thread-safe way of setting maximum burst size.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetBurst() int {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l.burst
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetMessage is thread-safe way of setting HTTP message when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetMessage(msg string) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.message = msg
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMessage is thread-safe way of getting HTTP message when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetMessage() string {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.message
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetMessageContentType is thread-safe way of setting HTTP message Content-Type when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetMessageContentType(contentType string) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.messageContentType = contentType
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMessageContentType is thread-safe way of getting HTTP message Content-Type when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetMessageContentType() string {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.messageContentType
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStatusCode is thread-safe way of setting HTTP status code when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetStatusCode(statusCode int) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.statusCode = statusCode
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetStatusCode is thread-safe way of getting HTTP status code when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetStatusCode() int {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.statusCode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetOnLimitReached is thread-safe way of setting after-rejection function when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetOnLimitReached(fn func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request)) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.onLimitReached = fn
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExecOnLimitReached is thread-safe way of executing after-rejection function when limit is reached.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) ExecOnLimitReached(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
fn := l.onLimitReached
|
||||
if fn != nil {
|
||||
fn(w, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetIPLookups is thread-safe way of setting list of places to look up IP address.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetIPLookups(ipLookups []string) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.ipLookups = ipLookups
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetIPLookups is thread-safe way of getting list of places to look up IP address.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetIPLookups() []string {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.ipLookups
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetForwardedForIndexFromBehind is thread-safe way of setting which X-Forwarded-For index to choose.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetForwardedForIndexFromBehind(forwardedForIndex int) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.forwardedForIndex = forwardedForIndex
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetForwardedForIndexFromBehind is thread-safe way of getting which X-Forwarded-For index to choose.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetForwardedForIndexFromBehind() int {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.forwardedForIndex
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetMethods is thread-safe way of setting list of HTTP Methods to limit (GET, POST, PUT, etc.).
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetMethods(methods []string) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.methods = methods
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMethods is thread-safe way of getting list of HTTP Methods to limit (GET, POST, PUT, etc.).
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetMethods() []string {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.methods
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBasicAuthUsers is thread-safe way of setting list of basic auth usernames to limit.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetBasicAuthUsers(basicAuthUsers []string) *Limiter {
|
||||
ttl := l.GetBasicAuthExpirationTTL()
|
||||
if ttl <= 0 {
|
||||
ttl = l.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, basicAuthUser := range basicAuthUsers {
|
||||
l.basicAuthUsers.Set(basicAuthUser, true, ttl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBasicAuthUsers is thread-safe way of getting list of basic auth usernames to limit.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetBasicAuthUsers() []string {
|
||||
asMap := l.basicAuthUsers.Items()
|
||||
|
||||
var basicAuthUsers []string
|
||||
for basicAuthUser, _ := range asMap {
|
||||
basicAuthUsers = append(basicAuthUsers, basicAuthUser)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return basicAuthUsers
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RemoveBasicAuthUsers is thread-safe way of removing basic auth usernames from existing list.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) RemoveBasicAuthUsers(basicAuthUsers []string) *Limiter {
|
||||
for _, toBeRemoved := range basicAuthUsers {
|
||||
l.basicAuthUsers.Delete(toBeRemoved)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHeaders is thread-safe way of setting map of HTTP headers to limit.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetHeaders(headers map[string][]string) *Limiter {
|
||||
if l.headers == nil {
|
||||
l.headers = make(map[string]*gocache.Cache)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for header, entries := range headers {
|
||||
l.SetHeader(header, entries)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHeaders is thread-safe way of getting map of HTTP headers to limit.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetHeaders() map[string][]string {
|
||||
results := make(map[string][]string)
|
||||
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
for header, entriesAsGoCache := range l.headers {
|
||||
entries := make([]string, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
for entry, _ := range entriesAsGoCache.Items() {
|
||||
entries = append(entries, entry)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
results[header] = entries
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return results
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHeader is thread-safe way of setting entries of 1 HTTP header.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) SetHeader(header string, entries []string) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
existing, found := l.headers[header]
|
||||
l.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
ttl := l.GetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL()
|
||||
if ttl <= 0 {
|
||||
ttl = l.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !found {
|
||||
existing = gocache.New(ttl, l.generalExpirableOptions.ExpireJobInterval)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, entry := range entries {
|
||||
existing.Set(entry, true, ttl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.headers[header] = existing
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHeader is thread-safe way of getting entries of 1 HTTP header.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) GetHeader(header string) []string {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
entriesAsGoCache := l.headers[header]
|
||||
l.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
entriesAsMap := entriesAsGoCache.Items()
|
||||
entries := make([]string, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
for entry, _ := range entriesAsMap {
|
||||
entries = append(entries, entry)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return entries
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RemoveHeader is thread-safe way of removing entries of 1 HTTP header.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) RemoveHeader(header string) *Limiter {
|
||||
ttl := l.GetHeaderEntryExpirationTTL()
|
||||
if ttl <= 0 {
|
||||
ttl = l.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
l.headers[header] = gocache.New(ttl, l.generalExpirableOptions.ExpireJobInterval)
|
||||
l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RemoveHeaderEntries is thread-safe way of adding new entries to 1 HTTP header rule.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) RemoveHeaderEntries(header string, entriesForRemoval []string) *Limiter {
|
||||
l.RLock()
|
||||
entries, found := l.headers[header]
|
||||
l.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if !found {
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, toBeRemoved := range entriesForRemoval {
|
||||
entries.Delete(toBeRemoved)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) limitReachedWithTokenBucketTTL(key string, tokenBucketTTL time.Duration) bool {
|
||||
lmtMax := l.GetMax()
|
||||
lmtBurst := l.GetBurst()
|
||||
l.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if _, found := l.tokenBuckets.Get(key); !found {
|
||||
l.tokenBuckets.Set(
|
||||
key,
|
||||
rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(lmtMax), lmtBurst),
|
||||
tokenBucketTTL,
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
expiringMap, found := l.tokenBuckets.Get(key)
|
||||
if !found {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return !expiringMap.(*rate.Limiter).Allow()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LimitReached returns a bool indicating if the Bucket identified by key ran out of tokens.
|
||||
func (l *Limiter) LimitReached(key string) bool {
|
||||
ttl := l.GetTokenBucketExpirationTTL()
|
||||
|
||||
if ttl <= 0 {
|
||||
ttl = l.generalExpirableOptions.DefaultExpirationTTL
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return l.limitReachedWithTokenBucketTTL(key, ttl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/limiter/limiter_options.go
generated
vendored
12
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/limiter/limiter_options.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package limiter
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type ExpirableOptions struct {
|
||||
DefaultExpirationTTL time.Duration
|
||||
|
||||
// How frequently expire job triggers
|
||||
ExpireJobInterval time.Duration
|
||||
}
|
||||
180
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/tollbooth.go
generated
vendored
180
vendor/github.com/didip/tollbooth/tollbooth.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,180 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package tollbooth provides rate-limiting logic to HTTP request handler.
|
||||
package tollbooth
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"github.com/didip/tollbooth/errors"
|
||||
"github.com/didip/tollbooth/libstring"
|
||||
"github.com/didip/tollbooth/limiter"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// setResponseHeaders configures X-Rate-Limit-Limit and X-Rate-Limit-Duration
|
||||
func setResponseHeaders(lmt *limiter.Limiter, w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
w.Header().Add("X-Rate-Limit-Limit", fmt.Sprintf("%.2f", lmt.GetMax()))
|
||||
w.Header().Add("X-Rate-Limit-Duration", "1")
|
||||
w.Header().Add("X-Rate-Limit-Request-Forwarded-For", r.Header.Get("X-Forwarded-For"))
|
||||
w.Header().Add("X-Rate-Limit-Request-Remote-Addr", r.RemoteAddr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewLimiter is a convenience function to limiter.New.
|
||||
func NewLimiter(max float64, tbOptions *limiter.ExpirableOptions) *limiter.Limiter {
|
||||
return limiter.New(tbOptions).SetMax(max).SetBurst(int(math.Max(1, max)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LimitByKeys keeps track number of request made by keys separated by pipe.
|
||||
// It returns HTTPError when limit is exceeded.
|
||||
func LimitByKeys(lmt *limiter.Limiter, keys []string) *errors.HTTPError {
|
||||
if lmt.LimitReached(strings.Join(keys, "|")) {
|
||||
return &errors.HTTPError{Message: lmt.GetMessage(), StatusCode: lmt.GetStatusCode()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BuildKeys generates a slice of keys to rate-limit by given limiter and request structs.
|
||||
func BuildKeys(lmt *limiter.Limiter, r *http.Request) [][]string {
|
||||
remoteIP := libstring.RemoteIP(lmt.GetIPLookups(), lmt.GetForwardedForIndexFromBehind(), r)
|
||||
path := r.URL.Path
|
||||
sliceKeys := make([][]string, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Don't BuildKeys if remoteIP is blank.
|
||||
if remoteIP == "" {
|
||||
return sliceKeys
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lmtMethods := lmt.GetMethods()
|
||||
lmtHeaders := lmt.GetHeaders()
|
||||
lmtBasicAuthUsers := lmt.GetBasicAuthUsers()
|
||||
|
||||
lmtHeadersIsSet := len(lmtHeaders) > 0
|
||||
lmtBasicAuthUsersIsSet := len(lmtBasicAuthUsers) > 0
|
||||
|
||||
if lmtMethods != nil && lmtHeadersIsSet && lmtBasicAuthUsersIsSet {
|
||||
// Limit by HTTP methods and HTTP headers+values and Basic Auth credentials.
|
||||
if libstring.StringInSlice(lmtMethods, r.Method) {
|
||||
for headerKey, headerValues := range lmtHeaders {
|
||||
if (headerValues == nil || len(headerValues) <= 0) && r.Header.Get(headerKey) != "" {
|
||||
// If header values are empty, rate-limit all request with headerKey.
|
||||
username, _, ok := r.BasicAuth()
|
||||
if ok && libstring.StringInSlice(lmtBasicAuthUsers, username) {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, r.Method, headerKey, username})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if len(headerValues) > 0 && r.Header.Get(headerKey) != "" {
|
||||
// If header values are not empty, rate-limit all request with headerKey and headerValues.
|
||||
for _, headerValue := range headerValues {
|
||||
username, _, ok := r.BasicAuth()
|
||||
if ok && libstring.StringInSlice(lmtBasicAuthUsers, username) {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, r.Method, headerKey, headerValue, username})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if lmtMethods != nil && lmtHeadersIsSet {
|
||||
// Limit by HTTP methods and HTTP headers+values.
|
||||
if libstring.StringInSlice(lmtMethods, r.Method) {
|
||||
for headerKey, headerValues := range lmtHeaders {
|
||||
if (headerValues == nil || len(headerValues) <= 0) && r.Header.Get(headerKey) != "" {
|
||||
// If header values are empty, rate-limit all request with headerKey.
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, r.Method, headerKey})
|
||||
|
||||
} else if len(headerValues) > 0 && r.Header.Get(headerKey) != "" {
|
||||
// If header values are not empty, rate-limit all request with headerKey and headerValues.
|
||||
for _, headerValue := range headerValues {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, r.Method, headerKey, headerValue})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if lmtMethods != nil && lmtBasicAuthUsersIsSet {
|
||||
// Limit by HTTP methods and Basic Auth credentials.
|
||||
if libstring.StringInSlice(lmtMethods, r.Method) {
|
||||
username, _, ok := r.BasicAuth()
|
||||
if ok && libstring.StringInSlice(lmtBasicAuthUsers, username) {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, r.Method, username})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if lmtMethods != nil {
|
||||
// Limit by HTTP methods.
|
||||
if libstring.StringInSlice(lmtMethods, r.Method) {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, r.Method})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if lmtHeadersIsSet {
|
||||
// Limit by HTTP headers+values.
|
||||
for headerKey, headerValues := range lmtHeaders {
|
||||
if (headerValues == nil || len(headerValues) <= 0) && r.Header.Get(headerKey) != "" {
|
||||
// If header values are empty, rate-limit all request with headerKey.
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, headerKey})
|
||||
|
||||
} else if len(headerValues) > 0 && r.Header.Get(headerKey) != "" {
|
||||
// If header values are not empty, rate-limit all request with headerKey and headerValues.
|
||||
for _, headerValue := range headerValues {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, headerKey, headerValue})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else if lmtBasicAuthUsersIsSet {
|
||||
// Limit by Basic Auth credentials.
|
||||
username, _, ok := r.BasicAuth()
|
||||
if ok && libstring.StringInSlice(lmtBasicAuthUsers, username) {
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path, username})
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Default: Limit by remoteIP and path.
|
||||
sliceKeys = append(sliceKeys, []string{remoteIP, path})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return sliceKeys
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LimitByRequest builds keys based on http.Request struct,
|
||||
// loops through all the keys, and check if any one of them returns HTTPError.
|
||||
func LimitByRequest(lmt *limiter.Limiter, w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) *errors.HTTPError {
|
||||
setResponseHeaders(lmt, w, r)
|
||||
|
||||
sliceKeys := BuildKeys(lmt, r)
|
||||
|
||||
// Loop sliceKeys and check if one of them has error.
|
||||
for _, keys := range sliceKeys {
|
||||
httpError := LimitByKeys(lmt, keys)
|
||||
if httpError != nil {
|
||||
return httpError
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LimitHandler is a middleware that performs rate-limiting given http.Handler struct.
|
||||
func LimitHandler(lmt *limiter.Limiter, next http.Handler) http.Handler {
|
||||
middle := func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
httpError := LimitByRequest(lmt, w, r)
|
||||
if httpError != nil {
|
||||
lmt.ExecOnLimitReached(w, r)
|
||||
w.Header().Add("Content-Type", lmt.GetMessageContentType())
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(httpError.StatusCode)
|
||||
w.Write([]byte(httpError.Message))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// There's no rate-limit error, serve the next handler.
|
||||
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return http.HandlerFunc(middle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LimitFuncHandler is a middleware that performs rate-limiting given request handler function.
|
||||
func LimitFuncHandler(lmt *limiter.Limiter, nextFunc func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request)) http.Handler {
|
||||
return LimitHandler(lmt, http.HandlerFunc(nextFunc))
|
||||
}
|
||||
3
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
3
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
language: go
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.5
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/LICENSE
generated
vendored
21
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
|||
The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2016 Florian Pigorsch
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
57
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/README.md
generated
vendored
57
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/README.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
|||
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser)
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/flopp/go-coordsparser)
|
||||
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/flopp/go-coordsparser)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser)
|
||||
|
||||
# go-coordsparser
|
||||
A library for parsing (geographic) coordinates in go (golang)
|
||||
|
||||
# What?
|
||||
|
||||
go-coordsparser allows you to parse lat/lng coordinates from strings in various popular formats. Currently supported formats are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **D** (decimal degrees), e.g. `40.76, -73.984`
|
||||
- **HD** (hemisphere prefix, decimal degrees), e.g. `N 40.76 W 73.984`
|
||||
- **HDM** (hemisphere prefix, integral degrees, decimal minutes), e.g. `N 40 45.600 W 73 59.040`
|
||||
- **HDMS** (hemisphere prefix, integral degrees, integral minutes, decimal seconds), e.g. `N 40 45 36.0 W 73 59 02.4`
|
||||
|
||||
# How?
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing
|
||||
Installing the library is as easy as
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ go get github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The package can then be used through an
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Using
|
||||
go-coordsparser provides several functions for parsing coordinate strings: a general parsing function `coordsparser.Parse`, which accepts all supported formats, as well as specialized functions `coordsparser.ParseD`, `coordsparser.ParseHD`, `coordsparser.ParseHDM`, `coordsparser.ParseHDMS` for the corresponding coordinate formats.
|
||||
|
||||
Each function takes a single string as a parameter and returns an idiomatic `lat, lng, error` triple, where `lat` and `lng` are decimal degrees (`float64`) with -90 ≤ `lat` ≤ 90 and -180 ≤ `lng` ≤ 180.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// parse any format
|
||||
s1 := "..."
|
||||
lat1, lng1, err := coordsparser.Parse(s1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse coordinates string:", s1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parse specific format, e.g. HDM
|
||||
s2 := "..."
|
||||
lat2, lng2, err = coordsparser.ParseHDM(s2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse coordinates string:", s2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||
Copyright 2016 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
172
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/coordsparser.go
generated
vendored
172
vendor/github.com/flopp/go-coordsparser/coordsparser.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016 Florian Pigorsch. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package coordsparser is a library for parsing (geographic) coordinates in various string formats
|
||||
package coordsparser
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses a coordinate string and returns a lat/lng pair or an error
|
||||
func Parse(s string) (float64, float64, error) {
|
||||
lat, lng, err := ParseD(s)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lat, lng, err = ParseHD(s)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lat, lng, err = ParseHDM(s)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lat, lng, err = ParseHDMS(s)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse coordinates: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseD parses a coordinate string of the form "D.DDDD D.DDDD" and returns a lat/lng pair or an error
|
||||
func ParseD(s string) (float64, float64, error) {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`^\s*([+-]?[\d\.]+)\s*(,|;|:|\s)\s*([+-]?[\d\.]+)\s*$`)
|
||||
|
||||
matches := re.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if matches == nil {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'D' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lat, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[1], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lat < -90 || lat > 90 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'D' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lng, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[3], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lng < -180 || lng > 180 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'D' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseHD parses a coordinate string of the form "H D.DDDD H D.DDDD" and returns a lat/lng pair or an error
|
||||
func ParseHD(s string) (float64, float64, error) {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`^\s*([NnSs])\s*([\d\.]+)\s+([EeWw])\s*([\d\.]+)\s*$`)
|
||||
|
||||
matches := re.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if matches == nil {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HD' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lat, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[2], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lat > 90 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HD' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if matches[1] == "S" || matches[1] == "s" {
|
||||
lat = -lat
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lng, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[4], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lng > 180 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HD' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if matches[3] == "W" || matches[3] == "w" {
|
||||
lng = -lng
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseHDM parses a coordinate string of the form "H D M.MMM H D M.MMM" and returns a lat/lng pair or an error
|
||||
func ParseHDM(s string) (float64, float64, error) {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`^\s*([NnSs])\s*([\d]+)\s+([\d.]+)\s+([EeWw])\s*([\d]+)\s+([\d.]+)\s*$`)
|
||||
|
||||
matches := re.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if matches == nil {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDM' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
latDeg, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[2], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || latDeg > 90 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDM' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
latMin, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[3], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || latMin >= 60 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDM' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lat := latDeg + latMin/60.0
|
||||
if matches[1] == "S" || matches[1] == "s" {
|
||||
lat = -lat
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lngDeg, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[5], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lngDeg > 180 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDM' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lngMin, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[6], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lngMin >= 60 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDM' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lng := lngDeg + lngMin/60.0
|
||||
if matches[4] == "W" || matches[4] == "w" {
|
||||
lng = -lng
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseHDMS parses a coordinate string of the form "H D M S.SSS H D M S.SSS" and returns a lat/lng pair or an error
|
||||
func ParseHDMS(s string) (float64, float64, error) {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`^\s*([NnSs])\s*([\d]+)\s+([\d]+)\s+([\d.]+)\s+([EeWw])\s*([\d]+)\s+([\d]+)\s+([\d.]+)\s*$`)
|
||||
|
||||
matches := re.FindStringSubmatch(s)
|
||||
if matches == nil {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
latDeg, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[2], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || latDeg > 90 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
latMin, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[3], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || latMin >= 60 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
latSec, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[4], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || latSec >= 60 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lat := latDeg + latMin/60.0 + latSec/3600.0
|
||||
if matches[1] == "S" || matches[1] == "s" {
|
||||
lat = -lat
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lngDeg, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[6], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lngDeg > 180 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lngMin, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[7], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lngMin >= 60 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lngSec, err := strconv.ParseFloat(matches[8], 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || lngSec >= 60 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, fmt.Errorf("Cannot parse 'HDMS' string: %s", s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
lng := lngDeg + lngMin/60.0 + lngSec/3600.0
|
||||
if matches[5] == "W" || matches[5] == "w" {
|
||||
lng = -lng
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lat, lng, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
2
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/.gitignore
generated
vendored
2
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/.gitignore
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
|||
*.png
|
||||
|
||||
19
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/LICENSE.md
generated
vendored
19
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/LICENSE.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Copyright (C) 2016 Michael Fogleman
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
220
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/README.md
generated
vendored
220
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/README.md
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,220 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# Go Graphics
|
||||
|
||||
`gg` is a library for rendering 2D graphics in pure Go.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
go get github.com/fogleman/gg
|
||||
|
||||
## GoDoc
|
||||
|
||||
https://godoc.org/github.com/fogleman/gg
|
||||
|
||||
## Hello, Circle!
|
||||
|
||||
Look how easy!
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
dc := gg.NewContext(1000, 1000)
|
||||
dc.DrawCircle(500, 500, 400)
|
||||
dc.SetRGB(0, 0, 0)
|
||||
dc.Fill()
|
||||
dc.SavePNG("out.png")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
|
||||
There are [lots of examples](https://github.com/fogleman/gg/tree/master/examples) included. They're mostly for testing the code, but they're good for learning, too.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating Contexts
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few ways of creating a context.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
NewContext(width, height int) *Context
|
||||
NewContextForImage(im image.Image) *Context
|
||||
NewContextForRGBA(im *image.RGBA) *Context
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Drawing Functions
|
||||
|
||||
Ever used a graphics library that didn't have functions for drawing rectangles
|
||||
or circles? What a pain!
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
DrawPoint(x, y, r float64)
|
||||
DrawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2 float64)
|
||||
DrawRectangle(x, y, w, h float64)
|
||||
DrawRoundedRectangle(x, y, w, h, r float64)
|
||||
DrawCircle(x, y, r float64)
|
||||
DrawArc(x, y, r, angle1, angle2 float64)
|
||||
DrawEllipse(x, y, rx, ry float64)
|
||||
DrawEllipticalArc(x, y, rx, ry, angle1, angle2 float64)
|
||||
DrawRegularPolygon(n int, x, y, r, rotation float64)
|
||||
DrawImage(im image.Image, x, y int)
|
||||
DrawImageAnchored(im image.Image, x, y int, ax, ay float64)
|
||||
SetPixel(x, y int)
|
||||
|
||||
MoveTo(x, y float64)
|
||||
LineTo(x, y float64)
|
||||
QuadraticTo(x1, y1, x2, y2 float64)
|
||||
CubicTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 float64)
|
||||
ClosePath()
|
||||
ClearPath()
|
||||
NewSubPath()
|
||||
|
||||
Clear()
|
||||
Stroke()
|
||||
Fill()
|
||||
StrokePreserve()
|
||||
FillPreserve()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is often desired to center an image at a point. Use `DrawImageAnchored` with `ax` and `ay` set to 0.5 to do this. Use 0 to left or top align. Use 1 to right or bottom align. `DrawStringAnchored` does the same for text, so you don't need to call `MeasureString` yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
## Text Functions
|
||||
|
||||
It will even do word wrap for you!
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
DrawString(s string, x, y float64)
|
||||
DrawStringAnchored(s string, x, y, ax, ay float64)
|
||||
DrawStringWrapped(s string, x, y, ax, ay, width, lineSpacing float64, align Align)
|
||||
MeasureString(s string) (w, h float64)
|
||||
WordWrap(s string, w float64) []string
|
||||
SetFontFace(fontFace font.Face)
|
||||
LoadFontFace(path string, points float64) error
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Color Functions
|
||||
|
||||
Colors can be set in several different ways for your convenience.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
SetRGB(r, g, b float64)
|
||||
SetRGBA(r, g, b, a float64)
|
||||
SetRGB255(r, g, b int)
|
||||
SetRGBA255(r, g, b, a int)
|
||||
SetColor(c color.Color)
|
||||
SetHexColor(x string)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Stroke & Fill Options
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
SetLineWidth(lineWidth float64)
|
||||
SetLineCap(lineCap LineCap)
|
||||
SetLineJoin(lineJoin LineJoin)
|
||||
SetDash(dashes ...float64)
|
||||
SetFillRule(fillRule FillRule)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Gradients & Patterns
|
||||
|
||||
`gg` supports linear and radial gradients and surface patterns. You can also implement your own patterns.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
SetFillStyle(pattern Pattern)
|
||||
SetStrokeStyle(pattern Pattern)
|
||||
NewSolidPattern(color color.Color)
|
||||
NewLinearGradient(x0, y0, x1, y1 float64)
|
||||
NewRadialGradient(x0, y0, r0, x1, y1, r1 float64)
|
||||
NewSurfacePattern(im image.Image, op RepeatOp)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Transformation Functions
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
Identity()
|
||||
Translate(x, y float64)
|
||||
Scale(x, y float64)
|
||||
Rotate(angle float64)
|
||||
Shear(x, y float64)
|
||||
ScaleAbout(sx, sy, x, y float64)
|
||||
RotateAbout(angle, x, y float64)
|
||||
ShearAbout(sx, sy, x, y float64)
|
||||
TransformPoint(x, y float64) (tx, ty float64)
|
||||
InvertY()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is often desired to rotate or scale about a point that is not the origin. The functions `RotateAbout`, `ScaleAbout`, `ShearAbout` are provided as a convenience.
|
||||
|
||||
`InvertY` is provided in case Y should increase from bottom to top vs. the default top to bottom.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: transforms do not currently affect `DrawImage` or `DrawString`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Stack Functions
|
||||
|
||||
Save and restore the state of the context. These can be nested.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
Push()
|
||||
Pop()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Clipping Functions
|
||||
|
||||
Use clipping regions to restrict drawing operations to an area that you
|
||||
defined using paths.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
Clip()
|
||||
ClipPreserve()
|
||||
ResetClip()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Helper Functions
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you just don't want to write these yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
Radians(degrees float64) float64
|
||||
Degrees(radians float64) float64
|
||||
LoadImage(path string) (image.Image, error)
|
||||
LoadPNG(path string) (image.Image, error)
|
||||
SavePNG(path string, im image.Image) error
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## How Do it Do?
|
||||
|
||||
`gg` is mostly a wrapper around `github.com/golang/freetype/raster`. The goal
|
||||
is to provide some more functionality and a nicer API that will suffice for
|
||||
most use cases.
|
||||
|
||||
## Another Example
|
||||
|
||||
See the output of this example below.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/fogleman/gg"
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
const S = 1024
|
||||
dc := gg.NewContext(S, S)
|
||||
dc.SetRGBA(0, 0, 0, 0.1)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 360; i += 15 {
|
||||
dc.Push()
|
||||
dc.RotateAbout(gg.Radians(float64(i)), S/2, S/2)
|
||||
dc.DrawEllipse(S/2, S/2, S*7/16, S/8)
|
||||
dc.Fill()
|
||||
dc.Pop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.SavePNG("out.png")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
59
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/bezier.go
generated
vendored
59
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/bezier.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,59 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import "math"
|
||||
|
||||
func quadratic(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, t float64) (x, y float64) {
|
||||
u := 1 - t
|
||||
a := u * u
|
||||
b := 2 * u * t
|
||||
c := t * t
|
||||
x = a*x0 + b*x1 + c*x2
|
||||
y = a*y0 + b*y1 + c*y2
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func QuadraticBezier(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2 float64) []Point {
|
||||
l := (math.Hypot(x1-x0, y1-y0) +
|
||||
math.Hypot(x2-x1, y2-y1))
|
||||
n := int(l + 0.5)
|
||||
if n < 4 {
|
||||
n = 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
d := float64(n) - 1
|
||||
result := make([]Point, n)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
t := float64(i) / d
|
||||
x, y := quadratic(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, t)
|
||||
result[i] = Point{x, y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func cubic(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, t float64) (x, y float64) {
|
||||
u := 1 - t
|
||||
a := u * u * u
|
||||
b := 3 * u * u * t
|
||||
c := 3 * u * t * t
|
||||
d := t * t * t
|
||||
x = a*x0 + b*x1 + c*x2 + d*x3
|
||||
y = a*y0 + b*y1 + c*y2 + d*y3
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func CubicBezier(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 float64) []Point {
|
||||
l := (math.Hypot(x1-x0, y1-y0) +
|
||||
math.Hypot(x2-x1, y2-y1) +
|
||||
math.Hypot(x3-x2, y3-y2))
|
||||
n := int(l + 0.5)
|
||||
if n < 4 {
|
||||
n = 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
d := float64(n) - 1
|
||||
result := make([]Point, n)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
t := float64(i) / d
|
||||
x, y := cubic(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, t)
|
||||
result[i] = Point{x, y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
768
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/context.go
generated
vendored
768
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/context.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,768 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Package gg provides a simple API for rendering 2D graphics in pure Go.
|
||||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"image/draw"
|
||||
"image/png"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/freetype/raster"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/font"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/font/basicfont"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type LineCap int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
LineCapRound LineCap = iota
|
||||
LineCapButt
|
||||
LineCapSquare
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type LineJoin int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
LineJoinRound LineJoin = iota
|
||||
LineJoinBevel
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type FillRule int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
FillRuleWinding FillRule = iota
|
||||
FillRuleEvenOdd
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Align int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
AlignLeft Align = iota
|
||||
AlignCenter
|
||||
AlignRight
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
defaultFillStyle = NewSolidPattern(color.White)
|
||||
defaultStrokeStyle = NewSolidPattern(color.Black)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Context struct {
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
im *image.RGBA
|
||||
mask *image.Alpha
|
||||
color color.Color
|
||||
fillPattern Pattern
|
||||
strokePattern Pattern
|
||||
strokePath raster.Path
|
||||
fillPath raster.Path
|
||||
start Point
|
||||
current Point
|
||||
hasCurrent bool
|
||||
dashes []float64
|
||||
lineWidth float64
|
||||
lineCap LineCap
|
||||
lineJoin LineJoin
|
||||
fillRule FillRule
|
||||
fontFace font.Face
|
||||
fontHeight float64
|
||||
matrix Matrix
|
||||
stack []*Context
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContext creates a new image.RGBA with the specified width and height
|
||||
// and prepares a context for rendering onto that image.
|
||||
func NewContext(width, height int) *Context {
|
||||
return NewContextForRGBA(image.NewRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, width, height)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContextForImage copies the specified image into a new image.RGBA
|
||||
// and prepares a context for rendering onto that image.
|
||||
func NewContextForImage(im image.Image) *Context {
|
||||
return NewContextForRGBA(imageToRGBA(im))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContextForRGBA prepares a context for rendering onto the specified image.
|
||||
// No copy is made.
|
||||
func NewContextForRGBA(im *image.RGBA) *Context {
|
||||
return &Context{
|
||||
width: im.Bounds().Size().X,
|
||||
height: im.Bounds().Size().Y,
|
||||
im: im,
|
||||
color: color.Transparent,
|
||||
fillPattern: defaultFillStyle,
|
||||
strokePattern: defaultStrokeStyle,
|
||||
lineWidth: 1,
|
||||
fillRule: FillRuleWinding,
|
||||
fontFace: basicfont.Face7x13,
|
||||
fontHeight: 13,
|
||||
matrix: Identity(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Image returns the image that has been drawn by this context.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Image() image.Image {
|
||||
return dc.im
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Width returns the width of the image in pixels.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Width() int {
|
||||
return dc.width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height returns the height of the image in pixels.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Height() int {
|
||||
return dc.height
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SavePNG encodes the image as a PNG and writes it to disk.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SavePNG(path string) error {
|
||||
return SavePNG(path, dc.im)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EncodePNG encodes the image as a PNG and writes it to the provided io.Writer.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) EncodePNG(w io.Writer) error {
|
||||
return png.Encode(w, dc.im)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDash sets the current dash pattern to use. Call with zero arguments to
|
||||
// disable dashes. The values specify the lengths of each dash, with
|
||||
// alternating on and off lengths.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetDash(dashes ...float64) {
|
||||
dc.dashes = dashes
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineWidth(lineWidth float64) {
|
||||
dc.lineWidth = lineWidth
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineCap(lineCap LineCap) {
|
||||
dc.lineCap = lineCap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineCapRound() {
|
||||
dc.lineCap = LineCapRound
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineCapButt() {
|
||||
dc.lineCap = LineCapButt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineCapSquare() {
|
||||
dc.lineCap = LineCapSquare
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineJoin(lineJoin LineJoin) {
|
||||
dc.lineJoin = lineJoin
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineJoinRound() {
|
||||
dc.lineJoin = LineJoinRound
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetLineJoinBevel() {
|
||||
dc.lineJoin = LineJoinBevel
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetFillRule(fillRule FillRule) {
|
||||
dc.fillRule = fillRule
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetFillRuleWinding() {
|
||||
dc.fillRule = FillRuleWinding
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetFillRuleEvenOdd() {
|
||||
dc.fillRule = FillRuleEvenOdd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Color Setters
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) setFillAndStrokeColor(c color.Color) {
|
||||
dc.color = c
|
||||
dc.fillPattern = NewSolidPattern(c)
|
||||
dc.strokePattern = NewSolidPattern(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetFillStyle sets current fill style
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetFillStyle(pattern Pattern) {
|
||||
// if pattern is SolidPattern, also change dc.color(for dc.Clear, dc.drawString)
|
||||
if fillStyle, ok := pattern.(*solidPattern); ok {
|
||||
dc.color = fillStyle.color
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.fillPattern = pattern
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStrokeStyle sets current stroke style
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetStrokeStyle(pattern Pattern) {
|
||||
dc.strokePattern = pattern
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColor sets the current color(for both fill and stroke).
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetColor(c color.Color) {
|
||||
dc.setFillAndStrokeColor(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHexColor sets the current color using a hex string. The leading pound
|
||||
// sign (#) is optional. Both 3- and 6-digit variations are supported. 8 digits
|
||||
// may be provided to set the alpha value as well.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetHexColor(x string) {
|
||||
r, g, b, a := parseHexColor(x)
|
||||
dc.SetRGBA255(r, g, b, a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetRGBA255 sets the current color. r, g, b, a values should be between 0 and
|
||||
// 255, inclusive.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetRGBA255(r, g, b, a int) {
|
||||
dc.color = color.NRGBA{uint8(r), uint8(g), uint8(b), uint8(a)}
|
||||
dc.setFillAndStrokeColor(dc.color)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetRGB255 sets the current color. r, g, b values should be between 0 and 255,
|
||||
// inclusive. Alpha will be set to 255 (fully opaque).
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetRGB255(r, g, b int) {
|
||||
dc.SetRGBA255(r, g, b, 255)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetRGBA sets the current color. r, g, b, a values should be between 0 and 1,
|
||||
// inclusive.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetRGBA(r, g, b, a float64) {
|
||||
dc.color = color.NRGBA{
|
||||
uint8(r * 255),
|
||||
uint8(g * 255),
|
||||
uint8(b * 255),
|
||||
uint8(a * 255),
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.setFillAndStrokeColor(dc.color)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetRGB sets the current color. r, g, b values should be between 0 and 1,
|
||||
// inclusive. Alpha will be set to 1 (fully opaque).
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetRGB(r, g, b float64) {
|
||||
dc.SetRGBA(r, g, b, 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Path Manipulation
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveTo starts a new subpath within the current path starting at the
|
||||
// specified point.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) MoveTo(x, y float64) {
|
||||
if dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Add1(dc.start.Fixed())
|
||||
}
|
||||
x, y = dc.TransformPoint(x, y)
|
||||
p := Point{x, y}
|
||||
dc.strokePath.Start(p.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Start(p.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.start = p
|
||||
dc.current = p
|
||||
dc.hasCurrent = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LineTo adds a line segment to the current path starting at the current
|
||||
// point. If there is no current point, it is equivalent to MoveTo(x, y)
|
||||
func (dc *Context) LineTo(x, y float64) {
|
||||
if !dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x, y)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
x, y = dc.TransformPoint(x, y)
|
||||
p := Point{x, y}
|
||||
dc.strokePath.Add1(p.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Add1(p.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.current = p
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// QuadraticTo adds a quadratic bezier curve to the current path starting at
|
||||
// the current point. If there is no current point, it first performs
|
||||
// MoveTo(x1, y1)
|
||||
func (dc *Context) QuadraticTo(x1, y1, x2, y2 float64) {
|
||||
if !dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x1, y1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
x1, y1 = dc.TransformPoint(x1, y1)
|
||||
x2, y2 = dc.TransformPoint(x2, y2)
|
||||
p1 := Point{x1, y1}
|
||||
p2 := Point{x2, y2}
|
||||
dc.strokePath.Add2(p1.Fixed(), p2.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Add2(p1.Fixed(), p2.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.current = p2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CubicTo adds a cubic bezier curve to the current path starting at the
|
||||
// current point. If there is no current point, it first performs
|
||||
// MoveTo(x1, y1). Because freetype/raster does not support cubic beziers,
|
||||
// this is emulated with many small line segments.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) CubicTo(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 float64) {
|
||||
if !dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x1, y1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
x0, y0 := dc.current.X, dc.current.Y
|
||||
x1, y1 = dc.TransformPoint(x1, y1)
|
||||
x2, y2 = dc.TransformPoint(x2, y2)
|
||||
x3, y3 = dc.TransformPoint(x3, y3)
|
||||
points := CubicBezier(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3)
|
||||
previous := dc.current.Fixed()
|
||||
for _, p := range points[1:] {
|
||||
f := p.Fixed()
|
||||
if f == previous {
|
||||
// TODO: this fixes some rendering issues but not all
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
previous = f
|
||||
dc.strokePath.Add1(f)
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Add1(f)
|
||||
dc.current = p
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClosePath adds a line segment from the current point to the beginning
|
||||
// of the current subpath. If there is no current point, this is a no-op.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) ClosePath() {
|
||||
if dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.strokePath.Add1(dc.start.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Add1(dc.start.Fixed())
|
||||
dc.current = dc.start
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearPath clears the current path. There is no current point after this
|
||||
// operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) ClearPath() {
|
||||
dc.strokePath.Clear()
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Clear()
|
||||
dc.hasCurrent = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewSubPath starts a new subpath within the current path. There is no current
|
||||
// point after this operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) NewSubPath() {
|
||||
if dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.fillPath.Add1(dc.start.Fixed())
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.hasCurrent = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Path Drawing
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) capper() raster.Capper {
|
||||
switch dc.lineCap {
|
||||
case LineCapButt:
|
||||
return raster.ButtCapper
|
||||
case LineCapRound:
|
||||
return raster.RoundCapper
|
||||
case LineCapSquare:
|
||||
return raster.SquareCapper
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) joiner() raster.Joiner {
|
||||
switch dc.lineJoin {
|
||||
case LineJoinBevel:
|
||||
return raster.BevelJoiner
|
||||
case LineJoinRound:
|
||||
return raster.RoundJoiner
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) stroke(painter raster.Painter) {
|
||||
path := dc.strokePath
|
||||
if len(dc.dashes) > 0 {
|
||||
path = dashed(path, dc.dashes)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// TODO: this is a temporary workaround to remove tiny segments
|
||||
// that result in rendering issues
|
||||
path = rasterPath(flattenPath(path))
|
||||
}
|
||||
r := raster.NewRasterizer(dc.width, dc.height)
|
||||
r.UseNonZeroWinding = true
|
||||
r.AddStroke(path, fix(dc.lineWidth), dc.capper(), dc.joiner())
|
||||
r.Rasterize(painter)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) fill(painter raster.Painter) {
|
||||
path := dc.fillPath
|
||||
if dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
path = make(raster.Path, len(dc.fillPath))
|
||||
copy(path, dc.fillPath)
|
||||
path.Add1(dc.start.Fixed())
|
||||
}
|
||||
r := raster.NewRasterizer(dc.width, dc.height)
|
||||
r.UseNonZeroWinding = dc.fillRule == FillRuleWinding
|
||||
r.AddPath(path)
|
||||
r.Rasterize(painter)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StrokePreserve strokes the current path with the current color, line width,
|
||||
// line cap, line join and dash settings. The path is preserved after this
|
||||
// operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) StrokePreserve() {
|
||||
painter := newPatternPainter(dc.im, dc.mask, dc.strokePattern)
|
||||
dc.stroke(painter)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stroke strokes the current path with the current color, line width,
|
||||
// line cap, line join and dash settings. The path is cleared after this
|
||||
// operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Stroke() {
|
||||
dc.StrokePreserve()
|
||||
dc.ClearPath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FillPreserve fills the current path with the current color. Open subpaths
|
||||
// are implicity closed. The path is preserved after this operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) FillPreserve() {
|
||||
painter := newPatternPainter(dc.im, dc.mask, dc.fillPattern)
|
||||
dc.fill(painter)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill fills the current path with the current color. Open subpaths
|
||||
// are implicity closed. The path is cleared after this operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Fill() {
|
||||
dc.FillPreserve()
|
||||
dc.ClearPath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClipPreserve updates the clipping region by intersecting the current
|
||||
// clipping region with the current path as it would be filled by dc.Fill().
|
||||
// The path is preserved after this operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) ClipPreserve() {
|
||||
clip := image.NewAlpha(image.Rect(0, 0, dc.width, dc.height))
|
||||
painter := raster.NewAlphaOverPainter(clip)
|
||||
dc.fill(painter)
|
||||
if dc.mask == nil {
|
||||
dc.mask = clip
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
mask := image.NewAlpha(image.Rect(0, 0, dc.width, dc.height))
|
||||
draw.DrawMask(mask, mask.Bounds(), clip, image.ZP, dc.mask, image.ZP, draw.Over)
|
||||
dc.mask = mask
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clip updates the clipping region by intersecting the current
|
||||
// clipping region with the current path as it would be filled by dc.Fill().
|
||||
// The path is cleared after this operation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Clip() {
|
||||
dc.ClipPreserve()
|
||||
dc.ClearPath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetClip clears the clipping region.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) ResetClip() {
|
||||
dc.mask = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Convenient Drawing Functions
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear fills the entire image with the current color.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Clear() {
|
||||
src := image.NewUniform(dc.color)
|
||||
draw.Draw(dc.im, dc.im.Bounds(), src, image.ZP, draw.Src)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPixel sets the color of the specified pixel using the current color.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetPixel(x, y int) {
|
||||
dc.im.Set(x, y, dc.color)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DrawPoint is like DrawCircle but ensures that a circle of the specified
|
||||
// size is drawn regardless of the current transformation matrix. The position
|
||||
// is still transformed, but not the shape of the point.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawPoint(x, y, r float64) {
|
||||
dc.Push()
|
||||
tx, ty := dc.TransformPoint(x, y)
|
||||
dc.Identity()
|
||||
dc.DrawCircle(tx, ty, r)
|
||||
dc.Pop()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2 float64) {
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x1, y1)
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x2, y2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawRectangle(x, y, w, h float64) {
|
||||
dc.NewSubPath()
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x, y)
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x+w, y)
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x+w, y+h)
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x, y+h)
|
||||
dc.ClosePath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawRoundedRectangle(x, y, w, h, r float64) {
|
||||
x0, x1, x2, x3 := x, x+r, x+w-r, x+w
|
||||
y0, y1, y2, y3 := y, y+r, y+h-r, y+h
|
||||
dc.NewSubPath()
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x1, y0)
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x2, y0)
|
||||
dc.DrawArc(x2, y1, r, Radians(270), Radians(360))
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x3, y2)
|
||||
dc.DrawArc(x2, y2, r, Radians(0), Radians(90))
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x1, y3)
|
||||
dc.DrawArc(x1, y2, r, Radians(90), Radians(180))
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x0, y1)
|
||||
dc.DrawArc(x1, y1, r, Radians(180), Radians(270))
|
||||
dc.ClosePath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawEllipticalArc(x, y, rx, ry, angle1, angle2 float64) {
|
||||
const n = 16
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
p1 := float64(i+0) / n
|
||||
p2 := float64(i+1) / n
|
||||
a1 := angle1 + (angle2-angle1)*p1
|
||||
a2 := angle1 + (angle2-angle1)*p2
|
||||
x0 := x + rx*math.Cos(a1)
|
||||
y0 := y + ry*math.Sin(a1)
|
||||
x1 := x + rx*math.Cos(a1+(a2-a1)/2)
|
||||
y1 := y + ry*math.Sin(a1+(a2-a1)/2)
|
||||
x2 := x + rx*math.Cos(a2)
|
||||
y2 := y + ry*math.Sin(a2)
|
||||
cx := 2*x1 - x0/2 - x2/2
|
||||
cy := 2*y1 - y0/2 - y2/2
|
||||
if i == 0 && !dc.hasCurrent {
|
||||
dc.MoveTo(x0, y0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.QuadraticTo(cx, cy, x2, y2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawEllipse(x, y, rx, ry float64) {
|
||||
dc.NewSubPath()
|
||||
dc.DrawEllipticalArc(x, y, rx, ry, 0, 2*math.Pi)
|
||||
dc.ClosePath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawArc(x, y, r, angle1, angle2 float64) {
|
||||
dc.DrawEllipticalArc(x, y, r, r, angle1, angle2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawCircle(x, y, r float64) {
|
||||
dc.NewSubPath()
|
||||
dc.DrawEllipticalArc(x, y, r, r, 0, 2*math.Pi)
|
||||
dc.ClosePath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawRegularPolygon(n int, x, y, r, rotation float64) {
|
||||
angle := 2 * math.Pi / float64(n)
|
||||
rotation -= math.Pi / 2
|
||||
if n%2 == 0 {
|
||||
rotation += angle / 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.NewSubPath()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
a := rotation + angle*float64(i)
|
||||
dc.LineTo(x+r*math.Cos(a), y+r*math.Sin(a))
|
||||
}
|
||||
dc.ClosePath()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DrawImage draws the specified image at the specified point.
|
||||
// Currently, rotation and scaling transforms are not supported.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawImage(im image.Image, x, y int) {
|
||||
dc.DrawImageAnchored(im, x, y, 0, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DrawImageAnchored draws the specified image at the specified anchor point.
|
||||
// The anchor point is x - w * ax, y - h * ay, where w, h is the size of the
|
||||
// image. Use ax=0.5, ay=0.5 to center the image at the specified point.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawImageAnchored(im image.Image, x, y int, ax, ay float64) {
|
||||
s := im.Bounds().Size()
|
||||
x -= int(ax * float64(s.X))
|
||||
y -= int(ay * float64(s.Y))
|
||||
p := image.Pt(x, y)
|
||||
r := image.Rectangle{p, p.Add(s)}
|
||||
if dc.mask == nil {
|
||||
draw.Draw(dc.im, r, im, image.ZP, draw.Over)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
draw.DrawMask(dc.im, r, im, image.ZP, dc.mask, p, draw.Over)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Text Functions
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) SetFontFace(fontFace font.Face) {
|
||||
dc.fontFace = fontFace
|
||||
dc.fontHeight = float64(fontFace.Metrics().Height) / 64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) LoadFontFace(path string, points float64) error {
|
||||
face, err := LoadFontFace(path, points)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
dc.fontFace = face
|
||||
dc.fontHeight = points * 72 / 96
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (dc *Context) drawString(im *image.RGBA, s string, x, y float64) {
|
||||
d := &font.Drawer{
|
||||
Dst: im,
|
||||
Src: image.NewUniform(dc.color),
|
||||
Face: dc.fontFace,
|
||||
Dot: fixp(x, y),
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.DrawString(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DrawString draws the specified text at the specified point.
|
||||
// Currently, rotation and scaling transforms are not supported.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawString(s string, x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.DrawStringAnchored(s, x, y, 0, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DrawStringAnchored draws the specified text at the specified anchor point.
|
||||
// The anchor point is x - w * ax, y - h * ay, where w, h is the size of the
|
||||
// text. Use ax=0.5, ay=0.5 to center the text at the specified point.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawStringAnchored(s string, x, y, ax, ay float64) {
|
||||
w, h := dc.MeasureString(s)
|
||||
x, y = dc.TransformPoint(x, y)
|
||||
x -= ax * w
|
||||
y += ay * h
|
||||
if dc.mask == nil {
|
||||
dc.drawString(dc.im, s, x, y)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
im := image.NewRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, dc.width, dc.height))
|
||||
dc.drawString(im, s, x, y)
|
||||
draw.DrawMask(dc.im, dc.im.Bounds(), im, image.ZP, dc.mask, image.ZP, draw.Over)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DrawStringWrapped word-wraps the specified string to the given max width
|
||||
// and then draws it at the specified anchor point using the given line
|
||||
// spacing and text alignment.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) DrawStringWrapped(s string, x, y, ax, ay, width, lineSpacing float64, align Align) {
|
||||
lines := dc.WordWrap(s, width)
|
||||
h := float64(len(lines)) * dc.fontHeight * lineSpacing
|
||||
h -= (lineSpacing - 1) * dc.fontHeight
|
||||
x -= ax * width
|
||||
y -= ay * h
|
||||
switch align {
|
||||
case AlignLeft:
|
||||
ax = 0
|
||||
case AlignCenter:
|
||||
ax = 0.5
|
||||
x += width / 2
|
||||
case AlignRight:
|
||||
ax = 1
|
||||
x += width
|
||||
}
|
||||
ay = 1
|
||||
for _, line := range lines {
|
||||
dc.DrawStringAnchored(line, x, y, ax, ay)
|
||||
y += dc.fontHeight * lineSpacing
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MeasureString returns the rendered width and height of the specified text
|
||||
// given the current font face.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) MeasureString(s string) (w, h float64) {
|
||||
d := &font.Drawer{
|
||||
Face: dc.fontFace,
|
||||
}
|
||||
a := d.MeasureString(s)
|
||||
return float64(a >> 6), dc.fontHeight
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WordWrap wraps the specified string to the given max width and current
|
||||
// font face.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) WordWrap(s string, w float64) []string {
|
||||
return wordWrap(dc, s, w)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transformation Matrix Operations
|
||||
|
||||
// Identity resets the current transformation matrix to the identity matrix.
|
||||
// This results in no translating, scaling, rotating, or shearing.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Identity() {
|
||||
dc.matrix = Identity()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Translate updates the current matrix with a translation.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Translate(x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.matrix = dc.matrix.Translate(x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Scale updates the current matrix with a scaling factor.
|
||||
// Scaling occurs about the origin.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Scale(x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.matrix = dc.matrix.Scale(x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScaleAbout updates the current matrix with a scaling factor.
|
||||
// Scaling occurs about the specified point.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) ScaleAbout(sx, sy, x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.Translate(x, y)
|
||||
dc.Scale(sx, sy)
|
||||
dc.Translate(-x, -y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rotate updates the current matrix with a clockwise rotation.
|
||||
// Rotation occurs about the origin. Angle is specified in radians.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Rotate(angle float64) {
|
||||
dc.matrix = dc.matrix.Rotate(angle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RotateAbout updates the current matrix with a clockwise rotation.
|
||||
// Rotation occurs about the specified point. Angle is specified in radians.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) RotateAbout(angle, x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.Translate(x, y)
|
||||
dc.Rotate(angle)
|
||||
dc.Translate(-x, -y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Shear updates the current matrix with a shearing angle.
|
||||
// Shearing occurs about the origin.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Shear(x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.matrix = dc.matrix.Shear(x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShearAbout updates the current matrix with a shearing angle.
|
||||
// Shearing occurs about the specified point.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) ShearAbout(sx, sy, x, y float64) {
|
||||
dc.Translate(x, y)
|
||||
dc.Shear(sx, sy)
|
||||
dc.Translate(-x, -y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TransformPoint multiplies the specified point by the current matrix,
|
||||
// returning a transformed position.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) TransformPoint(x, y float64) (tx, ty float64) {
|
||||
return dc.matrix.TransformPoint(x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InvertY flips the Y axis so that Y grows from bottom to top and Y=0 is at
|
||||
// the bottom of the image.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) InvertY() {
|
||||
dc.Translate(0, float64(dc.height))
|
||||
dc.Scale(1, -1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stack
|
||||
|
||||
// Push saves the current state of the context for later retrieval. These
|
||||
// can be nested.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Push() {
|
||||
x := *dc
|
||||
dc.stack = append(dc.stack, &x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Pop restores the last saved context state from the stack.
|
||||
func (dc *Context) Pop() {
|
||||
before := *dc
|
||||
s := dc.stack
|
||||
x, s := s[len(s)-1], s[:len(s)-1]
|
||||
*dc = *x
|
||||
dc.mask = before.mask
|
||||
dc.strokePath = before.strokePath
|
||||
dc.fillPath = before.fillPath
|
||||
dc.start = before.start
|
||||
dc.current = before.current
|
||||
dc.hasCurrent = before.hasCurrent
|
||||
}
|
||||
202
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/gradient.go
generated
vendored
202
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/gradient.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,202 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type stop struct {
|
||||
pos float64
|
||||
color color.Color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type stops []stop
|
||||
|
||||
// Len satisfies the Sort interface.
|
||||
func (s stops) Len() int {
|
||||
return len(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Less satisfies the Sort interface.
|
||||
func (s stops) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return s[i].pos < s[j].pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Swap satisfies the Sort interface.
|
||||
func (s stops) Swap(i, j int) {
|
||||
s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type Gradient interface {
|
||||
Pattern
|
||||
AddColorStop(offset float64, color color.Color)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Linear Gradient
|
||||
type linearGradient struct {
|
||||
x0, y0, x1, y1 float64
|
||||
stops stops
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *linearGradient) ColorAt(x, y int) color.Color {
|
||||
if len(g.stops) == 0 {
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fx, fy := float64(x), float64(y)
|
||||
x0, y0, x1, y1 := g.x0, g.y0, g.x1, g.y1
|
||||
dx, dy := x1-x0, y1-y0
|
||||
|
||||
// Horizontal
|
||||
if dy == 0 && dx != 0 {
|
||||
return getColor((fx-x0)/dx, g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Vertical
|
||||
if dx == 0 && dy != 0 {
|
||||
return getColor((fy-y0)/dy, g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Dot product
|
||||
s0 := dx*(fx-x0) + dy*(fy-y0)
|
||||
if s0 < 0 {
|
||||
return g.stops[0].color
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Calculate distance to (x0,y0) alone (x0,y0)->(x1,y1)
|
||||
mag := math.Hypot(dx, dy)
|
||||
u := ((fx-x0)*-dy + (fy-y0)*dx) / (mag * mag)
|
||||
x2, y2 := x0+u*-dy, y0+u*dx
|
||||
d := math.Hypot(fx-x2, fy-y2) / mag
|
||||
return getColor(d, g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *linearGradient) AddColorStop(offset float64, color color.Color) {
|
||||
g.stops = append(g.stops, stop{pos: offset, color: color})
|
||||
sort.Sort(g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewLinearGradient(x0, y0, x1, y1 float64) Gradient {
|
||||
g := &linearGradient{
|
||||
x0: x0, y0: y0,
|
||||
x1: x1, y1: y1,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return g
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Radial Gradient
|
||||
type circle struct {
|
||||
x, y, r float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type radialGradient struct {
|
||||
c0, c1, cd circle
|
||||
a, inva float64
|
||||
mindr float64
|
||||
stops stops
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func dot3(x0, y0, z0, x1, y1, z1 float64) float64 {
|
||||
return x0*x1 + y0*y1 + z0*z1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *radialGradient) ColorAt(x, y int) color.Color {
|
||||
if len(g.stops) == 0 {
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy from pixman's pixman-radial-gradient.c
|
||||
|
||||
dx, dy := float64(x)+0.5-g.c0.x, float64(y)+0.5-g.c0.y
|
||||
b := dot3(dx, dy, g.c0.r, g.cd.x, g.cd.y, g.cd.r)
|
||||
c := dot3(dx, dy, -g.c0.r, dx, dy, g.c0.r)
|
||||
|
||||
if g.a == 0 {
|
||||
if b == 0 {
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
t := 0.5 * c / b
|
||||
if t*g.cd.r >= g.mindr {
|
||||
return getColor(t, g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
discr := dot3(b, g.a, 0, b, -c, 0)
|
||||
if discr >= 0 {
|
||||
sqrtdiscr := math.Sqrt(discr)
|
||||
t0 := (b + sqrtdiscr) * g.inva
|
||||
t1 := (b - sqrtdiscr) * g.inva
|
||||
|
||||
if t0*g.cd.r >= g.mindr {
|
||||
return getColor(t0, g.stops)
|
||||
} else if t1*g.cd.r >= g.mindr {
|
||||
return getColor(t1, g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *radialGradient) AddColorStop(offset float64, color color.Color) {
|
||||
g.stops = append(g.stops, stop{pos: offset, color: color})
|
||||
sort.Sort(g.stops)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewRadialGradient(x0, y0, r0, x1, y1, r1 float64) Gradient {
|
||||
c0 := circle{x0, y0, r0}
|
||||
c1 := circle{x1, y1, r1}
|
||||
cd := circle{x1 - x0, y1 - y0, r1 - r0}
|
||||
a := dot3(cd.x, cd.y, -cd.r, cd.x, cd.y, cd.r)
|
||||
var inva float64
|
||||
if a != 0 {
|
||||
inva = 1.0 / a
|
||||
}
|
||||
mindr := -c0.r
|
||||
g := &radialGradient{
|
||||
c0: c0,
|
||||
c1: c1,
|
||||
cd: cd,
|
||||
a: a,
|
||||
inva: inva,
|
||||
mindr: mindr,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return g
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getColor(pos float64, stops stops) color.Color {
|
||||
if pos <= 0.0 || len(stops) == 1 {
|
||||
return stops[0].color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
last := stops[len(stops)-1]
|
||||
|
||||
if pos >= last.pos {
|
||||
return last.color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, stop := range stops[1:] {
|
||||
if pos < stop.pos {
|
||||
pos = (pos - stops[i].pos) / (stop.pos - stops[i].pos)
|
||||
return colorLerp(stops[i].color, stop.color, pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return last.color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func colorLerp(c0, c1 color.Color, t float64) color.Color {
|
||||
r0, g0, b0, a0 := c0.RGBA()
|
||||
r1, g1, b1, a1 := c1.RGBA()
|
||||
|
||||
return color.NRGBA{
|
||||
lerp(r0, r1, t),
|
||||
lerp(g0, g1, t),
|
||||
lerp(b0, b1, t),
|
||||
lerp(a0, a1, t),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lerp(a, b uint32, t float64) uint8 {
|
||||
return uint8(int32(float64(a)*(1.0-t)+float64(b)*t) >> 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
88
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/matrix.go
generated
vendored
88
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/matrix.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import "math"
|
||||
|
||||
type Matrix struct {
|
||||
XX, YX, XY, YY, X0, Y0 float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Identity() Matrix {
|
||||
return Matrix{
|
||||
1, 0,
|
||||
0, 1,
|
||||
0, 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Translate(x, y float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Matrix{
|
||||
1, 0,
|
||||
0, 1,
|
||||
x, y,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Scale(x, y float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Matrix{
|
||||
x, 0,
|
||||
0, y,
|
||||
0, 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Rotate(angle float64) Matrix {
|
||||
c := math.Cos(angle)
|
||||
s := math.Sin(angle)
|
||||
return Matrix{
|
||||
c, s,
|
||||
-s, c,
|
||||
0, 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Shear(x, y float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Matrix{
|
||||
1, y,
|
||||
x, 1,
|
||||
0, 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) Multiply(b Matrix) Matrix {
|
||||
return Matrix{
|
||||
a.XX*b.XX + a.YX*b.XY,
|
||||
a.XX*b.YX + a.YX*b.YY,
|
||||
a.XY*b.XX + a.YY*b.XY,
|
||||
a.XY*b.YX + a.YY*b.YY,
|
||||
a.X0*b.XX + a.Y0*b.XY + b.X0,
|
||||
a.X0*b.YX + a.Y0*b.YY + b.Y0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) TransformVector(x, y float64) (tx, ty float64) {
|
||||
tx = a.XX*x + a.XY*y
|
||||
ty = a.YX*x + a.YY*y
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) TransformPoint(x, y float64) (tx, ty float64) {
|
||||
tx = a.XX*x + a.XY*y + a.X0
|
||||
ty = a.YX*x + a.YY*y + a.Y0
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) Translate(x, y float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Translate(x, y).Multiply(a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) Scale(x, y float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Scale(x, y).Multiply(a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) Rotate(angle float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Rotate(angle).Multiply(a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Matrix) Shear(x, y float64) Matrix {
|
||||
return Shear(x, y).Multiply(a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
140
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/path.go
generated
vendored
140
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/path.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,140 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/golang/freetype/raster"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func flattenPath(p raster.Path) [][]Point {
|
||||
var result [][]Point
|
||||
var path []Point
|
||||
var cx, cy float64
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(p); {
|
||||
switch p[i] {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
if len(path) > 0 {
|
||||
result = append(result, path)
|
||||
path = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
x := unfix(p[i+1])
|
||||
y := unfix(p[i+2])
|
||||
path = append(path, Point{x, y})
|
||||
cx, cy = x, y
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
x := unfix(p[i+1])
|
||||
y := unfix(p[i+2])
|
||||
path = append(path, Point{x, y})
|
||||
cx, cy = x, y
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
x1 := unfix(p[i+1])
|
||||
y1 := unfix(p[i+2])
|
||||
x2 := unfix(p[i+3])
|
||||
y2 := unfix(p[i+4])
|
||||
points := QuadraticBezier(cx, cy, x1, y1, x2, y2)
|
||||
path = append(path, points...)
|
||||
cx, cy = x2, y2
|
||||
i += 6
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
x1 := unfix(p[i+1])
|
||||
y1 := unfix(p[i+2])
|
||||
x2 := unfix(p[i+3])
|
||||
y2 := unfix(p[i+4])
|
||||
x3 := unfix(p[i+5])
|
||||
y3 := unfix(p[i+6])
|
||||
points := CubicBezier(cx, cy, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3)
|
||||
path = append(path, points...)
|
||||
cx, cy = x3, y3
|
||||
i += 8
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(path) > 0 {
|
||||
result = append(result, path)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func dashPath(paths [][]Point, dashes []float64) [][]Point {
|
||||
var result [][]Point
|
||||
if len(dashes) == 0 {
|
||||
return paths
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(dashes) == 1 {
|
||||
dashes = append(dashes, dashes[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, path := range paths {
|
||||
if len(path) < 2 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
previous := path[0]
|
||||
pathIndex := 1
|
||||
dashIndex := 0
|
||||
segmentLength := 0.0
|
||||
var segment []Point
|
||||
segment = append(segment, previous)
|
||||
for pathIndex < len(path) {
|
||||
dashLength := dashes[dashIndex]
|
||||
point := path[pathIndex]
|
||||
d := previous.Distance(point)
|
||||
maxd := dashLength - segmentLength
|
||||
if d > maxd {
|
||||
t := maxd / d
|
||||
p := previous.Interpolate(point, t)
|
||||
segment = append(segment, p)
|
||||
if dashIndex%2 == 0 && len(segment) > 1 {
|
||||
result = append(result, segment)
|
||||
}
|
||||
segment = nil
|
||||
segment = append(segment, p)
|
||||
segmentLength = 0
|
||||
previous = p
|
||||
dashIndex = (dashIndex + 1) % len(dashes)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
segment = append(segment, point)
|
||||
previous = point
|
||||
segmentLength += d
|
||||
pathIndex++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dashIndex%2 == 0 && len(segment) > 1 {
|
||||
result = append(result, segment)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func rasterPath(paths [][]Point) raster.Path {
|
||||
var result raster.Path
|
||||
for _, path := range paths {
|
||||
var previous fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
for i, point := range path {
|
||||
f := point.Fixed()
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
result.Start(f)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dx := f.X - previous.X
|
||||
dy := f.Y - previous.Y
|
||||
if dx < 0 {
|
||||
dx = -dx
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dy < 0 {
|
||||
dy = -dy
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dx+dy > 8 {
|
||||
// TODO: this is a hack for cases where two points are
|
||||
// too close - causes rendering issues with joins / caps
|
||||
result.Add1(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
previous = f
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func dashed(path raster.Path, dashes []float64) raster.Path {
|
||||
return rasterPath(dashPath(flattenPath(path), dashes))
|
||||
}
|
||||
123
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/pattern.go
generated
vendored
123
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/pattern.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/freetype/raster"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type RepeatOp int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
RepeatBoth RepeatOp = iota
|
||||
RepeatX
|
||||
RepeatY
|
||||
RepeatNone
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Pattern interface {
|
||||
ColorAt(x, y int) color.Color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Solid Pattern
|
||||
type solidPattern struct {
|
||||
color color.Color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *solidPattern) ColorAt(x, y int) color.Color {
|
||||
return p.color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewSolidPattern(color color.Color) Pattern {
|
||||
return &solidPattern{color: color}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Surface Pattern
|
||||
type surfacePattern struct {
|
||||
im image.Image
|
||||
op RepeatOp
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *surfacePattern) ColorAt(x, y int) color.Color {
|
||||
b := p.im.Bounds()
|
||||
switch p.op {
|
||||
case RepeatX:
|
||||
if y >= b.Dy() {
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
case RepeatY:
|
||||
if x >= b.Dx() {
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
case RepeatNone:
|
||||
if x >= b.Dx() || y >= b.Dy() {
|
||||
return color.Transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = x%b.Dx() + b.Min.X
|
||||
y = y%b.Dy() + b.Min.Y
|
||||
return p.im.At(x, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func NewSurfacePattern(im image.Image, op RepeatOp) Pattern {
|
||||
return &surfacePattern{im: im, op: op}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type patternPainter struct {
|
||||
im *image.RGBA
|
||||
mask *image.Alpha
|
||||
p Pattern
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint satisfies the Painter interface.
|
||||
func (r *patternPainter) Paint(ss []raster.Span, done bool) {
|
||||
b := r.im.Bounds()
|
||||
for _, s := range ss {
|
||||
if s.Y < b.Min.Y {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.Y >= b.Max.Y {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 < b.Min.X {
|
||||
s.X0 = b.Min.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X1 > b.Max.X {
|
||||
s.X1 = b.Max.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 >= s.X1 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
const m = 1<<16 - 1
|
||||
y := s.Y - r.im.Rect.Min.Y
|
||||
x0 := s.X0 - r.im.Rect.Min.X
|
||||
// RGBAPainter.Paint() in $GOPATH/src/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/paint.go
|
||||
i0 := (s.Y-r.im.Rect.Min.Y)*r.im.Stride + (s.X0-r.im.Rect.Min.X)*4
|
||||
i1 := i0 + (s.X1-s.X0)*4
|
||||
for i, x := i0, x0; i < i1; i, x = i+4, x+1 {
|
||||
ma := s.Alpha
|
||||
if r.mask != nil {
|
||||
ma = ma * uint32(r.mask.AlphaAt(x, y).A) / 255
|
||||
if ma == 0 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
c := r.p.ColorAt(x, y)
|
||||
cr, cg, cb, ca := c.RGBA()
|
||||
dr := uint32(r.im.Pix[i+0])
|
||||
dg := uint32(r.im.Pix[i+1])
|
||||
db := uint32(r.im.Pix[i+2])
|
||||
da := uint32(r.im.Pix[i+3])
|
||||
a := (m - (ca * ma / m)) * 0x101
|
||||
r.im.Pix[i+0] = uint8((dr*a + cr*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.im.Pix[i+1] = uint8((dg*a + cg*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.im.Pix[i+2] = uint8((db*a + cb*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.im.Pix[i+3] = uint8((da*a + ca*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newPatternPainter(im *image.RGBA, mask *image.Alpha, p Pattern) *patternPainter {
|
||||
return &patternPainter{im, mask, p}
|
||||
}
|
||||
25
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/point.go
generated
vendored
25
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/point.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Point struct {
|
||||
X, Y float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Point) Fixed() fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixp(a.X, a.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Point) Distance(b Point) float64 {
|
||||
return math.Hypot(a.X-b.X, a.Y-b.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Point) Interpolate(b Point, t float64) Point {
|
||||
x := a.X + (b.X-a.X)*t
|
||||
y := a.Y + (b.Y-a.Y)*t
|
||||
return Point{x, y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
117
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/util.go
generated
vendored
117
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/util.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
"image/draw"
|
||||
_ "image/jpeg"
|
||||
"image/png"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/freetype/truetype"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/font"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func Radians(degrees float64) float64 {
|
||||
return degrees * math.Pi / 180
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func Degrees(radians float64) float64 {
|
||||
return radians * 180 / math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func LoadImage(path string) (image.Image, error) {
|
||||
file, err := os.Open(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
im, _, err := image.Decode(file)
|
||||
return im, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func LoadPNG(path string) (image.Image, error) {
|
||||
file, err := os.Open(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
return png.Decode(file)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func SavePNG(path string, im image.Image) error {
|
||||
file, err := os.Create(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer file.Close()
|
||||
return png.Encode(file, im)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func imageToRGBA(src image.Image) *image.RGBA {
|
||||
dst := image.NewRGBA(src.Bounds())
|
||||
draw.Draw(dst, dst.Rect, src, image.ZP, draw.Src)
|
||||
return dst
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseHexColor(x string) (r, g, b, a int) {
|
||||
x = strings.TrimPrefix(x, "#")
|
||||
a = 255
|
||||
if len(x) == 3 {
|
||||
format := "%1x%1x%1x"
|
||||
fmt.Sscanf(x, format, &r, &g, &b)
|
||||
r |= r << 4
|
||||
g |= g << 4
|
||||
b |= b << 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(x) == 6 {
|
||||
format := "%02x%02x%02x"
|
||||
fmt.Sscanf(x, format, &r, &g, &b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(x) == 8 {
|
||||
format := "%02x%02x%02x%02x"
|
||||
fmt.Sscanf(x, format, &r, &g, &b, &a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func fixp(x, y float64) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fix(x), fix(y)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func fix(x float64) fixed.Int26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Int26_6(x * 64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func unfix(x fixed.Int26_6) float64 {
|
||||
const shift, mask = 6, 1<<6 - 1
|
||||
if x >= 0 {
|
||||
return float64(x>>shift) + float64(x&mask)/64
|
||||
}
|
||||
x = -x
|
||||
if x >= 0 {
|
||||
return -(float64(x>>shift) + float64(x&mask)/64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func LoadFontFace(path string, points float64) (font.Face, error) {
|
||||
fontBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
f, err := truetype.Parse(fontBytes)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
face := truetype.NewFace(f, &truetype.Options{
|
||||
Size: points,
|
||||
// Hinting: font.HintingFull,
|
||||
})
|
||||
return face, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
58
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/wrap.go
generated
vendored
58
vendor/github.com/fogleman/gg/wrap.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
|||
package gg
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type measureStringer interface {
|
||||
MeasureString(s string) (w, h float64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func splitOnSpace(x string) []string {
|
||||
var result []string
|
||||
pi := 0
|
||||
ps := false
|
||||
for i, c := range x {
|
||||
s := unicode.IsSpace(c)
|
||||
if s != ps && i > 0 {
|
||||
result = append(result, x[pi:i])
|
||||
pi = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
ps = s
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = append(result, x[pi:])
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func wordWrap(m measureStringer, s string, width float64) []string {
|
||||
var result []string
|
||||
for _, line := range strings.Split(s, "\n") {
|
||||
fields := splitOnSpace(line)
|
||||
if len(fields)%2 == 1 {
|
||||
fields = append(fields, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
x := ""
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(fields); i += 2 {
|
||||
w, _ := m.MeasureString(x + fields[i])
|
||||
if w > width {
|
||||
if x == "" {
|
||||
result = append(result, fields[i])
|
||||
x = ""
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
result = append(result, x)
|
||||
x = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
x += fields[i] + fields[i+1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if x != "" {
|
||||
result = append(result, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, line := range result {
|
||||
result[i] = strings.TrimSpace(line)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/AUTHORS
generated
vendored
20
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/AUTHORS
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# This is the official list of Freetype-Go authors for copyright purposes.
|
||||
# This file is distinct from the CONTRIBUTORS files.
|
||||
# See the latter for an explanation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Freetype-Go is derived from Freetype, which is written in C. The latter
|
||||
# is copyright 1996-2010 David Turner, Robert Wilhelm, and Werner Lemberg.
|
||||
|
||||
# Names should be added to this file as
|
||||
# Name or Organization <email address>
|
||||
# The email address is not required for organizations.
|
||||
|
||||
# Please keep the list sorted.
|
||||
|
||||
Google Inc.
|
||||
Jeff R. Allen <jra@nella.org>
|
||||
Maksim Kochkin <maxxarts@gmail.com>
|
||||
Michael Fogleman <fogleman@gmail.com>
|
||||
Rémy Oudompheng <oudomphe@phare.normalesup.org>
|
||||
Roger Peppe <rogpeppe@gmail.com>
|
||||
Steven Edwards <steven@stephenwithav.com>
|
||||
38
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/CONTRIBUTORS
generated
vendored
38
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/CONTRIBUTORS
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
|||
# This is the official list of people who can contribute
|
||||
# (and typically have contributed) code to the Freetype-Go repository.
|
||||
# The AUTHORS file lists the copyright holders; this file
|
||||
# lists people. For example, Google employees are listed here
|
||||
# but not in AUTHORS, because Google holds the copyright.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The submission process automatically checks to make sure
|
||||
# that people submitting code are listed in this file (by email address).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Names should be added to this file only after verifying that
|
||||
# the individual or the individual's organization has agreed to
|
||||
# the appropriate Contributor License Agreement, found here:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://code.google.com/legal/individual-cla-v1.0.html
|
||||
# http://code.google.com/legal/corporate-cla-v1.0.html
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The agreement for individuals can be filled out on the web.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# When adding J Random Contributor's name to this file,
|
||||
# either J's name or J's organization's name should be
|
||||
# added to the AUTHORS file, depending on whether the
|
||||
# individual or corporate CLA was used.
|
||||
|
||||
# Names should be added to this file like so:
|
||||
# Name <email address>
|
||||
|
||||
# Please keep the list sorted.
|
||||
|
||||
Andrew Gerrand <adg@golang.org>
|
||||
Jeff R. Allen <jra@nella.org> <jeff.allen@gmail.com>
|
||||
Maksim Kochkin <maxxarts@gmail.com>
|
||||
Michael Fogleman <fogleman@gmail.com>
|
||||
Nigel Tao <nigeltao@golang.org>
|
||||
Rémy Oudompheng <oudomphe@phare.normalesup.org> <remyoudompheng@gmail.com>
|
||||
Rob Pike <r@golang.org>
|
||||
Roger Peppe <rogpeppe@gmail.com>
|
||||
Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
|
||||
Steven Edwards <steven@stephenwithav.com>
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/LICENSE
generated
vendored
12
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Use of the Freetype-Go software is subject to your choice of exactly one of
|
||||
the following two licenses:
|
||||
* The FreeType License, which is similar to the original BSD license with
|
||||
an advertising clause, or
|
||||
* The GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2 or later.
|
||||
|
||||
The text of these licenses are available in the licenses/ftl.txt and the
|
||||
licenses/gpl.txt files respectively. They are also available at
|
||||
http://freetype.sourceforge.net/license.html
|
||||
|
||||
The Luxi fonts in the testdata directory are licensed separately. See the
|
||||
testdata/COPYING file for details.
|
||||
245
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/geom.go
generated
vendored
245
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/geom.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,245 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2010 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package raster
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// maxAbs returns the maximum of abs(a) and abs(b).
|
||||
func maxAbs(a, b fixed.Int26_6) fixed.Int26_6 {
|
||||
if a < 0 {
|
||||
a = -a
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b < 0 {
|
||||
b = -b
|
||||
}
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pNeg returns the vector -p, or equivalently p rotated by 180 degrees.
|
||||
func pNeg(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{-p.X, -p.Y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pDot returns the dot product p·q.
|
||||
func pDot(p fixed.Point26_6, q fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Int52_12 {
|
||||
px, py := int64(p.X), int64(p.Y)
|
||||
qx, qy := int64(q.X), int64(q.Y)
|
||||
return fixed.Int52_12(px*qx + py*qy)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pLen returns the length of the vector p.
|
||||
func pLen(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Int26_6 {
|
||||
// TODO(nigeltao): use fixed point math.
|
||||
x := float64(p.X)
|
||||
y := float64(p.Y)
|
||||
return fixed.Int26_6(math.Sqrt(x*x + y*y))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pNorm returns the vector p normalized to the given length, or zero if p is
|
||||
// degenerate.
|
||||
func pNorm(p fixed.Point26_6, length fixed.Int26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
d := pLen(p)
|
||||
if d == 0 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s, t := int64(length), int64(d)
|
||||
x := int64(p.X) * s / t
|
||||
y := int64(p.Y) * s / t
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(x), fixed.Int26_6(y)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pRot45CW returns the vector p rotated clockwise by 45 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the Y-axis grows downwards, so {1, 0}.Rot45CW is {1/√2, 1/√2}.
|
||||
func pRot45CW(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
// 181/256 is approximately 1/√2, or sin(π/4).
|
||||
px, py := int64(p.X), int64(p.Y)
|
||||
qx := (+px - py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
qy := (+px + py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(qx), fixed.Int26_6(qy)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pRot90CW returns the vector p rotated clockwise by 90 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the Y-axis grows downwards, so {1, 0}.Rot90CW is {0, 1}.
|
||||
func pRot90CW(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{-p.Y, p.X}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pRot135CW returns the vector p rotated clockwise by 135 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the Y-axis grows downwards, so {1, 0}.Rot135CW is {-1/√2, 1/√2}.
|
||||
func pRot135CW(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
// 181/256 is approximately 1/√2, or sin(π/4).
|
||||
px, py := int64(p.X), int64(p.Y)
|
||||
qx := (-px - py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
qy := (+px - py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(qx), fixed.Int26_6(qy)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pRot45CCW returns the vector p rotated counter-clockwise by 45 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the Y-axis grows downwards, so {1, 0}.Rot45CCW is {1/√2, -1/√2}.
|
||||
func pRot45CCW(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
// 181/256 is approximately 1/√2, or sin(π/4).
|
||||
px, py := int64(p.X), int64(p.Y)
|
||||
qx := (+px + py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
qy := (-px + py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(qx), fixed.Int26_6(qy)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pRot90CCW returns the vector p rotated counter-clockwise by 90 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the Y-axis grows downwards, so {1, 0}.Rot90CCW is {0, -1}.
|
||||
func pRot90CCW(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{p.Y, -p.X}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pRot135CCW returns the vector p rotated counter-clockwise by 135 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the Y-axis grows downwards, so {1, 0}.Rot135CCW is {-1/√2, -1/√2}.
|
||||
func pRot135CCW(p fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
// 181/256 is approximately 1/√2, or sin(π/4).
|
||||
px, py := int64(p.X), int64(p.Y)
|
||||
qx := (-px + py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
qy := (-px - py) * 181 / 256
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(qx), fixed.Int26_6(qy)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An Adder accumulates points on a curve.
|
||||
type Adder interface {
|
||||
// Start starts a new curve at the given point.
|
||||
Start(a fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
// Add1 adds a linear segment to the current curve.
|
||||
Add1(b fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
// Add2 adds a quadratic segment to the current curve.
|
||||
Add2(b, c fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
// Add3 adds a cubic segment to the current curve.
|
||||
Add3(b, c, d fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Path is a sequence of curves, and a curve is a start point followed by a
|
||||
// sequence of linear, quadratic or cubic segments.
|
||||
type Path []fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a human-readable representation of a Path.
|
||||
func (p Path) String() string {
|
||||
s := ""
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(p); {
|
||||
if i != 0 {
|
||||
s += " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch p[i] {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
s += "S0" + fmt.Sprint([]fixed.Int26_6(p[i+1:i+3]))
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
s += "A1" + fmt.Sprint([]fixed.Int26_6(p[i+1:i+3]))
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
s += "A2" + fmt.Sprint([]fixed.Int26_6(p[i+1:i+5]))
|
||||
i += 6
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
s += "A3" + fmt.Sprint([]fixed.Int26_6(p[i+1:i+7]))
|
||||
i += 8
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear cancels any previous calls to p.Start or p.AddXxx.
|
||||
func (p *Path) Clear() {
|
||||
*p = (*p)[:0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Start starts a new curve at the given point.
|
||||
func (p *Path) Start(a fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
*p = append(*p, 0, a.X, a.Y, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add1 adds a linear segment to the current curve.
|
||||
func (p *Path) Add1(b fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
*p = append(*p, 1, b.X, b.Y, 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add2 adds a quadratic segment to the current curve.
|
||||
func (p *Path) Add2(b, c fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
*p = append(*p, 2, b.X, b.Y, c.X, c.Y, 2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add3 adds a cubic segment to the current curve.
|
||||
func (p *Path) Add3(b, c, d fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
*p = append(*p, 3, b.X, b.Y, c.X, c.Y, d.X, d.Y, 3)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPath adds the Path q to p.
|
||||
func (p *Path) AddPath(q Path) {
|
||||
*p = append(*p, q...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddStroke adds a stroked Path.
|
||||
func (p *Path) AddStroke(q Path, width fixed.Int26_6, cr Capper, jr Joiner) {
|
||||
Stroke(p, q, width, cr, jr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// firstPoint returns the first point in a non-empty Path.
|
||||
func (p Path) firstPoint() fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{p[1], p[2]}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lastPoint returns the last point in a non-empty Path.
|
||||
func (p Path) lastPoint() fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{p[len(p)-3], p[len(p)-2]}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// addPathReversed adds q reversed to p.
|
||||
// For example, if q consists of a linear segment from A to B followed by a
|
||||
// quadratic segment from B to C to D, then the values of q looks like:
|
||||
// index: 01234567890123
|
||||
// value: 0AA01BB12CCDD2
|
||||
// So, when adding q backwards to p, we want to Add2(C, B) followed by Add1(A).
|
||||
func addPathReversed(p Adder, q Path) {
|
||||
if len(q) == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
i := len(q) - 1
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch q[i] {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
i -= 4
|
||||
p.Add1(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i-2], q[i-1]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
i -= 6
|
||||
p.Add2(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+2], q[i+3]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i-2], q[i-1]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
i -= 8
|
||||
p.Add3(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+4], q[i+5]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+2], q[i+3]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i-2], q[i-1]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
287
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/paint.go
generated
vendored
287
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/paint.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,287 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2010 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package raster
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"image/draw"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A Span is a horizontal segment of pixels with constant alpha. X0 is an
|
||||
// inclusive bound and X1 is exclusive, the same as for slices. A fully opaque
|
||||
// Span has Alpha == 0xffff.
|
||||
type Span struct {
|
||||
Y, X0, X1 int
|
||||
Alpha uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Painter knows how to paint a batch of Spans. Rasterization may involve
|
||||
// Painting multiple batches, and done will be true for the final batch. The
|
||||
// Spans' Y values are monotonically increasing during a rasterization. Paint
|
||||
// may use all of ss as scratch space during the call.
|
||||
type Painter interface {
|
||||
Paint(ss []Span, done bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The PainterFunc type adapts an ordinary function to the Painter interface.
|
||||
type PainterFunc func(ss []Span, done bool)
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint just delegates the call to f.
|
||||
func (f PainterFunc) Paint(ss []Span, done bool) { f(ss, done) }
|
||||
|
||||
// An AlphaOverPainter is a Painter that paints Spans onto a *image.Alpha using
|
||||
// the Over Porter-Duff composition operator.
|
||||
type AlphaOverPainter struct {
|
||||
Image *image.Alpha
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint satisfies the Painter interface.
|
||||
func (r AlphaOverPainter) Paint(ss []Span, done bool) {
|
||||
b := r.Image.Bounds()
|
||||
for _, s := range ss {
|
||||
if s.Y < b.Min.Y {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.Y >= b.Max.Y {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 < b.Min.X {
|
||||
s.X0 = b.Min.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X1 > b.Max.X {
|
||||
s.X1 = b.Max.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 >= s.X1 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
base := (s.Y-r.Image.Rect.Min.Y)*r.Image.Stride - r.Image.Rect.Min.X
|
||||
p := r.Image.Pix[base+s.X0 : base+s.X1]
|
||||
a := int(s.Alpha >> 8)
|
||||
for i, c := range p {
|
||||
v := int(c)
|
||||
p[i] = uint8((v*255 + (255-v)*a) / 255)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewAlphaOverPainter creates a new AlphaOverPainter for the given image.
|
||||
func NewAlphaOverPainter(m *image.Alpha) AlphaOverPainter {
|
||||
return AlphaOverPainter{m}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An AlphaSrcPainter is a Painter that paints Spans onto a *image.Alpha using
|
||||
// the Src Porter-Duff composition operator.
|
||||
type AlphaSrcPainter struct {
|
||||
Image *image.Alpha
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint satisfies the Painter interface.
|
||||
func (r AlphaSrcPainter) Paint(ss []Span, done bool) {
|
||||
b := r.Image.Bounds()
|
||||
for _, s := range ss {
|
||||
if s.Y < b.Min.Y {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.Y >= b.Max.Y {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 < b.Min.X {
|
||||
s.X0 = b.Min.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X1 > b.Max.X {
|
||||
s.X1 = b.Max.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 >= s.X1 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
base := (s.Y-r.Image.Rect.Min.Y)*r.Image.Stride - r.Image.Rect.Min.X
|
||||
p := r.Image.Pix[base+s.X0 : base+s.X1]
|
||||
color := uint8(s.Alpha >> 8)
|
||||
for i := range p {
|
||||
p[i] = color
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewAlphaSrcPainter creates a new AlphaSrcPainter for the given image.
|
||||
func NewAlphaSrcPainter(m *image.Alpha) AlphaSrcPainter {
|
||||
return AlphaSrcPainter{m}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An RGBAPainter is a Painter that paints Spans onto a *image.RGBA.
|
||||
type RGBAPainter struct {
|
||||
// Image is the image to compose onto.
|
||||
Image *image.RGBA
|
||||
// Op is the Porter-Duff composition operator.
|
||||
Op draw.Op
|
||||
// cr, cg, cb and ca are the 16-bit color to paint the spans.
|
||||
cr, cg, cb, ca uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint satisfies the Painter interface.
|
||||
func (r *RGBAPainter) Paint(ss []Span, done bool) {
|
||||
b := r.Image.Bounds()
|
||||
for _, s := range ss {
|
||||
if s.Y < b.Min.Y {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.Y >= b.Max.Y {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 < b.Min.X {
|
||||
s.X0 = b.Min.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X1 > b.Max.X {
|
||||
s.X1 = b.Max.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 >= s.X1 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// This code mimics drawGlyphOver in $GOROOT/src/image/draw/draw.go.
|
||||
ma := s.Alpha
|
||||
const m = 1<<16 - 1
|
||||
i0 := (s.Y-r.Image.Rect.Min.Y)*r.Image.Stride + (s.X0-r.Image.Rect.Min.X)*4
|
||||
i1 := i0 + (s.X1-s.X0)*4
|
||||
if r.Op == draw.Over {
|
||||
for i := i0; i < i1; i += 4 {
|
||||
dr := uint32(r.Image.Pix[i+0])
|
||||
dg := uint32(r.Image.Pix[i+1])
|
||||
db := uint32(r.Image.Pix[i+2])
|
||||
da := uint32(r.Image.Pix[i+3])
|
||||
a := (m - (r.ca * ma / m)) * 0x101
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+0] = uint8((dr*a + r.cr*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+1] = uint8((dg*a + r.cg*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+2] = uint8((db*a + r.cb*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+3] = uint8((da*a + r.ca*ma) / m >> 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
for i := i0; i < i1; i += 4 {
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+0] = uint8(r.cr * ma / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+1] = uint8(r.cg * ma / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+2] = uint8(r.cb * ma / m >> 8)
|
||||
r.Image.Pix[i+3] = uint8(r.ca * ma / m >> 8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColor sets the color to paint the spans.
|
||||
func (r *RGBAPainter) SetColor(c color.Color) {
|
||||
r.cr, r.cg, r.cb, r.ca = c.RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewRGBAPainter creates a new RGBAPainter for the given image.
|
||||
func NewRGBAPainter(m *image.RGBA) *RGBAPainter {
|
||||
return &RGBAPainter{Image: m}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A MonochromePainter wraps another Painter, quantizing each Span's alpha to
|
||||
// be either fully opaque or fully transparent.
|
||||
type MonochromePainter struct {
|
||||
Painter Painter
|
||||
y, x0, x1 int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint delegates to the wrapped Painter after quantizing each Span's alpha
|
||||
// value and merging adjacent fully opaque Spans.
|
||||
func (m *MonochromePainter) Paint(ss []Span, done bool) {
|
||||
// We compact the ss slice, discarding any Spans whose alpha quantizes to zero.
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
for _, s := range ss {
|
||||
if s.Alpha >= 0x8000 {
|
||||
if m.y == s.Y && m.x1 == s.X0 {
|
||||
m.x1 = s.X1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ss[j] = Span{m.y, m.x0, m.x1, 1<<16 - 1}
|
||||
j++
|
||||
m.y, m.x0, m.x1 = s.Y, s.X0, s.X1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if done {
|
||||
// Flush the accumulated Span.
|
||||
finalSpan := Span{m.y, m.x0, m.x1, 1<<16 - 1}
|
||||
if j < len(ss) {
|
||||
ss[j] = finalSpan
|
||||
j++
|
||||
m.Painter.Paint(ss[:j], true)
|
||||
} else if j == len(ss) {
|
||||
m.Painter.Paint(ss, false)
|
||||
if cap(ss) > 0 {
|
||||
ss = ss[:1]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ss = make([]Span, 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
ss[0] = finalSpan
|
||||
m.Painter.Paint(ss, true)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
panic("unreachable")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Reset the accumulator, so that this Painter can be re-used.
|
||||
m.y, m.x0, m.x1 = 0, 0, 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
m.Painter.Paint(ss[:j], false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMonochromePainter creates a new MonochromePainter that wraps the given
|
||||
// Painter.
|
||||
func NewMonochromePainter(p Painter) *MonochromePainter {
|
||||
return &MonochromePainter{Painter: p}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A GammaCorrectionPainter wraps another Painter, performing gamma-correction
|
||||
// on each Span's alpha value.
|
||||
type GammaCorrectionPainter struct {
|
||||
// Painter is the wrapped Painter.
|
||||
Painter Painter
|
||||
// a is the precomputed alpha values for linear interpolation, with fully
|
||||
// opaque == 0xffff.
|
||||
a [256]uint16
|
||||
// gammaIsOne is whether gamma correction is a no-op.
|
||||
gammaIsOne bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Paint delegates to the wrapped Painter after performing gamma-correction on
|
||||
// each Span.
|
||||
func (g *GammaCorrectionPainter) Paint(ss []Span, done bool) {
|
||||
if !g.gammaIsOne {
|
||||
const n = 0x101
|
||||
for i, s := range ss {
|
||||
if s.Alpha == 0 || s.Alpha == 0xffff {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
p, q := s.Alpha/n, s.Alpha%n
|
||||
// The resultant alpha is a linear interpolation of g.a[p] and g.a[p+1].
|
||||
a := uint32(g.a[p])*(n-q) + uint32(g.a[p+1])*q
|
||||
ss[i].Alpha = (a + n/2) / n
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
g.Painter.Paint(ss, done)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetGamma sets the gamma value.
|
||||
func (g *GammaCorrectionPainter) SetGamma(gamma float64) {
|
||||
g.gammaIsOne = gamma == 1
|
||||
if g.gammaIsOne {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 256; i++ {
|
||||
a := float64(i) / 0xff
|
||||
a = math.Pow(a, gamma)
|
||||
g.a[i] = uint16(0xffff * a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewGammaCorrectionPainter creates a new GammaCorrectionPainter that wraps
|
||||
// the given Painter.
|
||||
func NewGammaCorrectionPainter(p Painter, gamma float64) *GammaCorrectionPainter {
|
||||
g := &GammaCorrectionPainter{Painter: p}
|
||||
g.SetGamma(gamma)
|
||||
return g
|
||||
}
|
||||
601
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/raster.go
generated
vendored
601
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/raster.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,601 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2010 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package raster provides an anti-aliasing 2-D rasterizer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It is part of the larger Freetype suite of font-related packages, but the
|
||||
// raster package is not specific to font rasterization, and can be used
|
||||
// standalone without any other Freetype package.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Rasterization is done by the same area/coverage accumulation algorithm as
|
||||
// the Freetype "smooth" module, and the Anti-Grain Geometry library. A
|
||||
// description of the area/coverage algorithm is at
|
||||
// http://projects.tuxee.net/cl-vectors/section-the-cl-aa-algorithm
|
||||
package raster // import "github.com/golang/freetype/raster"
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A cell is part of a linked list (for a given yi co-ordinate) of accumulated
|
||||
// area/coverage for the pixel at (xi, yi).
|
||||
type cell struct {
|
||||
xi int
|
||||
area, cover int
|
||||
next int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type Rasterizer struct {
|
||||
// If false, the default behavior is to use the even-odd winding fill
|
||||
// rule during Rasterize.
|
||||
UseNonZeroWinding bool
|
||||
// An offset (in pixels) to the painted spans.
|
||||
Dx, Dy int
|
||||
|
||||
// The width of the Rasterizer. The height is implicit in len(cellIndex).
|
||||
width int
|
||||
// splitScaleN is the scaling factor used to determine how many times
|
||||
// to decompose a quadratic or cubic segment into a linear approximation.
|
||||
splitScale2, splitScale3 int
|
||||
|
||||
// The current pen position.
|
||||
a fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
// The current cell and its area/coverage being accumulated.
|
||||
xi, yi int
|
||||
area, cover int
|
||||
|
||||
// Saved cells.
|
||||
cell []cell
|
||||
// Linked list of cells, one per row.
|
||||
cellIndex []int
|
||||
// Buffers.
|
||||
cellBuf [256]cell
|
||||
cellIndexBuf [64]int
|
||||
spanBuf [64]Span
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// findCell returns the index in r.cell for the cell corresponding to
|
||||
// (r.xi, r.yi). The cell is created if necessary.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) findCell() int {
|
||||
if r.yi < 0 || r.yi >= len(r.cellIndex) {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
xi := r.xi
|
||||
if xi < 0 {
|
||||
xi = -1
|
||||
} else if xi > r.width {
|
||||
xi = r.width
|
||||
}
|
||||
i, prev := r.cellIndex[r.yi], -1
|
||||
for i != -1 && r.cell[i].xi <= xi {
|
||||
if r.cell[i].xi == xi {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
i, prev = r.cell[i].next, i
|
||||
}
|
||||
c := len(r.cell)
|
||||
if c == cap(r.cell) {
|
||||
buf := make([]cell, c, 4*c)
|
||||
copy(buf, r.cell)
|
||||
r.cell = buf[0 : c+1]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.cell = r.cell[0 : c+1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.cell[c] = cell{xi, 0, 0, i}
|
||||
if prev == -1 {
|
||||
r.cellIndex[r.yi] = c
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.cell[prev].next = c
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// saveCell saves any accumulated r.area/r.cover for (r.xi, r.yi).
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) saveCell() {
|
||||
if r.area != 0 || r.cover != 0 {
|
||||
i := r.findCell()
|
||||
if i != -1 {
|
||||
r.cell[i].area += r.area
|
||||
r.cell[i].cover += r.cover
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.area = 0
|
||||
r.cover = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setCell sets the (xi, yi) cell that r is accumulating area/coverage for.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) setCell(xi, yi int) {
|
||||
if r.xi != xi || r.yi != yi {
|
||||
r.saveCell()
|
||||
r.xi, r.yi = xi, yi
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// scan accumulates area/coverage for the yi'th scanline, going from
|
||||
// x0 to x1 in the horizontal direction (in 26.6 fixed point co-ordinates)
|
||||
// and from y0f to y1f fractional vertical units within that scanline.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) scan(yi int, x0, y0f, x1, y1f fixed.Int26_6) {
|
||||
// Break the 26.6 fixed point X co-ordinates into integral and fractional parts.
|
||||
x0i := int(x0) / 64
|
||||
x0f := x0 - fixed.Int26_6(64*x0i)
|
||||
x1i := int(x1) / 64
|
||||
x1f := x1 - fixed.Int26_6(64*x1i)
|
||||
|
||||
// A perfectly horizontal scan.
|
||||
if y0f == y1f {
|
||||
r.setCell(x1i, yi)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
dx, dy := x1-x0, y1f-y0f
|
||||
// A single cell scan.
|
||||
if x0i == x1i {
|
||||
r.area += int((x0f + x1f) * dy)
|
||||
r.cover += int(dy)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// There are at least two cells. Apart from the first and last cells,
|
||||
// all intermediate cells go through the full width of the cell,
|
||||
// or 64 units in 26.6 fixed point format.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
p, q, edge0, edge1 fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
xiDelta int
|
||||
)
|
||||
if dx > 0 {
|
||||
p, q = (64-x0f)*dy, dx
|
||||
edge0, edge1, xiDelta = 0, 64, 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p, q = x0f*dy, -dx
|
||||
edge0, edge1, xiDelta = 64, 0, -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
yDelta, yRem := p/q, p%q
|
||||
if yRem < 0 {
|
||||
yDelta -= 1
|
||||
yRem += q
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do the first cell.
|
||||
xi, y := x0i, y0f
|
||||
r.area += int((x0f + edge1) * yDelta)
|
||||
r.cover += int(yDelta)
|
||||
xi, y = xi+xiDelta, y+yDelta
|
||||
r.setCell(xi, yi)
|
||||
if xi != x1i {
|
||||
// Do all the intermediate cells.
|
||||
p = 64 * (y1f - y + yDelta)
|
||||
fullDelta, fullRem := p/q, p%q
|
||||
if fullRem < 0 {
|
||||
fullDelta -= 1
|
||||
fullRem += q
|
||||
}
|
||||
yRem -= q
|
||||
for xi != x1i {
|
||||
yDelta = fullDelta
|
||||
yRem += fullRem
|
||||
if yRem >= 0 {
|
||||
yDelta += 1
|
||||
yRem -= q
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.area += int(64 * yDelta)
|
||||
r.cover += int(yDelta)
|
||||
xi, y = xi+xiDelta, y+yDelta
|
||||
r.setCell(xi, yi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do the last cell.
|
||||
yDelta = y1f - y
|
||||
r.area += int((edge0 + x1f) * yDelta)
|
||||
r.cover += int(yDelta)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Start starts a new curve at the given point.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) Start(a fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
r.setCell(int(a.X/64), int(a.Y/64))
|
||||
r.a = a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add1 adds a linear segment to the current curve.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) Add1(b fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
x0, y0 := r.a.X, r.a.Y
|
||||
x1, y1 := b.X, b.Y
|
||||
dx, dy := x1-x0, y1-y0
|
||||
// Break the 26.6 fixed point Y co-ordinates into integral and fractional
|
||||
// parts.
|
||||
y0i := int(y0) / 64
|
||||
y0f := y0 - fixed.Int26_6(64*y0i)
|
||||
y1i := int(y1) / 64
|
||||
y1f := y1 - fixed.Int26_6(64*y1i)
|
||||
|
||||
if y0i == y1i {
|
||||
// There is only one scanline.
|
||||
r.scan(y0i, x0, y0f, x1, y1f)
|
||||
|
||||
} else if dx == 0 {
|
||||
// This is a vertical line segment. We avoid calling r.scan and instead
|
||||
// manipulate r.area and r.cover directly.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
edge0, edge1 fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
yiDelta int
|
||||
)
|
||||
if dy > 0 {
|
||||
edge0, edge1, yiDelta = 0, 64, 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
edge0, edge1, yiDelta = 64, 0, -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
x0i, yi := int(x0)/64, y0i
|
||||
x0fTimes2 := (int(x0) - (64 * x0i)) * 2
|
||||
// Do the first pixel.
|
||||
dcover := int(edge1 - y0f)
|
||||
darea := int(x0fTimes2 * dcover)
|
||||
r.area += darea
|
||||
r.cover += dcover
|
||||
yi += yiDelta
|
||||
r.setCell(x0i, yi)
|
||||
// Do all the intermediate pixels.
|
||||
dcover = int(edge1 - edge0)
|
||||
darea = int(x0fTimes2 * dcover)
|
||||
for yi != y1i {
|
||||
r.area += darea
|
||||
r.cover += dcover
|
||||
yi += yiDelta
|
||||
r.setCell(x0i, yi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do the last pixel.
|
||||
dcover = int(y1f - edge0)
|
||||
darea = int(x0fTimes2 * dcover)
|
||||
r.area += darea
|
||||
r.cover += dcover
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// There are at least two scanlines. Apart from the first and last
|
||||
// scanlines, all intermediate scanlines go through the full height of
|
||||
// the row, or 64 units in 26.6 fixed point format.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
p, q, edge0, edge1 fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
yiDelta int
|
||||
)
|
||||
if dy > 0 {
|
||||
p, q = (64-y0f)*dx, dy
|
||||
edge0, edge1, yiDelta = 0, 64, 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p, q = y0f*dx, -dy
|
||||
edge0, edge1, yiDelta = 64, 0, -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
xDelta, xRem := p/q, p%q
|
||||
if xRem < 0 {
|
||||
xDelta -= 1
|
||||
xRem += q
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do the first scanline.
|
||||
x, yi := x0, y0i
|
||||
r.scan(yi, x, y0f, x+xDelta, edge1)
|
||||
x, yi = x+xDelta, yi+yiDelta
|
||||
r.setCell(int(x)/64, yi)
|
||||
if yi != y1i {
|
||||
// Do all the intermediate scanlines.
|
||||
p = 64 * dx
|
||||
fullDelta, fullRem := p/q, p%q
|
||||
if fullRem < 0 {
|
||||
fullDelta -= 1
|
||||
fullRem += q
|
||||
}
|
||||
xRem -= q
|
||||
for yi != y1i {
|
||||
xDelta = fullDelta
|
||||
xRem += fullRem
|
||||
if xRem >= 0 {
|
||||
xDelta += 1
|
||||
xRem -= q
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.scan(yi, x, edge0, x+xDelta, edge1)
|
||||
x, yi = x+xDelta, yi+yiDelta
|
||||
r.setCell(int(x)/64, yi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do the last scanline.
|
||||
r.scan(yi, x, edge0, x1, y1f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The next lineTo starts from b.
|
||||
r.a = b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add2 adds a quadratic segment to the current curve.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) Add2(b, c fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
// Calculate nSplit (the number of recursive decompositions) based on how
|
||||
// 'curvy' it is. Specifically, how much the middle point b deviates from
|
||||
// (a+c)/2.
|
||||
dev := maxAbs(r.a.X-2*b.X+c.X, r.a.Y-2*b.Y+c.Y) / fixed.Int26_6(r.splitScale2)
|
||||
nsplit := 0
|
||||
for dev > 0 {
|
||||
dev /= 4
|
||||
nsplit++
|
||||
}
|
||||
// dev is 32-bit, and nsplit++ every time we shift off 2 bits, so maxNsplit
|
||||
// is 16.
|
||||
const maxNsplit = 16
|
||||
if nsplit > maxNsplit {
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: Add2 nsplit too large: " + strconv.Itoa(nsplit))
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Recursively decompose the curve nSplit levels deep.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
pStack [2*maxNsplit + 3]fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
sStack [maxNsplit + 1]int
|
||||
i int
|
||||
)
|
||||
sStack[0] = nsplit
|
||||
pStack[0] = c
|
||||
pStack[1] = b
|
||||
pStack[2] = r.a
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
s := sStack[i]
|
||||
p := pStack[2*i:]
|
||||
if s > 0 {
|
||||
// Split the quadratic curve p[:3] into an equivalent set of two
|
||||
// shorter curves: p[:3] and p[2:5]. The new p[4] is the old p[2],
|
||||
// and p[0] is unchanged.
|
||||
mx := p[1].X
|
||||
p[4].X = p[2].X
|
||||
p[3].X = (p[4].X + mx) / 2
|
||||
p[1].X = (p[0].X + mx) / 2
|
||||
p[2].X = (p[1].X + p[3].X) / 2
|
||||
my := p[1].Y
|
||||
p[4].Y = p[2].Y
|
||||
p[3].Y = (p[4].Y + my) / 2
|
||||
p[1].Y = (p[0].Y + my) / 2
|
||||
p[2].Y = (p[1].Y + p[3].Y) / 2
|
||||
// The two shorter curves have one less split to do.
|
||||
sStack[i] = s - 1
|
||||
sStack[i+1] = s - 1
|
||||
i++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Replace the level-0 quadratic with a two-linear-piece
|
||||
// approximation.
|
||||
midx := (p[0].X + 2*p[1].X + p[2].X) / 4
|
||||
midy := (p[0].Y + 2*p[1].Y + p[2].Y) / 4
|
||||
r.Add1(fixed.Point26_6{midx, midy})
|
||||
r.Add1(p[0])
|
||||
i--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add3 adds a cubic segment to the current curve.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) Add3(b, c, d fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
// Calculate nSplit (the number of recursive decompositions) based on how
|
||||
// 'curvy' it is.
|
||||
dev2 := maxAbs(r.a.X-3*(b.X+c.X)+d.X, r.a.Y-3*(b.Y+c.Y)+d.Y) / fixed.Int26_6(r.splitScale2)
|
||||
dev3 := maxAbs(r.a.X-2*b.X+d.X, r.a.Y-2*b.Y+d.Y) / fixed.Int26_6(r.splitScale3)
|
||||
nsplit := 0
|
||||
for dev2 > 0 || dev3 > 0 {
|
||||
dev2 /= 8
|
||||
dev3 /= 4
|
||||
nsplit++
|
||||
}
|
||||
// devN is 32-bit, and nsplit++ every time we shift off 2 bits, so
|
||||
// maxNsplit is 16.
|
||||
const maxNsplit = 16
|
||||
if nsplit > maxNsplit {
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: Add3 nsplit too large: " + strconv.Itoa(nsplit))
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Recursively decompose the curve nSplit levels deep.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
pStack [3*maxNsplit + 4]fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
sStack [maxNsplit + 1]int
|
||||
i int
|
||||
)
|
||||
sStack[0] = nsplit
|
||||
pStack[0] = d
|
||||
pStack[1] = c
|
||||
pStack[2] = b
|
||||
pStack[3] = r.a
|
||||
for i >= 0 {
|
||||
s := sStack[i]
|
||||
p := pStack[3*i:]
|
||||
if s > 0 {
|
||||
// Split the cubic curve p[:4] into an equivalent set of two
|
||||
// shorter curves: p[:4] and p[3:7]. The new p[6] is the old p[3],
|
||||
// and p[0] is unchanged.
|
||||
m01x := (p[0].X + p[1].X) / 2
|
||||
m12x := (p[1].X + p[2].X) / 2
|
||||
m23x := (p[2].X + p[3].X) / 2
|
||||
p[6].X = p[3].X
|
||||
p[5].X = m23x
|
||||
p[1].X = m01x
|
||||
p[2].X = (m01x + m12x) / 2
|
||||
p[4].X = (m12x + m23x) / 2
|
||||
p[3].X = (p[2].X + p[4].X) / 2
|
||||
m01y := (p[0].Y + p[1].Y) / 2
|
||||
m12y := (p[1].Y + p[2].Y) / 2
|
||||
m23y := (p[2].Y + p[3].Y) / 2
|
||||
p[6].Y = p[3].Y
|
||||
p[5].Y = m23y
|
||||
p[1].Y = m01y
|
||||
p[2].Y = (m01y + m12y) / 2
|
||||
p[4].Y = (m12y + m23y) / 2
|
||||
p[3].Y = (p[2].Y + p[4].Y) / 2
|
||||
// The two shorter curves have one less split to do.
|
||||
sStack[i] = s - 1
|
||||
sStack[i+1] = s - 1
|
||||
i++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Replace the level-0 cubic with a two-linear-piece approximation.
|
||||
midx := (p[0].X + 3*(p[1].X+p[2].X) + p[3].X) / 8
|
||||
midy := (p[0].Y + 3*(p[1].Y+p[2].Y) + p[3].Y) / 8
|
||||
r.Add1(fixed.Point26_6{midx, midy})
|
||||
r.Add1(p[0])
|
||||
i--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPath adds the given Path.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) AddPath(p Path) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(p); {
|
||||
switch p[i] {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
r.Start(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+1], p[i+2]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
r.Add1(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+1], p[i+2]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
r.Add2(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+1], p[i+2]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+3], p[i+4]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 6
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
r.Add3(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+1], p[i+2]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+3], p[i+4]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{p[i+5], p[i+6]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 8
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddStroke adds a stroked Path.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) AddStroke(q Path, width fixed.Int26_6, cr Capper, jr Joiner) {
|
||||
Stroke(r, q, width, cr, jr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// areaToAlpha converts an area value to a uint32 alpha value. A completely
|
||||
// filled pixel corresponds to an area of 64*64*2, and an alpha of 0xffff. The
|
||||
// conversion of area values greater than this depends on the winding rule:
|
||||
// even-odd or non-zero.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) areaToAlpha(area int) uint32 {
|
||||
// The C Freetype implementation (version 2.3.12) does "alpha := area>>1"
|
||||
// without the +1. Round-to-nearest gives a more symmetric result than
|
||||
// round-down. The C implementation also returns 8-bit alpha, not 16-bit
|
||||
// alpha.
|
||||
a := (area + 1) >> 1
|
||||
if a < 0 {
|
||||
a = -a
|
||||
}
|
||||
alpha := uint32(a)
|
||||
if r.UseNonZeroWinding {
|
||||
if alpha > 0x0fff {
|
||||
alpha = 0x0fff
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
alpha &= 0x1fff
|
||||
if alpha > 0x1000 {
|
||||
alpha = 0x2000 - alpha
|
||||
} else if alpha == 0x1000 {
|
||||
alpha = 0x0fff
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// alpha is now in the range [0x0000, 0x0fff]. Convert that 12-bit alpha to
|
||||
// 16-bit alpha.
|
||||
return alpha<<4 | alpha>>8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rasterize converts r's accumulated curves into Spans for p. The Spans passed
|
||||
// to p are non-overlapping, and sorted by Y and then X. They all have non-zero
|
||||
// width (and 0 <= X0 < X1 <= r.width) and non-zero A, except for the final
|
||||
// Span, which has Y, X0, X1 and A all equal to zero.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) Rasterize(p Painter) {
|
||||
r.saveCell()
|
||||
s := 0
|
||||
for yi := 0; yi < len(r.cellIndex); yi++ {
|
||||
xi, cover := 0, 0
|
||||
for c := r.cellIndex[yi]; c != -1; c = r.cell[c].next {
|
||||
if cover != 0 && r.cell[c].xi > xi {
|
||||
alpha := r.areaToAlpha(cover * 64 * 2)
|
||||
if alpha != 0 {
|
||||
xi0, xi1 := xi, r.cell[c].xi
|
||||
if xi0 < 0 {
|
||||
xi0 = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if xi1 >= r.width {
|
||||
xi1 = r.width
|
||||
}
|
||||
if xi0 < xi1 {
|
||||
r.spanBuf[s] = Span{yi + r.Dy, xi0 + r.Dx, xi1 + r.Dx, alpha}
|
||||
s++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
cover += r.cell[c].cover
|
||||
alpha := r.areaToAlpha(cover*64*2 - r.cell[c].area)
|
||||
xi = r.cell[c].xi + 1
|
||||
if alpha != 0 {
|
||||
xi0, xi1 := r.cell[c].xi, xi
|
||||
if xi0 < 0 {
|
||||
xi0 = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if xi1 >= r.width {
|
||||
xi1 = r.width
|
||||
}
|
||||
if xi0 < xi1 {
|
||||
r.spanBuf[s] = Span{yi + r.Dy, xi0 + r.Dx, xi1 + r.Dx, alpha}
|
||||
s++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s > len(r.spanBuf)-2 {
|
||||
p.Paint(r.spanBuf[:s], false)
|
||||
s = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.Paint(r.spanBuf[:s], true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear cancels any previous calls to r.Start or r.AddXxx.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) Clear() {
|
||||
r.a = fixed.Point26_6{}
|
||||
r.xi = 0
|
||||
r.yi = 0
|
||||
r.area = 0
|
||||
r.cover = 0
|
||||
r.cell = r.cell[:0]
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(r.cellIndex); i++ {
|
||||
r.cellIndex[i] = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBounds sets the maximum width and height of the rasterized image and
|
||||
// calls Clear. The width and height are in pixels, not fixed.Int26_6 units.
|
||||
func (r *Rasterizer) SetBounds(width, height int) {
|
||||
if width < 0 {
|
||||
width = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if height < 0 {
|
||||
height = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Use the same ssN heuristic as the C Freetype (version 2.4.0)
|
||||
// implementation.
|
||||
ss2, ss3 := 32, 16
|
||||
if width > 24 || height > 24 {
|
||||
ss2, ss3 = 2*ss2, 2*ss3
|
||||
if width > 120 || height > 120 {
|
||||
ss2, ss3 = 2*ss2, 2*ss3
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.width = width
|
||||
r.splitScale2 = ss2
|
||||
r.splitScale3 = ss3
|
||||
r.cell = r.cellBuf[:0]
|
||||
if height > len(r.cellIndexBuf) {
|
||||
r.cellIndex = make([]int, height)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
r.cellIndex = r.cellIndexBuf[:height]
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.Clear()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewRasterizer creates a new Rasterizer with the given bounds.
|
||||
func NewRasterizer(width, height int) *Rasterizer {
|
||||
r := new(Rasterizer)
|
||||
r.SetBounds(width, height)
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
483
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/stroke.go
generated
vendored
483
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/raster/stroke.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,483 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2010 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package raster
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Two points are considered practically equal if the square of the distance
|
||||
// between them is less than one quarter (i.e. 1024 / 4096).
|
||||
const epsilon = fixed.Int52_12(1024)
|
||||
|
||||
// A Capper signifies how to begin or end a stroked path.
|
||||
type Capper interface {
|
||||
// Cap adds a cap to p given a pivot point and the normal vector of a
|
||||
// terminal segment. The normal's length is half of the stroke width.
|
||||
Cap(p Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n1 fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The CapperFunc type adapts an ordinary function to be a Capper.
|
||||
type CapperFunc func(Adder, fixed.Int26_6, fixed.Point26_6, fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
|
||||
func (f CapperFunc) Cap(p Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
f(p, halfWidth, pivot, n1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Joiner signifies how to join interior nodes of a stroked path.
|
||||
type Joiner interface {
|
||||
// Join adds a join to the two sides of a stroked path given a pivot
|
||||
// point and the normal vectors of the trailing and leading segments.
|
||||
// Both normals have length equal to half of the stroke width.
|
||||
Join(lhs, rhs Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n0, n1 fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The JoinerFunc type adapts an ordinary function to be a Joiner.
|
||||
type JoinerFunc func(lhs, rhs Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n0, n1 fixed.Point26_6)
|
||||
|
||||
func (f JoinerFunc) Join(lhs, rhs Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n0, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
f(lhs, rhs, halfWidth, pivot, n0, n1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RoundCapper adds round caps to a stroked path.
|
||||
var RoundCapper Capper = CapperFunc(roundCapper)
|
||||
|
||||
func roundCapper(p Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
// The cubic Bézier approximation to a circle involves the magic number
|
||||
// (√2 - 1) * 4/3, which is approximately 35/64.
|
||||
const k = 35
|
||||
e := pRot90CCW(n1)
|
||||
side := pivot.Add(e)
|
||||
start, end := pivot.Sub(n1), pivot.Add(n1)
|
||||
d, e := n1.Mul(k), e.Mul(k)
|
||||
p.Add3(start.Add(e), side.Sub(d), side)
|
||||
p.Add3(side.Add(d), end.Add(e), end)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ButtCapper adds butt caps to a stroked path.
|
||||
var ButtCapper Capper = CapperFunc(buttCapper)
|
||||
|
||||
func buttCapper(p Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
p.Add1(pivot.Add(n1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SquareCapper adds square caps to a stroked path.
|
||||
var SquareCapper Capper = CapperFunc(squareCapper)
|
||||
|
||||
func squareCapper(p Adder, halfWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
e := pRot90CCW(n1)
|
||||
side := pivot.Add(e)
|
||||
p.Add1(side.Sub(n1))
|
||||
p.Add1(side.Add(n1))
|
||||
p.Add1(pivot.Add(n1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RoundJoiner adds round joins to a stroked path.
|
||||
var RoundJoiner Joiner = JoinerFunc(roundJoiner)
|
||||
|
||||
func roundJoiner(lhs, rhs Adder, haflWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n0, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
dot := pDot(pRot90CW(n0), n1)
|
||||
if dot >= 0 {
|
||||
addArc(lhs, pivot, n0, n1)
|
||||
rhs.Add1(pivot.Sub(n1))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
lhs.Add1(pivot.Add(n1))
|
||||
addArc(rhs, pivot, pNeg(n0), pNeg(n1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BevelJoiner adds bevel joins to a stroked path.
|
||||
var BevelJoiner Joiner = JoinerFunc(bevelJoiner)
|
||||
|
||||
func bevelJoiner(lhs, rhs Adder, haflWidth fixed.Int26_6, pivot, n0, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
lhs.Add1(pivot.Add(n1))
|
||||
rhs.Add1(pivot.Sub(n1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// addArc adds a circular arc from pivot+n0 to pivot+n1 to p. The shorter of
|
||||
// the two possible arcs is taken, i.e. the one spanning <= 180 degrees. The
|
||||
// two vectors n0 and n1 must be of equal length.
|
||||
func addArc(p Adder, pivot, n0, n1 fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
// r2 is the square of the length of n0.
|
||||
r2 := pDot(n0, n0)
|
||||
if r2 < epsilon {
|
||||
// The arc radius is so small that we collapse to a straight line.
|
||||
p.Add1(pivot.Add(n1))
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We approximate the arc by 0, 1, 2 or 3 45-degree quadratic segments plus
|
||||
// a final quadratic segment from s to n1. Each 45-degree segment has
|
||||
// control points {1, 0}, {1, tan(π/8)} and {1/√2, 1/√2} suitably scaled,
|
||||
// rotated and translated. tan(π/8) is approximately 27/64.
|
||||
const tpo8 = 27
|
||||
var s fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
// We determine which octant the angle between n0 and n1 is in via three
|
||||
// dot products. m0, m1 and m2 are n0 rotated clockwise by 45, 90 and 135
|
||||
// degrees.
|
||||
m0 := pRot45CW(n0)
|
||||
m1 := pRot90CW(n0)
|
||||
m2 := pRot90CW(m0)
|
||||
if pDot(m1, n1) >= 0 {
|
||||
if pDot(n0, n1) >= 0 {
|
||||
if pDot(m2, n1) <= 0 {
|
||||
// n1 is between 0 and 45 degrees clockwise of n0.
|
||||
s = n0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// n1 is between 45 and 90 degrees clockwise of n0.
|
||||
p.Add2(pivot.Add(n0).Add(m1.Mul(tpo8)), pivot.Add(m0))
|
||||
s = m0
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pm1, n0t := pivot.Add(m1), n0.Mul(tpo8)
|
||||
p.Add2(pivot.Add(n0).Add(m1.Mul(tpo8)), pivot.Add(m0))
|
||||
p.Add2(pm1.Add(n0t), pm1)
|
||||
if pDot(m0, n1) >= 0 {
|
||||
// n1 is between 90 and 135 degrees clockwise of n0.
|
||||
s = m1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// n1 is between 135 and 180 degrees clockwise of n0.
|
||||
p.Add2(pm1.Sub(n0t), pivot.Add(m2))
|
||||
s = m2
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if pDot(n0, n1) >= 0 {
|
||||
if pDot(m0, n1) >= 0 {
|
||||
// n1 is between 0 and 45 degrees counter-clockwise of n0.
|
||||
s = n0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// n1 is between 45 and 90 degrees counter-clockwise of n0.
|
||||
p.Add2(pivot.Add(n0).Sub(m1.Mul(tpo8)), pivot.Sub(m2))
|
||||
s = pNeg(m2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pm1, n0t := pivot.Sub(m1), n0.Mul(tpo8)
|
||||
p.Add2(pivot.Add(n0).Sub(m1.Mul(tpo8)), pivot.Sub(m2))
|
||||
p.Add2(pm1.Add(n0t), pm1)
|
||||
if pDot(m2, n1) <= 0 {
|
||||
// n1 is between 90 and 135 degrees counter-clockwise of n0.
|
||||
s = pNeg(m1)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// n1 is between 135 and 180 degrees counter-clockwise of n0.
|
||||
p.Add2(pm1.Sub(n0t), pivot.Sub(m0))
|
||||
s = pNeg(m0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The final quadratic segment has two endpoints s and n1 and the middle
|
||||
// control point is a multiple of s.Add(n1), i.e. it is on the angle
|
||||
// bisector of those two points. The multiple ranges between 128/256 and
|
||||
// 150/256 as the angle between s and n1 ranges between 0 and 45 degrees.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// When the angle is 0 degrees (i.e. s and n1 are coincident) then
|
||||
// s.Add(n1) is twice s and so the middle control point of the degenerate
|
||||
// quadratic segment should be half s.Add(n1), and half = 128/256.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// When the angle is 45 degrees then 150/256 is the ratio of the lengths of
|
||||
// the two vectors {1, tan(π/8)} and {1 + 1/√2, 1/√2}.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// d is the normalized dot product between s and n1. Since the angle ranges
|
||||
// between 0 and 45 degrees then d ranges between 256/256 and 181/256.
|
||||
d := 256 * pDot(s, n1) / r2
|
||||
multiple := fixed.Int26_6(150-(150-128)*(d-181)/(256-181)) >> 2
|
||||
p.Add2(pivot.Add(s.Add(n1).Mul(multiple)), pivot.Add(n1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// midpoint returns the midpoint of two Points.
|
||||
func midpoint(a, b fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{(a.X + b.X) / 2, (a.Y + b.Y) / 2}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// angleGreaterThan45 returns whether the angle between two vectors is more
|
||||
// than 45 degrees.
|
||||
func angleGreaterThan45(v0, v1 fixed.Point26_6) bool {
|
||||
v := pRot45CCW(v0)
|
||||
return pDot(v, v1) < 0 || pDot(pRot90CW(v), v1) < 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// interpolate returns the point (1-t)*a + t*b.
|
||||
func interpolate(a, b fixed.Point26_6, t fixed.Int52_12) fixed.Point26_6 {
|
||||
s := 1<<12 - t
|
||||
x := s*fixed.Int52_12(a.X) + t*fixed.Int52_12(b.X)
|
||||
y := s*fixed.Int52_12(a.Y) + t*fixed.Int52_12(b.Y)
|
||||
return fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(x >> 12), fixed.Int26_6(y >> 12)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// curviest2 returns the value of t for which the quadratic parametric curve
|
||||
// (1-t)²*a + 2*t*(1-t).b + t²*c has maximum curvature.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The curvature of the parametric curve f(t) = (x(t), y(t)) is
|
||||
// |x′y″-y′x″| / (x′²+y′²)^(3/2).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Let d = b-a and e = c-2*b+a, so that f′(t) = 2*d+2*e*t and f″(t) = 2*e.
|
||||
// The curvature's numerator is (2*dx+2*ex*t)*(2*ey)-(2*dy+2*ey*t)*(2*ex),
|
||||
// which simplifies to 4*dx*ey-4*dy*ex, which is constant with respect to t.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Thus, curvature is extreme where the denominator is extreme, i.e. where
|
||||
// (x′²+y′²) is extreme. The first order condition is that
|
||||
// 2*x′*x″+2*y′*y″ = 0, or (dx+ex*t)*ex + (dy+ey*t)*ey = 0.
|
||||
// Solving for t gives t = -(dx*ex+dy*ey) / (ex*ex+ey*ey).
|
||||
func curviest2(a, b, c fixed.Point26_6) fixed.Int52_12 {
|
||||
dx := int64(b.X - a.X)
|
||||
dy := int64(b.Y - a.Y)
|
||||
ex := int64(c.X - 2*b.X + a.X)
|
||||
ey := int64(c.Y - 2*b.Y + a.Y)
|
||||
if ex == 0 && ey == 0 {
|
||||
return 2048
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fixed.Int52_12(-4096 * (dx*ex + dy*ey) / (ex*ex + ey*ey))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A stroker holds state for stroking a path.
|
||||
type stroker struct {
|
||||
// p is the destination that records the stroked path.
|
||||
p Adder
|
||||
// u is the half-width of the stroke.
|
||||
u fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
// cr and jr specify how to end and connect path segments.
|
||||
cr Capper
|
||||
jr Joiner
|
||||
// r is the reverse path. Stroking a path involves constructing two
|
||||
// parallel paths 2*u apart. The first path is added immediately to p,
|
||||
// the second path is accumulated in r and eventually added in reverse.
|
||||
r Path
|
||||
// a is the most recent segment point. anorm is the segment normal of
|
||||
// length u at that point.
|
||||
a, anorm fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// addNonCurvy2 adds a quadratic segment to the stroker, where the segment
|
||||
// defined by (k.a, b, c) achieves maximum curvature at either k.a or c.
|
||||
func (k *stroker) addNonCurvy2(b, c fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
// We repeatedly divide the segment at its middle until it is straight
|
||||
// enough to approximate the stroke by just translating the control points.
|
||||
// ds and ps are stacks of depths and points. t is the top of the stack.
|
||||
const maxDepth = 5
|
||||
var (
|
||||
ds [maxDepth + 1]int
|
||||
ps [2*maxDepth + 3]fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
t int
|
||||
)
|
||||
// Initially the ps stack has one quadratic segment of depth zero.
|
||||
ds[0] = 0
|
||||
ps[2] = k.a
|
||||
ps[1] = b
|
||||
ps[0] = c
|
||||
anorm := k.anorm
|
||||
var cnorm fixed.Point26_6
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
depth := ds[t]
|
||||
a := ps[2*t+2]
|
||||
b := ps[2*t+1]
|
||||
c := ps[2*t+0]
|
||||
ab := b.Sub(a)
|
||||
bc := c.Sub(b)
|
||||
abIsSmall := pDot(ab, ab) < fixed.Int52_12(1<<12)
|
||||
bcIsSmall := pDot(bc, bc) < fixed.Int52_12(1<<12)
|
||||
if abIsSmall && bcIsSmall {
|
||||
// Approximate the segment by a circular arc.
|
||||
cnorm = pRot90CCW(pNorm(bc, k.u))
|
||||
mac := midpoint(a, c)
|
||||
addArc(k.p, mac, anorm, cnorm)
|
||||
addArc(&k.r, mac, pNeg(anorm), pNeg(cnorm))
|
||||
} else if depth < maxDepth && angleGreaterThan45(ab, bc) {
|
||||
// Divide the segment in two and push both halves on the stack.
|
||||
mab := midpoint(a, b)
|
||||
mbc := midpoint(b, c)
|
||||
t++
|
||||
ds[t+0] = depth + 1
|
||||
ds[t-1] = depth + 1
|
||||
ps[2*t+2] = a
|
||||
ps[2*t+1] = mab
|
||||
ps[2*t+0] = midpoint(mab, mbc)
|
||||
ps[2*t-1] = mbc
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Translate the control points.
|
||||
bnorm := pRot90CCW(pNorm(c.Sub(a), k.u))
|
||||
cnorm = pRot90CCW(pNorm(bc, k.u))
|
||||
k.p.Add2(b.Add(bnorm), c.Add(cnorm))
|
||||
k.r.Add2(b.Sub(bnorm), c.Sub(cnorm))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t == 0 {
|
||||
k.a, k.anorm = c, cnorm
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
t--
|
||||
anorm = cnorm
|
||||
}
|
||||
panic("unreachable")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add1 adds a linear segment to the stroker.
|
||||
func (k *stroker) Add1(b fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
bnorm := pRot90CCW(pNorm(b.Sub(k.a), k.u))
|
||||
if len(k.r) == 0 {
|
||||
k.p.Start(k.a.Add(bnorm))
|
||||
k.r.Start(k.a.Sub(bnorm))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
k.jr.Join(k.p, &k.r, k.u, k.a, k.anorm, bnorm)
|
||||
}
|
||||
k.p.Add1(b.Add(bnorm))
|
||||
k.r.Add1(b.Sub(bnorm))
|
||||
k.a, k.anorm = b, bnorm
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add2 adds a quadratic segment to the stroker.
|
||||
func (k *stroker) Add2(b, c fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
ab := b.Sub(k.a)
|
||||
bc := c.Sub(b)
|
||||
abnorm := pRot90CCW(pNorm(ab, k.u))
|
||||
if len(k.r) == 0 {
|
||||
k.p.Start(k.a.Add(abnorm))
|
||||
k.r.Start(k.a.Sub(abnorm))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
k.jr.Join(k.p, &k.r, k.u, k.a, k.anorm, abnorm)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Approximate nearly-degenerate quadratics by linear segments.
|
||||
abIsSmall := pDot(ab, ab) < epsilon
|
||||
bcIsSmall := pDot(bc, bc) < epsilon
|
||||
if abIsSmall || bcIsSmall {
|
||||
acnorm := pRot90CCW(pNorm(c.Sub(k.a), k.u))
|
||||
k.p.Add1(c.Add(acnorm))
|
||||
k.r.Add1(c.Sub(acnorm))
|
||||
k.a, k.anorm = c, acnorm
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The quadratic segment (k.a, b, c) has a point of maximum curvature.
|
||||
// If this occurs at an end point, we process the segment as a whole.
|
||||
t := curviest2(k.a, b, c)
|
||||
if t <= 0 || 4096 <= t {
|
||||
k.addNonCurvy2(b, c)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, we perform a de Casteljau decomposition at the point of
|
||||
// maximum curvature and process the two straighter parts.
|
||||
mab := interpolate(k.a, b, t)
|
||||
mbc := interpolate(b, c, t)
|
||||
mabc := interpolate(mab, mbc, t)
|
||||
|
||||
// If the vectors ab and bc are close to being in opposite directions,
|
||||
// then the decomposition can become unstable, so we approximate the
|
||||
// quadratic segment by two linear segments joined by an arc.
|
||||
bcnorm := pRot90CCW(pNorm(bc, k.u))
|
||||
if pDot(abnorm, bcnorm) < -fixed.Int52_12(k.u)*fixed.Int52_12(k.u)*2047/2048 {
|
||||
pArc := pDot(abnorm, bc) < 0
|
||||
|
||||
k.p.Add1(mabc.Add(abnorm))
|
||||
if pArc {
|
||||
z := pRot90CW(abnorm)
|
||||
addArc(k.p, mabc, abnorm, z)
|
||||
addArc(k.p, mabc, z, bcnorm)
|
||||
}
|
||||
k.p.Add1(mabc.Add(bcnorm))
|
||||
k.p.Add1(c.Add(bcnorm))
|
||||
|
||||
k.r.Add1(mabc.Sub(abnorm))
|
||||
if !pArc {
|
||||
z := pRot90CW(abnorm)
|
||||
addArc(&k.r, mabc, pNeg(abnorm), z)
|
||||
addArc(&k.r, mabc, z, pNeg(bcnorm))
|
||||
}
|
||||
k.r.Add1(mabc.Sub(bcnorm))
|
||||
k.r.Add1(c.Sub(bcnorm))
|
||||
|
||||
k.a, k.anorm = c, bcnorm
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Process the decomposed parts.
|
||||
k.addNonCurvy2(mab, mabc)
|
||||
k.addNonCurvy2(mbc, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add3 adds a cubic segment to the stroker.
|
||||
func (k *stroker) Add3(b, c, d fixed.Point26_6) {
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: stroke unimplemented for cubic segments")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stroke adds the stroked Path q to p, where q consists of exactly one curve.
|
||||
func (k *stroker) stroke(q Path) {
|
||||
// Stroking is implemented by deriving two paths each k.u apart from q.
|
||||
// The left-hand-side path is added immediately to k.p; the right-hand-side
|
||||
// path is accumulated in k.r. Once we've finished adding the LHS to k.p,
|
||||
// we add the RHS in reverse order.
|
||||
k.r = make(Path, 0, len(q))
|
||||
k.a = fixed.Point26_6{q[1], q[2]}
|
||||
for i := 4; i < len(q); {
|
||||
switch q[i] {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
k.Add1(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+1], q[i+2]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 4
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
k.Add2(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+1], q[i+2]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+3], q[i+4]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 6
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
k.Add3(
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+1], q[i+2]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+3], q[i+4]},
|
||||
fixed.Point26_6{q[i+5], q[i+6]},
|
||||
)
|
||||
i += 8
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(k.r) == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO(nigeltao): if q is a closed curve then we should join the first and
|
||||
// last segments instead of capping them.
|
||||
k.cr.Cap(k.p, k.u, q.lastPoint(), pNeg(k.anorm))
|
||||
addPathReversed(k.p, k.r)
|
||||
pivot := q.firstPoint()
|
||||
k.cr.Cap(k.p, k.u, pivot, pivot.Sub(fixed.Point26_6{k.r[1], k.r[2]}))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stroke adds q stroked with the given width to p. The result is typically
|
||||
// self-intersecting and should be rasterized with UseNonZeroWinding.
|
||||
// cr and jr may be nil, which defaults to a RoundCapper or RoundJoiner.
|
||||
func Stroke(p Adder, q Path, width fixed.Int26_6, cr Capper, jr Joiner) {
|
||||
if len(q) == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if cr == nil {
|
||||
cr = RoundCapper
|
||||
}
|
||||
if jr == nil {
|
||||
jr = RoundJoiner
|
||||
}
|
||||
if q[0] != 0 {
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
s := stroker{p: p, u: width / 2, cr: cr, jr: jr}
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for j := 4; j < len(q); {
|
||||
switch q[j] {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
s.stroke(q[i:j])
|
||||
i, j = j, j+4
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
j += 4
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
j += 6
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
j += 8
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("freetype/raster: bad path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.stroke(q[i:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
42
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/testdata/COPYING
generated
vendored
42
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/testdata/COPYING
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
|
|||
Luxi fonts copyright (c) 2001 by Bigelow & Holmes Inc. Luxi font
|
||||
instruction code copyright (c) 2001 by URW++ GmbH. All Rights
|
||||
Reserved. Luxi is a registered trademark of Bigelow & Holmes Inc.
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining
|
||||
a copy of these Fonts and associated documentation files (the "Font
|
||||
Software"), to deal in the Font Software, including without
|
||||
limitation the rights to use, copy, merge, publish, distribute,
|
||||
sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Font Software, and to permit
|
||||
persons to whom the Font Software is furnished to do so, subject to
|
||||
the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright and trademark notices and this permission notice
|
||||
shall be included in all copies of one or more of the Font Software.
|
||||
|
||||
The Font Software may not be modified, altered, or added to, and in
|
||||
particular the designs of glyphs or characters in the Fonts may not
|
||||
be modified nor may additional glyphs or characters be added to the
|
||||
Fonts. This License becomes null and void when the Fonts or Font
|
||||
Software have been modified.
|
||||
|
||||
THE FONT SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
|
||||
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTIES OF
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT
|
||||
OF COPYRIGHT, PATENT, TRADEMARK, OR OTHER RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
|
||||
BIGELOW & HOLMES INC. OR URW++ GMBH. BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES
|
||||
OR OTHER LIABILITY, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INDIRECT,
|
||||
INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF
|
||||
CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF THE USE OR
|
||||
INABILITY TO USE THE FONT SOFTWARE OR FROM OTHER DEALINGS IN THE FONT
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
|
||||
Except as contained in this notice, the names of Bigelow & Holmes
|
||||
Inc. and URW++ GmbH. shall not be used in advertising or otherwise to
|
||||
promote the sale, use or other dealings in this Font Software without
|
||||
prior written authorization from Bigelow & Holmes Inc. and URW++ GmbH.
|
||||
|
||||
For further information, contact:
|
||||
|
||||
info@urwpp.de
|
||||
or
|
||||
design@bigelowandholmes.com
|
||||
507
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/face.go
generated
vendored
507
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/face.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,507 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2015 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package truetype
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/freetype/raster"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/font"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func powerOf2(i int) bool {
|
||||
return i != 0 && (i&(i-1)) == 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Options are optional arguments to NewFace.
|
||||
type Options struct {
|
||||
// Size is the font size in points, as in "a 10 point font size".
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A zero value means to use a 12 point font size.
|
||||
Size float64
|
||||
|
||||
// DPI is the dots-per-inch resolution.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A zero value means to use 72 DPI.
|
||||
DPI float64
|
||||
|
||||
// Hinting is how to quantize the glyph nodes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A zero value means to use no hinting.
|
||||
Hinting font.Hinting
|
||||
|
||||
// GlyphCacheEntries is the number of entries in the glyph mask image
|
||||
// cache.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If non-zero, it must be a power of 2.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A zero value means to use 512 entries.
|
||||
GlyphCacheEntries int
|
||||
|
||||
// SubPixelsX is the number of sub-pixel locations a glyph's dot is
|
||||
// quantized to, in the horizontal direction. For example, a value of 8
|
||||
// means that the dot is quantized to 1/8th of a pixel. This quantization
|
||||
// only affects the glyph mask image, not its bounding box or advance
|
||||
// width. A higher value gives a more faithful glyph image, but reduces the
|
||||
// effectiveness of the glyph cache.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If non-zero, it must be a power of 2, and be between 1 and 64 inclusive.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A zero value means to use 4 sub-pixel locations.
|
||||
SubPixelsX int
|
||||
|
||||
// SubPixelsY is the number of sub-pixel locations a glyph's dot is
|
||||
// quantized to, in the vertical direction. For example, a value of 8
|
||||
// means that the dot is quantized to 1/8th of a pixel. This quantization
|
||||
// only affects the glyph mask image, not its bounding box or advance
|
||||
// width. A higher value gives a more faithful glyph image, but reduces the
|
||||
// effectiveness of the glyph cache.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If non-zero, it must be a power of 2, and be between 1 and 64 inclusive.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A zero value means to use 1 sub-pixel location.
|
||||
SubPixelsY int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *Options) size() float64 {
|
||||
if o != nil && o.Size > 0 {
|
||||
return o.Size
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 12
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *Options) dpi() float64 {
|
||||
if o != nil && o.DPI > 0 {
|
||||
return o.DPI
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 72
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *Options) hinting() font.Hinting {
|
||||
if o != nil {
|
||||
switch o.Hinting {
|
||||
case font.HintingVertical, font.HintingFull:
|
||||
// TODO: support vertical hinting.
|
||||
return font.HintingFull
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return font.HintingNone
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *Options) glyphCacheEntries() int {
|
||||
if o != nil && powerOf2(o.GlyphCacheEntries) {
|
||||
return o.GlyphCacheEntries
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 512 is 128 * 4 * 1, which lets us cache 128 glyphs at 4 * 1 subpixel
|
||||
// locations in the X and Y direction.
|
||||
return 512
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *Options) subPixelsX() (value uint32, halfQuantum, mask fixed.Int26_6) {
|
||||
if o != nil {
|
||||
switch o.SubPixelsX {
|
||||
case 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64:
|
||||
return subPixels(o.SubPixelsX)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// This default value of 4 isn't based on anything scientific, merely as
|
||||
// small a number as possible that looks almost as good as no quantization,
|
||||
// or returning subPixels(64).
|
||||
return subPixels(4)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (o *Options) subPixelsY() (value uint32, halfQuantum, mask fixed.Int26_6) {
|
||||
if o != nil {
|
||||
switch o.SubPixelsX {
|
||||
case 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64:
|
||||
return subPixels(o.SubPixelsX)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// This default value of 1 isn't based on anything scientific, merely that
|
||||
// vertical sub-pixel glyph rendering is pretty rare. Baseline locations
|
||||
// can usually afford to snap to the pixel grid, so the vertical direction
|
||||
// doesn't have the deal with the horizontal's fractional advance widths.
|
||||
return subPixels(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// subPixels returns q and the bias and mask that leads to q quantized
|
||||
// sub-pixel locations per full pixel.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, q == 4 leads to a bias of 8 and a mask of 0xfffffff0, or -16,
|
||||
// because we want to round fractions of fixed.Int26_6 as:
|
||||
// - 0 to 7 rounds to 0.
|
||||
// - 8 to 23 rounds to 16.
|
||||
// - 24 to 39 rounds to 32.
|
||||
// - 40 to 55 rounds to 48.
|
||||
// - 56 to 63 rounds to 64.
|
||||
// which means to add 8 and then bitwise-and with -16, in two's complement
|
||||
// representation.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// When q == 1, we want bias == 32 and mask == -64.
|
||||
// When q == 2, we want bias == 16 and mask == -32.
|
||||
// When q == 4, we want bias == 8 and mask == -16.
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
// When q == 64, we want bias == 0 and mask == -1. (The no-op case).
|
||||
// The pattern is clear.
|
||||
func subPixels(q int) (value uint32, bias, mask fixed.Int26_6) {
|
||||
return uint32(q), 32 / fixed.Int26_6(q), -64 / fixed.Int26_6(q)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// glyphCacheEntry caches the arguments and return values of rasterize.
|
||||
type glyphCacheEntry struct {
|
||||
key glyphCacheKey
|
||||
val glyphCacheVal
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type glyphCacheKey struct {
|
||||
index Index
|
||||
fx, fy uint8
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type glyphCacheVal struct {
|
||||
advanceWidth fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
offset image.Point
|
||||
gw int
|
||||
gh int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type indexCacheEntry struct {
|
||||
rune rune
|
||||
index Index
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewFace returns a new font.Face for the given Font.
|
||||
func NewFace(f *Font, opts *Options) font.Face {
|
||||
a := &face{
|
||||
f: f,
|
||||
hinting: opts.hinting(),
|
||||
scale: fixed.Int26_6(0.5 + (opts.size() * opts.dpi() * 64 / 72)),
|
||||
glyphCache: make([]glyphCacheEntry, opts.glyphCacheEntries()),
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.subPixelX, a.subPixelBiasX, a.subPixelMaskX = opts.subPixelsX()
|
||||
a.subPixelY, a.subPixelBiasY, a.subPixelMaskY = opts.subPixelsY()
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill the cache with invalid entries. Valid glyph cache entries have fx
|
||||
// and fy in the range [0, 64). Valid index cache entries have rune >= 0.
|
||||
for i := range a.glyphCache {
|
||||
a.glyphCache[i].key.fy = 0xff
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := range a.indexCache {
|
||||
a.indexCache[i].rune = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set the rasterizer's bounds to be big enough to handle the largest glyph.
|
||||
b := f.Bounds(a.scale)
|
||||
xmin := +int(b.Min.X) >> 6
|
||||
ymin := -int(b.Max.Y) >> 6
|
||||
xmax := +int(b.Max.X+63) >> 6
|
||||
ymax := -int(b.Min.Y-63) >> 6
|
||||
a.maxw = xmax - xmin
|
||||
a.maxh = ymax - ymin
|
||||
a.masks = image.NewAlpha(image.Rect(0, 0, a.maxw, a.maxh*len(a.glyphCache)))
|
||||
a.r.SetBounds(a.maxw, a.maxh)
|
||||
a.p = facePainter{a}
|
||||
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type face struct {
|
||||
f *Font
|
||||
hinting font.Hinting
|
||||
scale fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
subPixelX uint32
|
||||
subPixelBiasX fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
subPixelMaskX fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
subPixelY uint32
|
||||
subPixelBiasY fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
subPixelMaskY fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
masks *image.Alpha
|
||||
glyphCache []glyphCacheEntry
|
||||
r raster.Rasterizer
|
||||
p raster.Painter
|
||||
paintOffset int
|
||||
maxw int
|
||||
maxh int
|
||||
glyphBuf GlyphBuf
|
||||
indexCache [indexCacheLen]indexCacheEntry
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: clip rectangle?
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const indexCacheLen = 256
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *face) index(r rune) Index {
|
||||
const mask = indexCacheLen - 1
|
||||
c := &a.indexCache[r&mask]
|
||||
if c.rune == r {
|
||||
return c.index
|
||||
}
|
||||
i := a.f.Index(r)
|
||||
c.rune = r
|
||||
c.index = i
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Close satisfies the font.Face interface.
|
||||
func (a *face) Close() error { return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// Metrics satisfies the font.Face interface.
|
||||
func (a *face) Metrics() font.Metrics {
|
||||
scale := float64(a.scale)
|
||||
fupe := float64(a.f.FUnitsPerEm())
|
||||
return font.Metrics{
|
||||
Height: a.scale,
|
||||
Ascent: fixed.Int26_6(math.Ceil(scale * float64(+a.f.ascent) / fupe)),
|
||||
Descent: fixed.Int26_6(math.Ceil(scale * float64(-a.f.descent) / fupe)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Kern satisfies the font.Face interface.
|
||||
func (a *face) Kern(r0, r1 rune) fixed.Int26_6 {
|
||||
i0 := a.index(r0)
|
||||
i1 := a.index(r1)
|
||||
kern := a.f.Kern(a.scale, i0, i1)
|
||||
if a.hinting != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
kern = (kern + 32) &^ 63
|
||||
}
|
||||
return kern
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Glyph satisfies the font.Face interface.
|
||||
func (a *face) Glyph(dot fixed.Point26_6, r rune) (
|
||||
dr image.Rectangle, mask image.Image, maskp image.Point, advance fixed.Int26_6, ok bool) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Quantize to the sub-pixel granularity.
|
||||
dotX := (dot.X + a.subPixelBiasX) & a.subPixelMaskX
|
||||
dotY := (dot.Y + a.subPixelBiasY) & a.subPixelMaskY
|
||||
|
||||
// Split the coordinates into their integer and fractional parts.
|
||||
ix, fx := int(dotX>>6), dotX&0x3f
|
||||
iy, fy := int(dotY>>6), dotY&0x3f
|
||||
|
||||
index := a.index(r)
|
||||
cIndex := uint32(index)
|
||||
cIndex = cIndex*a.subPixelX - uint32(fx/a.subPixelMaskX)
|
||||
cIndex = cIndex*a.subPixelY - uint32(fy/a.subPixelMaskY)
|
||||
cIndex &= uint32(len(a.glyphCache) - 1)
|
||||
a.paintOffset = a.maxh * int(cIndex)
|
||||
k := glyphCacheKey{
|
||||
index: index,
|
||||
fx: uint8(fx),
|
||||
fy: uint8(fy),
|
||||
}
|
||||
var v glyphCacheVal
|
||||
if a.glyphCache[cIndex].key != k {
|
||||
var ok bool
|
||||
v, ok = a.rasterize(index, fx, fy)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return image.Rectangle{}, nil, image.Point{}, 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.glyphCache[cIndex] = glyphCacheEntry{k, v}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
v = a.glyphCache[cIndex].val
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dr.Min = image.Point{
|
||||
X: ix + v.offset.X,
|
||||
Y: iy + v.offset.Y,
|
||||
}
|
||||
dr.Max = image.Point{
|
||||
X: dr.Min.X + v.gw,
|
||||
Y: dr.Min.Y + v.gh,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dr, a.masks, image.Point{Y: a.paintOffset}, v.advanceWidth, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *face) GlyphBounds(r rune) (bounds fixed.Rectangle26_6, advance fixed.Int26_6, ok bool) {
|
||||
if err := a.glyphBuf.Load(a.f, a.scale, a.index(r), a.hinting); err != nil {
|
||||
return fixed.Rectangle26_6{}, 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
xmin := +a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Min.X
|
||||
ymin := -a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Max.Y
|
||||
xmax := +a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Max.X
|
||||
ymax := -a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Min.Y
|
||||
if xmin > xmax || ymin > ymax {
|
||||
return fixed.Rectangle26_6{}, 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fixed.Rectangle26_6{
|
||||
Min: fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: xmin,
|
||||
Y: ymin,
|
||||
},
|
||||
Max: fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: xmax,
|
||||
Y: ymax,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}, a.glyphBuf.AdvanceWidth, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *face) GlyphAdvance(r rune) (advance fixed.Int26_6, ok bool) {
|
||||
if err := a.glyphBuf.Load(a.f, a.scale, a.index(r), a.hinting); err != nil {
|
||||
return 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return a.glyphBuf.AdvanceWidth, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// rasterize returns the advance width, integer-pixel offset to render at, and
|
||||
// the width and height of the given glyph at the given sub-pixel offsets.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The 26.6 fixed point arguments fx and fy must be in the range [0, 1).
|
||||
func (a *face) rasterize(index Index, fx, fy fixed.Int26_6) (v glyphCacheVal, ok bool) {
|
||||
if err := a.glyphBuf.Load(a.f, a.scale, index, a.hinting); err != nil {
|
||||
return glyphCacheVal{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Calculate the integer-pixel bounds for the glyph.
|
||||
xmin := int(fx+a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Min.X) >> 6
|
||||
ymin := int(fy-a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Max.Y) >> 6
|
||||
xmax := int(fx+a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Max.X+0x3f) >> 6
|
||||
ymax := int(fy-a.glyphBuf.Bounds.Min.Y+0x3f) >> 6
|
||||
if xmin > xmax || ymin > ymax {
|
||||
return glyphCacheVal{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
// A TrueType's glyph's nodes can have negative co-ordinates, but the
|
||||
// rasterizer clips anything left of x=0 or above y=0. xmin and ymin are
|
||||
// the pixel offsets, based on the font's FUnit metrics, that let a
|
||||
// negative co-ordinate in TrueType space be non-negative in rasterizer
|
||||
// space. xmin and ymin are typically <= 0.
|
||||
fx -= fixed.Int26_6(xmin << 6)
|
||||
fy -= fixed.Int26_6(ymin << 6)
|
||||
// Rasterize the glyph's vectors.
|
||||
a.r.Clear()
|
||||
pixOffset := a.paintOffset * a.maxw
|
||||
clear(a.masks.Pix[pixOffset : pixOffset+a.maxw*a.maxh])
|
||||
e0 := 0
|
||||
for _, e1 := range a.glyphBuf.Ends {
|
||||
a.drawContour(a.glyphBuf.Points[e0:e1], fx, fy)
|
||||
e0 = e1
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.r.Rasterize(a.p)
|
||||
return glyphCacheVal{
|
||||
a.glyphBuf.AdvanceWidth,
|
||||
image.Point{xmin, ymin},
|
||||
xmax - xmin,
|
||||
ymax - ymin,
|
||||
}, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func clear(pix []byte) {
|
||||
for i := range pix {
|
||||
pix[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// drawContour draws the given closed contour with the given offset.
|
||||
func (a *face) drawContour(ps []Point, dx, dy fixed.Int26_6) {
|
||||
if len(ps) == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The low bit of each point's Flags value is whether the point is on the
|
||||
// curve. Truetype fonts only have quadratic Bézier curves, not cubics.
|
||||
// Thus, two consecutive off-curve points imply an on-curve point in the
|
||||
// middle of those two.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://chanae.walon.org/pub/ttf/ttf_glyphs.htm for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
// ps[0] is a truetype.Point measured in FUnits and positive Y going
|
||||
// upwards. start is the same thing measured in fixed point units and
|
||||
// positive Y going downwards, and offset by (dx, dy).
|
||||
start := fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: dx + ps[0].X,
|
||||
Y: dy - ps[0].Y,
|
||||
}
|
||||
var others []Point
|
||||
if ps[0].Flags&0x01 != 0 {
|
||||
others = ps[1:]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
last := fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: dx + ps[len(ps)-1].X,
|
||||
Y: dy - ps[len(ps)-1].Y,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ps[len(ps)-1].Flags&0x01 != 0 {
|
||||
start = last
|
||||
others = ps[:len(ps)-1]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
start = fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: (start.X + last.X) / 2,
|
||||
Y: (start.Y + last.Y) / 2,
|
||||
}
|
||||
others = ps
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.r.Start(start)
|
||||
q0, on0 := start, true
|
||||
for _, p := range others {
|
||||
q := fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: dx + p.X,
|
||||
Y: dy - p.Y,
|
||||
}
|
||||
on := p.Flags&0x01 != 0
|
||||
if on {
|
||||
if on0 {
|
||||
a.r.Add1(q)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
a.r.Add2(q0, q)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if on0 {
|
||||
// No-op.
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
mid := fixed.Point26_6{
|
||||
X: (q0.X + q.X) / 2,
|
||||
Y: (q0.Y + q.Y) / 2,
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.r.Add2(q0, mid)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
q0, on0 = q, on
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Close the curve.
|
||||
if on0 {
|
||||
a.r.Add1(start)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
a.r.Add2(q0, start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// facePainter is like a raster.AlphaSrcPainter, with an additional Y offset
|
||||
// (face.paintOffset) to the painted spans.
|
||||
type facePainter struct {
|
||||
a *face
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p facePainter) Paint(ss []raster.Span, done bool) {
|
||||
m := p.a.masks
|
||||
b := m.Bounds()
|
||||
b.Min.Y = p.a.paintOffset
|
||||
b.Max.Y = p.a.paintOffset + p.a.maxh
|
||||
for _, s := range ss {
|
||||
s.Y += p.a.paintOffset
|
||||
if s.Y < b.Min.Y {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.Y >= b.Max.Y {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 < b.Min.X {
|
||||
s.X0 = b.Min.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X1 > b.Max.X {
|
||||
s.X1 = b.Max.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.X0 >= s.X1 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
base := (s.Y-m.Rect.Min.Y)*m.Stride - m.Rect.Min.X
|
||||
p := m.Pix[base+s.X0 : base+s.X1]
|
||||
color := uint8(s.Alpha >> 8)
|
||||
for i := range p {
|
||||
p[i] = color
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
522
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/glyph.go
generated
vendored
522
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/glyph.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,522 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2010 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package truetype
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/font"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: implement VerticalHinting.
|
||||
|
||||
// A Point is a co-ordinate pair plus whether it is 'on' a contour or an 'off'
|
||||
// control point.
|
||||
type Point struct {
|
||||
X, Y fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
// The Flags' LSB means whether or not this Point is 'on' the contour.
|
||||
// Other bits are reserved for internal use.
|
||||
Flags uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A GlyphBuf holds a glyph's contours. A GlyphBuf can be re-used to load a
|
||||
// series of glyphs from a Font.
|
||||
type GlyphBuf struct {
|
||||
// AdvanceWidth is the glyph's advance width.
|
||||
AdvanceWidth fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
// Bounds is the glyph's bounding box.
|
||||
Bounds fixed.Rectangle26_6
|
||||
// Points contains all Points from all contours of the glyph. If hinting
|
||||
// was used to load a glyph then Unhinted contains those Points before they
|
||||
// were hinted, and InFontUnits contains those Points before they were
|
||||
// hinted and scaled.
|
||||
Points, Unhinted, InFontUnits []Point
|
||||
// Ends is the point indexes of the end point of each contour. The length
|
||||
// of Ends is the number of contours in the glyph. The i'th contour
|
||||
// consists of points Points[Ends[i-1]:Ends[i]], where Ends[-1] is
|
||||
// interpreted to mean zero.
|
||||
Ends []int
|
||||
|
||||
font *Font
|
||||
scale fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
hinting font.Hinting
|
||||
hinter hinter
|
||||
// phantomPoints are the co-ordinates of the synthetic phantom points
|
||||
// used for hinting and bounding box calculations.
|
||||
phantomPoints [4]Point
|
||||
// pp1x is the X co-ordinate of the first phantom point. The '1' is
|
||||
// using 1-based indexing; pp1x is almost always phantomPoints[0].X.
|
||||
// TODO: eliminate this and consistently use phantomPoints[0].X.
|
||||
pp1x fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
// metricsSet is whether the glyph's metrics have been set yet. For a
|
||||
// compound glyph, a sub-glyph may override the outer glyph's metrics.
|
||||
metricsSet bool
|
||||
// tmp is a scratch buffer.
|
||||
tmp []Point
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Flags for decoding a glyph's contours. These flags are documented at
|
||||
// http://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM06/Chap6glyf.html.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
flagOnCurve = 1 << iota
|
||||
flagXShortVector
|
||||
flagYShortVector
|
||||
flagRepeat
|
||||
flagPositiveXShortVector
|
||||
flagPositiveYShortVector
|
||||
|
||||
// The remaining flags are for internal use.
|
||||
flagTouchedX
|
||||
flagTouchedY
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// The same flag bits (0x10 and 0x20) are overloaded to have two meanings,
|
||||
// dependent on the value of the flag{X,Y}ShortVector bits.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
flagThisXIsSame = flagPositiveXShortVector
|
||||
flagThisYIsSame = flagPositiveYShortVector
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Load loads a glyph's contours from a Font, overwriting any previously loaded
|
||||
// contours for this GlyphBuf. scale is the number of 26.6 fixed point units in
|
||||
// 1 em, i is the glyph index, and h is the hinting policy.
|
||||
func (g *GlyphBuf) Load(f *Font, scale fixed.Int26_6, i Index, h font.Hinting) error {
|
||||
g.Points = g.Points[:0]
|
||||
g.Unhinted = g.Unhinted[:0]
|
||||
g.InFontUnits = g.InFontUnits[:0]
|
||||
g.Ends = g.Ends[:0]
|
||||
g.font = f
|
||||
g.hinting = h
|
||||
g.scale = scale
|
||||
g.pp1x = 0
|
||||
g.phantomPoints = [4]Point{}
|
||||
g.metricsSet = false
|
||||
|
||||
if h != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
if err := g.hinter.init(f, scale); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := g.load(0, i, true); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: this selection of either g.pp1x or g.phantomPoints[0].X isn't ideal,
|
||||
// and should be cleaned up once we have all the testScaling tests passing,
|
||||
// plus additional tests for Freetype-Go's bounding boxes matching C Freetype's.
|
||||
pp1x := g.pp1x
|
||||
if h != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
pp1x = g.phantomPoints[0].X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if pp1x != 0 {
|
||||
for i := range g.Points {
|
||||
g.Points[i].X -= pp1x
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
advanceWidth := g.phantomPoints[1].X - g.phantomPoints[0].X
|
||||
if h != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
if len(f.hdmx) >= 8 {
|
||||
if n := u32(f.hdmx, 4); n > 3+uint32(i) {
|
||||
for hdmx := f.hdmx[8:]; uint32(len(hdmx)) >= n; hdmx = hdmx[n:] {
|
||||
if fixed.Int26_6(hdmx[0]) == scale>>6 {
|
||||
advanceWidth = fixed.Int26_6(hdmx[2+i]) << 6
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
advanceWidth = (advanceWidth + 32) &^ 63
|
||||
}
|
||||
g.AdvanceWidth = advanceWidth
|
||||
|
||||
// Set g.Bounds to the 'control box', which is the bounding box of the
|
||||
// Bézier curves' control points. This is easier to calculate, no smaller
|
||||
// than and often equal to the tightest possible bounding box of the curves
|
||||
// themselves. This approach is what C Freetype does. We can't just scale
|
||||
// the nominal bounding box in the glyf data as the hinting process and
|
||||
// phantom point adjustment may move points outside of that box.
|
||||
if len(g.Points) == 0 {
|
||||
g.Bounds = fixed.Rectangle26_6{}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p := g.Points[0]
|
||||
g.Bounds.Min.X = p.X
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.X = p.X
|
||||
g.Bounds.Min.Y = p.Y
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.Y = p.Y
|
||||
for _, p := range g.Points[1:] {
|
||||
if g.Bounds.Min.X > p.X {
|
||||
g.Bounds.Min.X = p.X
|
||||
} else if g.Bounds.Max.X < p.X {
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.X = p.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if g.Bounds.Min.Y > p.Y {
|
||||
g.Bounds.Min.Y = p.Y
|
||||
} else if g.Bounds.Max.Y < p.Y {
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.Y = p.Y
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Snap the box to the grid, if hinting is on.
|
||||
if h != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
g.Bounds.Min.X &^= 63
|
||||
g.Bounds.Min.Y &^= 63
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.X += 63
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.X &^= 63
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.Y += 63
|
||||
g.Bounds.Max.Y &^= 63
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *GlyphBuf) load(recursion uint32, i Index, useMyMetrics bool) (err error) {
|
||||
// The recursion limit here is arbitrary, but defends against malformed glyphs.
|
||||
if recursion >= 32 {
|
||||
return UnsupportedError("excessive compound glyph recursion")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Find the relevant slice of g.font.glyf.
|
||||
var g0, g1 uint32
|
||||
if g.font.locaOffsetFormat == locaOffsetFormatShort {
|
||||
g0 = 2 * uint32(u16(g.font.loca, 2*int(i)))
|
||||
g1 = 2 * uint32(u16(g.font.loca, 2*int(i)+2))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
g0 = u32(g.font.loca, 4*int(i))
|
||||
g1 = u32(g.font.loca, 4*int(i)+4)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode the contour count and nominal bounding box, from the first
|
||||
// 10 bytes of the glyf data. boundsYMin and boundsXMax, at offsets 4
|
||||
// and 6, are unused.
|
||||
glyf, ne, boundsXMin, boundsYMax := []byte(nil), 0, fixed.Int26_6(0), fixed.Int26_6(0)
|
||||
if g0+10 <= g1 {
|
||||
glyf = g.font.glyf[g0:g1]
|
||||
ne = int(int16(u16(glyf, 0)))
|
||||
boundsXMin = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(glyf, 2)))
|
||||
boundsYMax = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(glyf, 8)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Create the phantom points.
|
||||
uhm, pp1x := g.font.unscaledHMetric(i), fixed.Int26_6(0)
|
||||
uvm := g.font.unscaledVMetric(i, boundsYMax)
|
||||
g.phantomPoints = [4]Point{
|
||||
{X: boundsXMin - uhm.LeftSideBearing},
|
||||
{X: boundsXMin - uhm.LeftSideBearing + uhm.AdvanceWidth},
|
||||
{X: uhm.AdvanceWidth / 2, Y: boundsYMax + uvm.TopSideBearing},
|
||||
{X: uhm.AdvanceWidth / 2, Y: boundsYMax + uvm.TopSideBearing - uvm.AdvanceHeight},
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(glyf) == 0 {
|
||||
g.addPhantomsAndScale(len(g.Points), len(g.Points), true, true)
|
||||
copy(g.phantomPoints[:], g.Points[len(g.Points)-4:])
|
||||
g.Points = g.Points[:len(g.Points)-4]
|
||||
// TODO: also trim g.InFontUnits and g.Unhinted?
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Load and hint the contours.
|
||||
if ne < 0 {
|
||||
if ne != -1 {
|
||||
// http://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM06/Chap6glyf.html says that
|
||||
// "the values -2, -3, and so forth, are reserved for future use."
|
||||
return UnsupportedError("negative number of contours")
|
||||
}
|
||||
pp1x = g.font.scale(g.scale * (boundsXMin - uhm.LeftSideBearing))
|
||||
if err := g.loadCompound(recursion, uhm, i, glyf, useMyMetrics); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
np0, ne0 := len(g.Points), len(g.Ends)
|
||||
program := g.loadSimple(glyf, ne)
|
||||
g.addPhantomsAndScale(np0, np0, true, true)
|
||||
pp1x = g.Points[len(g.Points)-4].X
|
||||
if g.hinting != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
if len(program) != 0 {
|
||||
err := g.hinter.run(
|
||||
program,
|
||||
g.Points[np0:],
|
||||
g.Unhinted[np0:],
|
||||
g.InFontUnits[np0:],
|
||||
g.Ends[ne0:],
|
||||
)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Drop the four phantom points.
|
||||
g.InFontUnits = g.InFontUnits[:len(g.InFontUnits)-4]
|
||||
g.Unhinted = g.Unhinted[:len(g.Unhinted)-4]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if useMyMetrics {
|
||||
copy(g.phantomPoints[:], g.Points[len(g.Points)-4:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
g.Points = g.Points[:len(g.Points)-4]
|
||||
if np0 != 0 {
|
||||
// The hinting program expects the []Ends values to be indexed
|
||||
// relative to the inner glyph, not the outer glyph, so we delay
|
||||
// adding np0 until after the hinting program (if any) has run.
|
||||
for i := ne0; i < len(g.Ends); i++ {
|
||||
g.Ends[i] += np0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if useMyMetrics && !g.metricsSet {
|
||||
g.metricsSet = true
|
||||
g.pp1x = pp1x
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// loadOffset is the initial offset for loadSimple and loadCompound. The first
|
||||
// 10 bytes are the number of contours and the bounding box.
|
||||
const loadOffset = 10
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *GlyphBuf) loadSimple(glyf []byte, ne int) (program []byte) {
|
||||
offset := loadOffset
|
||||
for i := 0; i < ne; i++ {
|
||||
g.Ends = append(g.Ends, 1+int(u16(glyf, offset)))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Note the TrueType hinting instructions.
|
||||
instrLen := int(u16(glyf, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
program = glyf[offset : offset+instrLen]
|
||||
offset += instrLen
|
||||
|
||||
if ne == 0 {
|
||||
return program
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
np0 := len(g.Points)
|
||||
np1 := np0 + int(g.Ends[len(g.Ends)-1])
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode the flags.
|
||||
for i := np0; i < np1; {
|
||||
c := uint32(glyf[offset])
|
||||
offset++
|
||||
g.Points = append(g.Points, Point{Flags: c})
|
||||
i++
|
||||
if c&flagRepeat != 0 {
|
||||
count := glyf[offset]
|
||||
offset++
|
||||
for ; count > 0; count-- {
|
||||
g.Points = append(g.Points, Point{Flags: c})
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode the co-ordinates.
|
||||
var x int16
|
||||
for i := np0; i < np1; i++ {
|
||||
f := g.Points[i].Flags
|
||||
if f&flagXShortVector != 0 {
|
||||
dx := int16(glyf[offset])
|
||||
offset++
|
||||
if f&flagPositiveXShortVector == 0 {
|
||||
x -= dx
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
x += dx
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if f&flagThisXIsSame == 0 {
|
||||
x += int16(u16(glyf, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
g.Points[i].X = fixed.Int26_6(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
var y int16
|
||||
for i := np0; i < np1; i++ {
|
||||
f := g.Points[i].Flags
|
||||
if f&flagYShortVector != 0 {
|
||||
dy := int16(glyf[offset])
|
||||
offset++
|
||||
if f&flagPositiveYShortVector == 0 {
|
||||
y -= dy
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
y += dy
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if f&flagThisYIsSame == 0 {
|
||||
y += int16(u16(glyf, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
g.Points[i].Y = fixed.Int26_6(y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return program
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *GlyphBuf) loadCompound(recursion uint32, uhm HMetric, i Index,
|
||||
glyf []byte, useMyMetrics bool) error {
|
||||
|
||||
// Flags for decoding a compound glyph. These flags are documented at
|
||||
// http://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM06/Chap6glyf.html.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
flagArg1And2AreWords = 1 << iota
|
||||
flagArgsAreXYValues
|
||||
flagRoundXYToGrid
|
||||
flagWeHaveAScale
|
||||
flagUnused
|
||||
flagMoreComponents
|
||||
flagWeHaveAnXAndYScale
|
||||
flagWeHaveATwoByTwo
|
||||
flagWeHaveInstructions
|
||||
flagUseMyMetrics
|
||||
flagOverlapCompound
|
||||
)
|
||||
np0, ne0 := len(g.Points), len(g.Ends)
|
||||
offset := loadOffset
|
||||
for {
|
||||
flags := u16(glyf, offset)
|
||||
component := Index(u16(glyf, offset+2))
|
||||
dx, dy, transform, hasTransform := fixed.Int26_6(0), fixed.Int26_6(0), [4]int16{}, false
|
||||
if flags&flagArg1And2AreWords != 0 {
|
||||
dx = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(glyf, offset+4)))
|
||||
dy = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(glyf, offset+6)))
|
||||
offset += 8
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dx = fixed.Int26_6(int16(int8(glyf[offset+4])))
|
||||
dy = fixed.Int26_6(int16(int8(glyf[offset+5])))
|
||||
offset += 6
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&flagArgsAreXYValues == 0 {
|
||||
return UnsupportedError("compound glyph transform vector")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&(flagWeHaveAScale|flagWeHaveAnXAndYScale|flagWeHaveATwoByTwo) != 0 {
|
||||
hasTransform = true
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case flags&flagWeHaveAScale != 0:
|
||||
transform[0] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+0))
|
||||
transform[3] = transform[0]
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
case flags&flagWeHaveAnXAndYScale != 0:
|
||||
transform[0] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+0))
|
||||
transform[3] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+2))
|
||||
offset += 4
|
||||
case flags&flagWeHaveATwoByTwo != 0:
|
||||
transform[0] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+0))
|
||||
transform[1] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+2))
|
||||
transform[2] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+4))
|
||||
transform[3] = int16(u16(glyf, offset+6))
|
||||
offset += 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
savedPP := g.phantomPoints
|
||||
np0 := len(g.Points)
|
||||
componentUMM := useMyMetrics && (flags&flagUseMyMetrics != 0)
|
||||
if err := g.load(recursion+1, component, componentUMM); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flags&flagUseMyMetrics == 0 {
|
||||
g.phantomPoints = savedPP
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasTransform {
|
||||
for j := np0; j < len(g.Points); j++ {
|
||||
p := &g.Points[j]
|
||||
newX := 0 +
|
||||
fixed.Int26_6((int64(p.X)*int64(transform[0])+1<<13)>>14) +
|
||||
fixed.Int26_6((int64(p.Y)*int64(transform[2])+1<<13)>>14)
|
||||
newY := 0 +
|
||||
fixed.Int26_6((int64(p.X)*int64(transform[1])+1<<13)>>14) +
|
||||
fixed.Int26_6((int64(p.Y)*int64(transform[3])+1<<13)>>14)
|
||||
p.X, p.Y = newX, newY
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dx = g.font.scale(g.scale * dx)
|
||||
dy = g.font.scale(g.scale * dy)
|
||||
if flags&flagRoundXYToGrid != 0 {
|
||||
dx = (dx + 32) &^ 63
|
||||
dy = (dy + 32) &^ 63
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j := np0; j < len(g.Points); j++ {
|
||||
p := &g.Points[j]
|
||||
p.X += dx
|
||||
p.Y += dy
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: also adjust g.InFontUnits and g.Unhinted?
|
||||
if flags&flagMoreComponents == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
instrLen := 0
|
||||
if g.hinting != font.HintingNone && offset+2 <= len(glyf) {
|
||||
instrLen = int(u16(glyf, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
g.addPhantomsAndScale(np0, len(g.Points), false, instrLen > 0)
|
||||
points, ends := g.Points[np0:], g.Ends[ne0:]
|
||||
g.Points = g.Points[:len(g.Points)-4]
|
||||
for j := range points {
|
||||
points[j].Flags &^= flagTouchedX | flagTouchedY
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if instrLen == 0 {
|
||||
if !g.metricsSet {
|
||||
copy(g.phantomPoints[:], points[len(points)-4:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Hint the compound glyph.
|
||||
program := glyf[offset : offset+instrLen]
|
||||
// Temporarily adjust the ends to be relative to this compound glyph.
|
||||
if np0 != 0 {
|
||||
for i := range ends {
|
||||
ends[i] -= np0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Hinting instructions of a composite glyph completely refer to the
|
||||
// (already) hinted subglyphs.
|
||||
g.tmp = append(g.tmp[:0], points...)
|
||||
if err := g.hinter.run(program, points, g.tmp, g.tmp, ends); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if np0 != 0 {
|
||||
for i := range ends {
|
||||
ends[i] += np0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !g.metricsSet {
|
||||
copy(g.phantomPoints[:], points[len(points)-4:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (g *GlyphBuf) addPhantomsAndScale(np0, np1 int, simple, adjust bool) {
|
||||
// Add the four phantom points.
|
||||
g.Points = append(g.Points, g.phantomPoints[:]...)
|
||||
// Scale the points.
|
||||
if simple && g.hinting != font.HintingNone {
|
||||
g.InFontUnits = append(g.InFontUnits, g.Points[np1:]...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := np1; i < len(g.Points); i++ {
|
||||
p := &g.Points[i]
|
||||
p.X = g.font.scale(g.scale * p.X)
|
||||
p.Y = g.font.scale(g.scale * p.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if g.hinting == font.HintingNone {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Round the 1st phantom point to the grid, shifting all other points equally.
|
||||
// Note that "all other points" starts from np0, not np1.
|
||||
// TODO: delete this adjustment and the np0/np1 distinction, when
|
||||
// we update the compatibility tests to C Freetype 2.5.3.
|
||||
// See http://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/freetype/freetype2.git/commit/?id=05c786d990390a7ca18e62962641dac740bacb06
|
||||
if adjust {
|
||||
pp1x := g.Points[len(g.Points)-4].X
|
||||
if dx := ((pp1x + 32) &^ 63) - pp1x; dx != 0 {
|
||||
for i := np0; i < len(g.Points); i++ {
|
||||
g.Points[i].X += dx
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if simple {
|
||||
g.Unhinted = append(g.Unhinted, g.Points[np1:]...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Round the 2nd and 4th phantom point to the grid.
|
||||
p := &g.Points[len(g.Points)-3]
|
||||
p.X = (p.X + 32) &^ 63
|
||||
p = &g.Points[len(g.Points)-1]
|
||||
p.Y = (p.Y + 32) &^ 63
|
||||
}
|
||||
1770
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/hint.go
generated
vendored
1770
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/hint.go
generated
vendored
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load diff
289
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/opcodes.go
generated
vendored
289
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/opcodes.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,289 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2012 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package truetype
|
||||
|
||||
// The Truetype opcodes are summarized at
|
||||
// https://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM07/appendixA.html
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
opSVTCA0 = 0x00 // Set freedom and projection Vectors To Coordinate Axis
|
||||
opSVTCA1 = 0x01 // .
|
||||
opSPVTCA0 = 0x02 // Set Projection Vector To Coordinate Axis
|
||||
opSPVTCA1 = 0x03 // .
|
||||
opSFVTCA0 = 0x04 // Set Freedom Vector to Coordinate Axis
|
||||
opSFVTCA1 = 0x05 // .
|
||||
opSPVTL0 = 0x06 // Set Projection Vector To Line
|
||||
opSPVTL1 = 0x07 // .
|
||||
opSFVTL0 = 0x08 // Set Freedom Vector To Line
|
||||
opSFVTL1 = 0x09 // .
|
||||
opSPVFS = 0x0a // Set Projection Vector From Stack
|
||||
opSFVFS = 0x0b // Set Freedom Vector From Stack
|
||||
opGPV = 0x0c // Get Projection Vector
|
||||
opGFV = 0x0d // Get Freedom Vector
|
||||
opSFVTPV = 0x0e // Set Freedom Vector To Projection Vector
|
||||
opISECT = 0x0f // moves point p to the InterSECTion of two lines
|
||||
opSRP0 = 0x10 // Set Reference Point 0
|
||||
opSRP1 = 0x11 // Set Reference Point 1
|
||||
opSRP2 = 0x12 // Set Reference Point 2
|
||||
opSZP0 = 0x13 // Set Zone Pointer 0
|
||||
opSZP1 = 0x14 // Set Zone Pointer 1
|
||||
opSZP2 = 0x15 // Set Zone Pointer 2
|
||||
opSZPS = 0x16 // Set Zone PointerS
|
||||
opSLOOP = 0x17 // Set LOOP variable
|
||||
opRTG = 0x18 // Round To Grid
|
||||
opRTHG = 0x19 // Round To Half Grid
|
||||
opSMD = 0x1a // Set Minimum Distance
|
||||
opELSE = 0x1b // ELSE clause
|
||||
opJMPR = 0x1c // JuMP Relative
|
||||
opSCVTCI = 0x1d // Set Control Value Table Cut-In
|
||||
opSSWCI = 0x1e // Set Single Width Cut-In
|
||||
opSSW = 0x1f // Set Single Width
|
||||
opDUP = 0x20 // DUPlicate top stack element
|
||||
opPOP = 0x21 // POP top stack element
|
||||
opCLEAR = 0x22 // CLEAR the stack
|
||||
opSWAP = 0x23 // SWAP the top two elements on the stack
|
||||
opDEPTH = 0x24 // DEPTH of the stack
|
||||
opCINDEX = 0x25 // Copy the INDEXed element to the top of the stack
|
||||
opMINDEX = 0x26 // Move the INDEXed element to the top of the stack
|
||||
opALIGNPTS = 0x27 // ALIGN PoinTS
|
||||
op_0x28 = 0x28 // deprecated
|
||||
opUTP = 0x29 // UnTouch Point
|
||||
opLOOPCALL = 0x2a // LOOP and CALL function
|
||||
opCALL = 0x2b // CALL function
|
||||
opFDEF = 0x2c // Function DEFinition
|
||||
opENDF = 0x2d // END Function definition
|
||||
opMDAP0 = 0x2e // Move Direct Absolute Point
|
||||
opMDAP1 = 0x2f // .
|
||||
opIUP0 = 0x30 // Interpolate Untouched Points through the outline
|
||||
opIUP1 = 0x31 // .
|
||||
opSHP0 = 0x32 // SHift Point using reference point
|
||||
opSHP1 = 0x33 // .
|
||||
opSHC0 = 0x34 // SHift Contour using reference point
|
||||
opSHC1 = 0x35 // .
|
||||
opSHZ0 = 0x36 // SHift Zone using reference point
|
||||
opSHZ1 = 0x37 // .
|
||||
opSHPIX = 0x38 // SHift point by a PIXel amount
|
||||
opIP = 0x39 // Interpolate Point
|
||||
opMSIRP0 = 0x3a // Move Stack Indirect Relative Point
|
||||
opMSIRP1 = 0x3b // .
|
||||
opALIGNRP = 0x3c // ALIGN to Reference Point
|
||||
opRTDG = 0x3d // Round To Double Grid
|
||||
opMIAP0 = 0x3e // Move Indirect Absolute Point
|
||||
opMIAP1 = 0x3f // .
|
||||
opNPUSHB = 0x40 // PUSH N Bytes
|
||||
opNPUSHW = 0x41 // PUSH N Words
|
||||
opWS = 0x42 // Write Store
|
||||
opRS = 0x43 // Read Store
|
||||
opWCVTP = 0x44 // Write Control Value Table in Pixel units
|
||||
opRCVT = 0x45 // Read Control Value Table entry
|
||||
opGC0 = 0x46 // Get Coordinate projected onto the projection vector
|
||||
opGC1 = 0x47 // .
|
||||
opSCFS = 0x48 // Sets Coordinate From the Stack using projection vector and freedom vector
|
||||
opMD0 = 0x49 // Measure Distance
|
||||
opMD1 = 0x4a // .
|
||||
opMPPEM = 0x4b // Measure Pixels Per EM
|
||||
opMPS = 0x4c // Measure Point Size
|
||||
opFLIPON = 0x4d // set the auto FLIP Boolean to ON
|
||||
opFLIPOFF = 0x4e // set the auto FLIP Boolean to OFF
|
||||
opDEBUG = 0x4f // DEBUG call
|
||||
opLT = 0x50 // Less Than
|
||||
opLTEQ = 0x51 // Less Than or EQual
|
||||
opGT = 0x52 // Greater Than
|
||||
opGTEQ = 0x53 // Greater Than or EQual
|
||||
opEQ = 0x54 // EQual
|
||||
opNEQ = 0x55 // Not EQual
|
||||
opODD = 0x56 // ODD
|
||||
opEVEN = 0x57 // EVEN
|
||||
opIF = 0x58 // IF test
|
||||
opEIF = 0x59 // End IF
|
||||
opAND = 0x5a // logical AND
|
||||
opOR = 0x5b // logical OR
|
||||
opNOT = 0x5c // logical NOT
|
||||
opDELTAP1 = 0x5d // DELTA exception P1
|
||||
opSDB = 0x5e // Set Delta Base in the graphics state
|
||||
opSDS = 0x5f // Set Delta Shift in the graphics state
|
||||
opADD = 0x60 // ADD
|
||||
opSUB = 0x61 // SUBtract
|
||||
opDIV = 0x62 // DIVide
|
||||
opMUL = 0x63 // MULtiply
|
||||
opABS = 0x64 // ABSolute value
|
||||
opNEG = 0x65 // NEGate
|
||||
opFLOOR = 0x66 // FLOOR
|
||||
opCEILING = 0x67 // CEILING
|
||||
opROUND00 = 0x68 // ROUND value
|
||||
opROUND01 = 0x69 // .
|
||||
opROUND10 = 0x6a // .
|
||||
opROUND11 = 0x6b // .
|
||||
opNROUND00 = 0x6c // No ROUNDing of value
|
||||
opNROUND01 = 0x6d // .
|
||||
opNROUND10 = 0x6e // .
|
||||
opNROUND11 = 0x6f // .
|
||||
opWCVTF = 0x70 // Write Control Value Table in Funits
|
||||
opDELTAP2 = 0x71 // DELTA exception P2
|
||||
opDELTAP3 = 0x72 // DELTA exception P3
|
||||
opDELTAC1 = 0x73 // DELTA exception C1
|
||||
opDELTAC2 = 0x74 // DELTA exception C2
|
||||
opDELTAC3 = 0x75 // DELTA exception C3
|
||||
opSROUND = 0x76 // Super ROUND
|
||||
opS45ROUND = 0x77 // Super ROUND 45 degrees
|
||||
opJROT = 0x78 // Jump Relative On True
|
||||
opJROF = 0x79 // Jump Relative On False
|
||||
opROFF = 0x7a // Round OFF
|
||||
op_0x7b = 0x7b // deprecated
|
||||
opRUTG = 0x7c // Round Up To Grid
|
||||
opRDTG = 0x7d // Round Down To Grid
|
||||
opSANGW = 0x7e // Set ANGle Weight
|
||||
opAA = 0x7f // Adjust Angle
|
||||
opFLIPPT = 0x80 // FLIP PoinT
|
||||
opFLIPRGON = 0x81 // FLIP RanGe ON
|
||||
opFLIPRGOFF = 0x82 // FLIP RanGe OFF
|
||||
op_0x83 = 0x83 // deprecated
|
||||
op_0x84 = 0x84 // deprecated
|
||||
opSCANCTRL = 0x85 // SCAN conversion ConTRoL
|
||||
opSDPVTL0 = 0x86 // Set Dual Projection Vector To Line
|
||||
opSDPVTL1 = 0x87 // .
|
||||
opGETINFO = 0x88 // GET INFOrmation
|
||||
opIDEF = 0x89 // Instruction DEFinition
|
||||
opROLL = 0x8a // ROLL the top three stack elements
|
||||
opMAX = 0x8b // MAXimum of top two stack elements
|
||||
opMIN = 0x8c // MINimum of top two stack elements
|
||||
opSCANTYPE = 0x8d // SCANTYPE
|
||||
opINSTCTRL = 0x8e // INSTRuction execution ConTRoL
|
||||
op_0x8f = 0x8f
|
||||
op_0x90 = 0x90
|
||||
op_0x91 = 0x91
|
||||
op_0x92 = 0x92
|
||||
op_0x93 = 0x93
|
||||
op_0x94 = 0x94
|
||||
op_0x95 = 0x95
|
||||
op_0x96 = 0x96
|
||||
op_0x97 = 0x97
|
||||
op_0x98 = 0x98
|
||||
op_0x99 = 0x99
|
||||
op_0x9a = 0x9a
|
||||
op_0x9b = 0x9b
|
||||
op_0x9c = 0x9c
|
||||
op_0x9d = 0x9d
|
||||
op_0x9e = 0x9e
|
||||
op_0x9f = 0x9f
|
||||
op_0xa0 = 0xa0
|
||||
op_0xa1 = 0xa1
|
||||
op_0xa2 = 0xa2
|
||||
op_0xa3 = 0xa3
|
||||
op_0xa4 = 0xa4
|
||||
op_0xa5 = 0xa5
|
||||
op_0xa6 = 0xa6
|
||||
op_0xa7 = 0xa7
|
||||
op_0xa8 = 0xa8
|
||||
op_0xa9 = 0xa9
|
||||
op_0xaa = 0xaa
|
||||
op_0xab = 0xab
|
||||
op_0xac = 0xac
|
||||
op_0xad = 0xad
|
||||
op_0xae = 0xae
|
||||
op_0xaf = 0xaf
|
||||
opPUSHB000 = 0xb0 // PUSH Bytes
|
||||
opPUSHB001 = 0xb1 // .
|
||||
opPUSHB010 = 0xb2 // .
|
||||
opPUSHB011 = 0xb3 // .
|
||||
opPUSHB100 = 0xb4 // .
|
||||
opPUSHB101 = 0xb5 // .
|
||||
opPUSHB110 = 0xb6 // .
|
||||
opPUSHB111 = 0xb7 // .
|
||||
opPUSHW000 = 0xb8 // PUSH Words
|
||||
opPUSHW001 = 0xb9 // .
|
||||
opPUSHW010 = 0xba // .
|
||||
opPUSHW011 = 0xbb // .
|
||||
opPUSHW100 = 0xbc // .
|
||||
opPUSHW101 = 0xbd // .
|
||||
opPUSHW110 = 0xbe // .
|
||||
opPUSHW111 = 0xbf // .
|
||||
opMDRP00000 = 0xc0 // Move Direct Relative Point
|
||||
opMDRP00001 = 0xc1 // .
|
||||
opMDRP00010 = 0xc2 // .
|
||||
opMDRP00011 = 0xc3 // .
|
||||
opMDRP00100 = 0xc4 // .
|
||||
opMDRP00101 = 0xc5 // .
|
||||
opMDRP00110 = 0xc6 // .
|
||||
opMDRP00111 = 0xc7 // .
|
||||
opMDRP01000 = 0xc8 // .
|
||||
opMDRP01001 = 0xc9 // .
|
||||
opMDRP01010 = 0xca // .
|
||||
opMDRP01011 = 0xcb // .
|
||||
opMDRP01100 = 0xcc // .
|
||||
opMDRP01101 = 0xcd // .
|
||||
opMDRP01110 = 0xce // .
|
||||
opMDRP01111 = 0xcf // .
|
||||
opMDRP10000 = 0xd0 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10001 = 0xd1 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10010 = 0xd2 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10011 = 0xd3 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10100 = 0xd4 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10101 = 0xd5 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10110 = 0xd6 // .
|
||||
opMDRP10111 = 0xd7 // .
|
||||
opMDRP11000 = 0xd8 // .
|
||||
opMDRP11001 = 0xd9 // .
|
||||
opMDRP11010 = 0xda // .
|
||||
opMDRP11011 = 0xdb // .
|
||||
opMDRP11100 = 0xdc // .
|
||||
opMDRP11101 = 0xdd // .
|
||||
opMDRP11110 = 0xde // .
|
||||
opMDRP11111 = 0xdf // .
|
||||
opMIRP00000 = 0xe0 // Move Indirect Relative Point
|
||||
opMIRP00001 = 0xe1 // .
|
||||
opMIRP00010 = 0xe2 // .
|
||||
opMIRP00011 = 0xe3 // .
|
||||
opMIRP00100 = 0xe4 // .
|
||||
opMIRP00101 = 0xe5 // .
|
||||
opMIRP00110 = 0xe6 // .
|
||||
opMIRP00111 = 0xe7 // .
|
||||
opMIRP01000 = 0xe8 // .
|
||||
opMIRP01001 = 0xe9 // .
|
||||
opMIRP01010 = 0xea // .
|
||||
opMIRP01011 = 0xeb // .
|
||||
opMIRP01100 = 0xec // .
|
||||
opMIRP01101 = 0xed // .
|
||||
opMIRP01110 = 0xee // .
|
||||
opMIRP01111 = 0xef // .
|
||||
opMIRP10000 = 0xf0 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10001 = 0xf1 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10010 = 0xf2 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10011 = 0xf3 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10100 = 0xf4 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10101 = 0xf5 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10110 = 0xf6 // .
|
||||
opMIRP10111 = 0xf7 // .
|
||||
opMIRP11000 = 0xf8 // .
|
||||
opMIRP11001 = 0xf9 // .
|
||||
opMIRP11010 = 0xfa // .
|
||||
opMIRP11011 = 0xfb // .
|
||||
opMIRP11100 = 0xfc // .
|
||||
opMIRP11101 = 0xfd // .
|
||||
opMIRP11110 = 0xfe // .
|
||||
opMIRP11111 = 0xff // .
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// popCount is the number of stack elements that each opcode pops.
|
||||
var popCount = [256]uint8{
|
||||
// 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, a, b, c, d, e, f
|
||||
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 5, // 0x00 - 0x0f
|
||||
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, // 0x10 - 0x1f
|
||||
1, 1, 0, 2, 0, 1, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, // 0x20 - 0x2f
|
||||
0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 2, 2, // 0x30 - 0x3f
|
||||
0, 0, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, // 0x40 - 0x4f
|
||||
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, // 0x50 - 0x5f
|
||||
2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, // 0x60 - 0x6f
|
||||
2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, // 0x70 - 0x7f
|
||||
0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2, 2, 1, 2, 0, // 0x80 - 0x8f
|
||||
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, // 0x90 - 0x9f
|
||||
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, // 0xa0 - 0xaf
|
||||
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, // 0xb0 - 0xbf
|
||||
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, // 0xc0 - 0xcf
|
||||
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, // 0xd0 - 0xdf
|
||||
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, // 0xe0 - 0xef
|
||||
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, // 0xf0 - 0xff
|
||||
}
|
||||
653
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/truetype.go
generated
vendored
653
vendor/github.com/golang/freetype/truetype/truetype.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,653 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2010 The Freetype-Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by your choice of either the
|
||||
// FreeType License or the GNU General Public License version 2 (or
|
||||
// any later version), both of which can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package truetype provides a parser for the TTF and TTC file formats.
|
||||
// Those formats are documented at http://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/
|
||||
// and http://www.microsoft.com/typography/otspec/
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Some of a font's methods provide lengths or co-ordinates, e.g. bounds, font
|
||||
// metrics and control points. All these methods take a scale parameter, which
|
||||
// is the number of pixels in 1 em, expressed as a 26.6 fixed point value. For
|
||||
// example, if 1 em is 10 pixels then scale is fixed.I(10), which is equal to
|
||||
// fixed.Int26_6(10 << 6).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To measure a TrueType font in ideal FUnit space, use scale equal to
|
||||
// font.FUnitsPerEm().
|
||||
package truetype // import "github.com/golang/freetype/truetype"
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// An Index is a Font's index of a rune.
|
||||
type Index uint16
|
||||
|
||||
// A NameID identifies a name table entry.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://developer.apple.com/fonts/TrueType-Reference-Manual/RM06/Chap6name.html
|
||||
type NameID uint16
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NameIDCopyright NameID = 0
|
||||
NameIDFontFamily = 1
|
||||
NameIDFontSubfamily = 2
|
||||
NameIDUniqueSubfamilyID = 3
|
||||
NameIDFontFullName = 4
|
||||
NameIDNameTableVersion = 5
|
||||
NameIDPostscriptName = 6
|
||||
NameIDTrademarkNotice = 7
|
||||
NameIDManufacturerName = 8
|
||||
NameIDDesignerName = 9
|
||||
NameIDFontDescription = 10
|
||||
NameIDFontVendorURL = 11
|
||||
NameIDFontDesignerURL = 12
|
||||
NameIDFontLicense = 13
|
||||
NameIDFontLicenseURL = 14
|
||||
NameIDPreferredFamily = 16
|
||||
NameIDPreferredSubfamily = 17
|
||||
NameIDCompatibleName = 18
|
||||
NameIDSampleText = 19
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// A 32-bit encoding consists of a most-significant 16-bit Platform ID and a
|
||||
// least-significant 16-bit Platform Specific ID. The magic numbers are
|
||||
// specified at https://www.microsoft.com/typography/otspec/name.htm
|
||||
unicodeEncodingBMPOnly = 0x00000003 // PID = 0 (Unicode), PSID = 3 (Unicode 2.0 BMP Only)
|
||||
unicodeEncodingFull = 0x00000004 // PID = 0 (Unicode), PSID = 4 (Unicode 2.0 Full Repertoire)
|
||||
microsoftSymbolEncoding = 0x00030000 // PID = 3 (Microsoft), PSID = 0 (Symbol)
|
||||
microsoftUCS2Encoding = 0x00030001 // PID = 3 (Microsoft), PSID = 1 (UCS-2)
|
||||
microsoftUCS4Encoding = 0x0003000a // PID = 3 (Microsoft), PSID = 10 (UCS-4)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// An HMetric holds the horizontal metrics of a single glyph.
|
||||
type HMetric struct {
|
||||
AdvanceWidth, LeftSideBearing fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A VMetric holds the vertical metrics of a single glyph.
|
||||
type VMetric struct {
|
||||
AdvanceHeight, TopSideBearing fixed.Int26_6
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A FormatError reports that the input is not a valid TrueType font.
|
||||
type FormatError string
|
||||
|
||||
func (e FormatError) Error() string {
|
||||
return "freetype: invalid TrueType format: " + string(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An UnsupportedError reports that the input uses a valid but unimplemented
|
||||
// TrueType feature.
|
||||
type UnsupportedError string
|
||||
|
||||
func (e UnsupportedError) Error() string {
|
||||
return "freetype: unsupported TrueType feature: " + string(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// u32 returns the big-endian uint32 at b[i:].
|
||||
func u32(b []byte, i int) uint32 {
|
||||
return uint32(b[i])<<24 | uint32(b[i+1])<<16 | uint32(b[i+2])<<8 | uint32(b[i+3])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// u16 returns the big-endian uint16 at b[i:].
|
||||
func u16(b []byte, i int) uint16 {
|
||||
return uint16(b[i])<<8 | uint16(b[i+1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// readTable returns a slice of the TTF data given by a table's directory entry.
|
||||
func readTable(ttf []byte, offsetLength []byte) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
offset := int(u32(offsetLength, 0))
|
||||
if offset < 0 {
|
||||
return nil, FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("offset too large: %d", uint32(offset)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
length := int(u32(offsetLength, 4))
|
||||
if length < 0 {
|
||||
return nil, FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("length too large: %d", uint32(length)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
end := offset + length
|
||||
if end < 0 || end > len(ttf) {
|
||||
return nil, FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("offset + length too large: %d", uint32(offset)+uint32(length)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ttf[offset:end], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseSubtables returns the offset and platformID of the best subtable in
|
||||
// table, where best favors a Unicode cmap encoding, and failing that, a
|
||||
// Microsoft cmap encoding. offset is the offset of the first subtable in
|
||||
// table, and size is the size of each subtable.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If pred is non-nil, then only subtables that satisfy that predicate will be
|
||||
// considered.
|
||||
func parseSubtables(table []byte, name string, offset, size int, pred func([]byte) bool) (
|
||||
bestOffset int, bestPID uint32, retErr error) {
|
||||
|
||||
if len(table) < 4 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, FormatError(name + " too short")
|
||||
}
|
||||
nSubtables := int(u16(table, 2))
|
||||
if len(table) < size*nSubtables+offset {
|
||||
return 0, 0, FormatError(name + " too short")
|
||||
}
|
||||
ok := false
|
||||
for i := 0; i < nSubtables; i, offset = i+1, offset+size {
|
||||
if pred != nil && !pred(table[offset:]) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We read the 16-bit Platform ID and 16-bit Platform Specific ID as a single uint32.
|
||||
// All values are big-endian.
|
||||
pidPsid := u32(table, offset)
|
||||
// We prefer the Unicode cmap encoding. Failing to find that, we fall
|
||||
// back onto the Microsoft cmap encoding.
|
||||
if pidPsid == unicodeEncodingBMPOnly || pidPsid == unicodeEncodingFull {
|
||||
bestOffset, bestPID, ok = offset, pidPsid>>16, true
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
} else if pidPsid == microsoftSymbolEncoding ||
|
||||
pidPsid == microsoftUCS2Encoding ||
|
||||
pidPsid == microsoftUCS4Encoding {
|
||||
|
||||
bestOffset, bestPID, ok = offset, pidPsid>>16, true
|
||||
// We don't break out of the for loop, so that Unicode can override Microsoft.
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return 0, 0, UnsupportedError(name + " encoding")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bestOffset, bestPID, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
locaOffsetFormatUnknown int = iota
|
||||
locaOffsetFormatShort
|
||||
locaOffsetFormatLong
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A cm holds a parsed cmap entry.
|
||||
type cm struct {
|
||||
start, end, delta, offset uint32
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Font represents a Truetype font.
|
||||
type Font struct {
|
||||
// Tables sliced from the TTF data. The different tables are documented
|
||||
// at http://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM06/Chap6.html
|
||||
cmap, cvt, fpgm, glyf, hdmx, head, hhea, hmtx, kern, loca, maxp, name, os2, prep, vmtx []byte
|
||||
|
||||
cmapIndexes []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// Cached values derived from the raw ttf data.
|
||||
cm []cm
|
||||
locaOffsetFormat int
|
||||
nGlyph, nHMetric, nKern int
|
||||
fUnitsPerEm int32
|
||||
ascent int32 // In FUnits.
|
||||
descent int32 // In FUnits; typically negative.
|
||||
bounds fixed.Rectangle26_6 // In FUnits.
|
||||
// Values from the maxp section.
|
||||
maxTwilightPoints, maxStorage, maxFunctionDefs, maxStackElements uint16
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *Font) parseCmap() error {
|
||||
const (
|
||||
cmapFormat4 = 4
|
||||
cmapFormat12 = 12
|
||||
languageIndependent = 0
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
offset, _, err := parseSubtables(f.cmap, "cmap", 4, 8, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset = int(u32(f.cmap, offset+4))
|
||||
if offset <= 0 || offset > len(f.cmap) {
|
||||
return FormatError("bad cmap offset")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cmapFormat := u16(f.cmap, offset)
|
||||
switch cmapFormat {
|
||||
case cmapFormat4:
|
||||
language := u16(f.cmap, offset+4)
|
||||
if language != languageIndependent {
|
||||
return UnsupportedError(fmt.Sprintf("language: %d", language))
|
||||
}
|
||||
segCountX2 := int(u16(f.cmap, offset+6))
|
||||
if segCountX2%2 == 1 {
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("bad segCountX2: %d", segCountX2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
segCount := segCountX2 / 2
|
||||
offset += 14
|
||||
f.cm = make([]cm, segCount)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < segCount; i++ {
|
||||
f.cm[i].end = uint32(u16(f.cmap, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
for i := 0; i < segCount; i++ {
|
||||
f.cm[i].start = uint32(u16(f.cmap, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < segCount; i++ {
|
||||
f.cm[i].delta = uint32(u16(f.cmap, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < segCount; i++ {
|
||||
f.cm[i].offset = uint32(u16(f.cmap, offset))
|
||||
offset += 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.cmapIndexes = f.cmap[offset:]
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
|
||||
case cmapFormat12:
|
||||
if u16(f.cmap, offset+2) != 0 {
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("cmap format: % x", f.cmap[offset:offset+4]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
length := u32(f.cmap, offset+4)
|
||||
language := u32(f.cmap, offset+8)
|
||||
if language != languageIndependent {
|
||||
return UnsupportedError(fmt.Sprintf("language: %d", language))
|
||||
}
|
||||
nGroups := u32(f.cmap, offset+12)
|
||||
if length != 12*nGroups+16 {
|
||||
return FormatError("inconsistent cmap length")
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset += 16
|
||||
f.cm = make([]cm, nGroups)
|
||||
for i := uint32(0); i < nGroups; i++ {
|
||||
f.cm[i].start = u32(f.cmap, offset+0)
|
||||
f.cm[i].end = u32(f.cmap, offset+4)
|
||||
f.cm[i].delta = u32(f.cmap, offset+8) - f.cm[i].start
|
||||
offset += 12
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return UnsupportedError(fmt.Sprintf("cmap format: %d", cmapFormat))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *Font) parseHead() error {
|
||||
if len(f.head) != 54 {
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("bad head length: %d", len(f.head)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.fUnitsPerEm = int32(u16(f.head, 18))
|
||||
f.bounds.Min.X = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.head, 36)))
|
||||
f.bounds.Min.Y = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.head, 38)))
|
||||
f.bounds.Max.X = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.head, 40)))
|
||||
f.bounds.Max.Y = fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.head, 42)))
|
||||
switch i := u16(f.head, 50); i {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
f.locaOffsetFormat = locaOffsetFormatShort
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
f.locaOffsetFormat = locaOffsetFormatLong
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("bad indexToLocFormat: %d", i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *Font) parseHhea() error {
|
||||
if len(f.hhea) != 36 {
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("bad hhea length: %d", len(f.hhea)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.ascent = int32(int16(u16(f.hhea, 4)))
|
||||
f.descent = int32(int16(u16(f.hhea, 6)))
|
||||
f.nHMetric = int(u16(f.hhea, 34))
|
||||
if 4*f.nHMetric+2*(f.nGlyph-f.nHMetric) != len(f.hmtx) {
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("bad hmtx length: %d", len(f.hmtx)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *Font) parseKern() error {
|
||||
// Apple's TrueType documentation (http://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM06/Chap6kern.html) says:
|
||||
// "Previous versions of the 'kern' table defined both the version and nTables fields in the header
|
||||
// as UInt16 values and not UInt32 values. Use of the older format on the Mac OS is discouraged
|
||||
// (although AAT can sense an old kerning table and still make correct use of it). Microsoft
|
||||
// Windows still uses the older format for the 'kern' table and will not recognize the newer one.
|
||||
// Fonts targeted for the Mac OS only should use the new format; fonts targeted for both the Mac OS
|
||||
// and Windows should use the old format."
|
||||
// Since we expect that almost all fonts aim to be Windows-compatible, we only parse the "older" format,
|
||||
// just like the C Freetype implementation.
|
||||
if len(f.kern) == 0 {
|
||||
if f.nKern != 0 {
|
||||
return FormatError("bad kern table length")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(f.kern) < 18 {
|
||||
return FormatError("kern data too short")
|
||||
}
|
||||
version, offset := u16(f.kern, 0), 2
|
||||
if version != 0 {
|
||||
return UnsupportedError(fmt.Sprintf("kern version: %d", version))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n, offset := u16(f.kern, offset), offset+2
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return UnsupportedError("kern nTables: 0")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: support multiple subtables. In practice, almost all .ttf files
|
||||
// have only one subtable, if they have a kern table at all. But it's not
|
||||
// impossible. Xolonium Regular (https://fontlibrary.org/en/font/xolonium)
|
||||
// has 3 subtables. Those subtables appear to be disjoint, rather than
|
||||
// being the same kerning pairs encoded in three different ways.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For now, we'll use only the first subtable.
|
||||
|
||||
offset += 2 // Skip the version.
|
||||
length, offset := int(u16(f.kern, offset)), offset+2
|
||||
coverage, offset := u16(f.kern, offset), offset+2
|
||||
if coverage != 0x0001 {
|
||||
// We only support horizontal kerning.
|
||||
return UnsupportedError(fmt.Sprintf("kern coverage: 0x%04x", coverage))
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.nKern, offset = int(u16(f.kern, offset)), offset+2
|
||||
if 6*f.nKern != length-14 {
|
||||
return FormatError("bad kern table length")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *Font) parseMaxp() error {
|
||||
if len(f.maxp) != 32 {
|
||||
return FormatError(fmt.Sprintf("bad maxp length: %d", len(f.maxp)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.nGlyph = int(u16(f.maxp, 4))
|
||||
f.maxTwilightPoints = u16(f.maxp, 16)
|
||||
f.maxStorage = u16(f.maxp, 18)
|
||||
f.maxFunctionDefs = u16(f.maxp, 20)
|
||||
f.maxStackElements = u16(f.maxp, 24)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// scale returns x divided by f.fUnitsPerEm, rounded to the nearest integer.
|
||||
func (f *Font) scale(x fixed.Int26_6) fixed.Int26_6 {
|
||||
if x >= 0 {
|
||||
x += fixed.Int26_6(f.fUnitsPerEm) / 2
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
x -= fixed.Int26_6(f.fUnitsPerEm) / 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
return x / fixed.Int26_6(f.fUnitsPerEm)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bounds returns the union of a Font's glyphs' bounds.
|
||||
func (f *Font) Bounds(scale fixed.Int26_6) fixed.Rectangle26_6 {
|
||||
b := f.bounds
|
||||
b.Min.X = f.scale(scale * b.Min.X)
|
||||
b.Min.Y = f.scale(scale * b.Min.Y)
|
||||
b.Max.X = f.scale(scale * b.Max.X)
|
||||
b.Max.Y = f.scale(scale * b.Max.Y)
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FUnitsPerEm returns the number of FUnits in a Font's em-square's side.
|
||||
func (f *Font) FUnitsPerEm() int32 {
|
||||
return f.fUnitsPerEm
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Index returns a Font's index for the given rune.
|
||||
func (f *Font) Index(x rune) Index {
|
||||
c := uint32(x)
|
||||
for i, j := 0, len(f.cm); i < j; {
|
||||
h := i + (j-i)/2
|
||||
cm := &f.cm[h]
|
||||
if c < cm.start {
|
||||
j = h
|
||||
} else if cm.end < c {
|
||||
i = h + 1
|
||||
} else if cm.offset == 0 {
|
||||
return Index(c + cm.delta)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
offset := int(cm.offset) + 2*(h-len(f.cm)+int(c-cm.start))
|
||||
return Index(u16(f.cmapIndexes, offset))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Name returns the Font's name value for the given NameID. It returns "" if
|
||||
// there was an error, or if that name was not found.
|
||||
func (f *Font) Name(id NameID) string {
|
||||
x, platformID, err := parseSubtables(f.name, "name", 6, 12, func(b []byte) bool {
|
||||
return NameID(u16(b, 6)) == id
|
||||
})
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
offset, length := u16(f.name, 4)+u16(f.name, x+10), u16(f.name, x+8)
|
||||
// Return the ASCII value of the encoded string.
|
||||
// The string is encoded as UTF-16 on non-Apple platformIDs; Apple is platformID 1.
|
||||
src := f.name[offset : offset+length]
|
||||
var dst []byte
|
||||
if platformID != 1 { // UTF-16.
|
||||
if len(src)&1 != 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst = make([]byte, len(src)/2)
|
||||
for i := range dst {
|
||||
dst[i] = printable(u16(src, 2*i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // ASCII.
|
||||
dst = make([]byte, len(src))
|
||||
for i, c := range src {
|
||||
dst[i] = printable(uint16(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return string(dst)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func printable(r uint16) byte {
|
||||
if 0x20 <= r && r < 0x7f {
|
||||
return byte(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return '?'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unscaledHMetric returns the unscaled horizontal metrics for the glyph with
|
||||
// the given index.
|
||||
func (f *Font) unscaledHMetric(i Index) (h HMetric) {
|
||||
j := int(i)
|
||||
if j < 0 || f.nGlyph <= j {
|
||||
return HMetric{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j >= f.nHMetric {
|
||||
p := 4 * (f.nHMetric - 1)
|
||||
return HMetric{
|
||||
AdvanceWidth: fixed.Int26_6(u16(f.hmtx, p)),
|
||||
LeftSideBearing: fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.hmtx, p+2*(j-f.nHMetric)+4))),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return HMetric{
|
||||
AdvanceWidth: fixed.Int26_6(u16(f.hmtx, 4*j)),
|
||||
LeftSideBearing: fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.hmtx, 4*j+2))),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HMetric returns the horizontal metrics for the glyph with the given index.
|
||||
func (f *Font) HMetric(scale fixed.Int26_6, i Index) HMetric {
|
||||
h := f.unscaledHMetric(i)
|
||||
h.AdvanceWidth = f.scale(scale * h.AdvanceWidth)
|
||||
h.LeftSideBearing = f.scale(scale * h.LeftSideBearing)
|
||||
return h
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unscaledVMetric returns the unscaled vertical metrics for the glyph with
|
||||
// the given index. yMax is the top of the glyph's bounding box.
|
||||
func (f *Font) unscaledVMetric(i Index, yMax fixed.Int26_6) (v VMetric) {
|
||||
j := int(i)
|
||||
if j < 0 || f.nGlyph <= j {
|
||||
return VMetric{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if 4*j+4 <= len(f.vmtx) {
|
||||
return VMetric{
|
||||
AdvanceHeight: fixed.Int26_6(u16(f.vmtx, 4*j)),
|
||||
TopSideBearing: fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.vmtx, 4*j+2))),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The OS/2 table has grown over time.
|
||||
// https://developer.apple.com/fonts/TTRefMan/RM06/Chap6OS2.html
|
||||
// says that it was originally 68 bytes. Optional fields, including
|
||||
// the ascender and descender, are described at
|
||||
// http://www.microsoft.com/typography/otspec/os2.htm
|
||||
if len(f.os2) >= 72 {
|
||||
sTypoAscender := fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.os2, 68)))
|
||||
sTypoDescender := fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.os2, 70)))
|
||||
return VMetric{
|
||||
AdvanceHeight: sTypoAscender - sTypoDescender,
|
||||
TopSideBearing: sTypoAscender - yMax,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return VMetric{
|
||||
AdvanceHeight: fixed.Int26_6(f.fUnitsPerEm),
|
||||
TopSideBearing: 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VMetric returns the vertical metrics for the glyph with the given index.
|
||||
func (f *Font) VMetric(scale fixed.Int26_6, i Index) VMetric {
|
||||
// TODO: should 0 be bounds.YMax?
|
||||
v := f.unscaledVMetric(i, 0)
|
||||
v.AdvanceHeight = f.scale(scale * v.AdvanceHeight)
|
||||
v.TopSideBearing = f.scale(scale * v.TopSideBearing)
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Kern returns the horizontal adjustment for the given glyph pair. A positive
|
||||
// kern means to move the glyphs further apart.
|
||||
func (f *Font) Kern(scale fixed.Int26_6, i0, i1 Index) fixed.Int26_6 {
|
||||
if f.nKern == 0 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
g := uint32(i0)<<16 | uint32(i1)
|
||||
lo, hi := 0, f.nKern
|
||||
for lo < hi {
|
||||
i := (lo + hi) / 2
|
||||
ig := u32(f.kern, 18+6*i)
|
||||
if ig < g {
|
||||
lo = i + 1
|
||||
} else if ig > g {
|
||||
hi = i
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return f.scale(scale * fixed.Int26_6(int16(u16(f.kern, 22+6*i))))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse returns a new Font for the given TTF or TTC data.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For TrueType Collections, the first font in the collection is parsed.
|
||||
func Parse(ttf []byte) (font *Font, err error) {
|
||||
return parse(ttf, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parse(ttf []byte, offset int) (font *Font, err error) {
|
||||
if len(ttf)-offset < 12 {
|
||||
err = FormatError("TTF data is too short")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
originalOffset := offset
|
||||
magic, offset := u32(ttf, offset), offset+4
|
||||
switch magic {
|
||||
case 0x00010000:
|
||||
// No-op.
|
||||
case 0x74746366: // "ttcf" as a big-endian uint32.
|
||||
if originalOffset != 0 {
|
||||
err = FormatError("recursive TTC")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
ttcVersion, offset := u32(ttf, offset), offset+4
|
||||
if ttcVersion != 0x00010000 && ttcVersion != 0x00020000 {
|
||||
err = FormatError("bad TTC version")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
numFonts, offset := int(u32(ttf, offset)), offset+4
|
||||
if numFonts <= 0 {
|
||||
err = FormatError("bad number of TTC fonts")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(ttf[offset:])/4 < numFonts {
|
||||
err = FormatError("TTC offset table is too short")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: provide an API to select which font in a TrueType collection to return,
|
||||
// not just the first one. This may require an API to parse a TTC's name tables,
|
||||
// so users of this package can select the font in a TTC by name.
|
||||
offset = int(u32(ttf, offset))
|
||||
if offset <= 0 || offset > len(ttf) {
|
||||
err = FormatError("bad TTC offset")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parse(ttf, offset)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
err = FormatError("bad TTF version")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, offset := int(u16(ttf, offset)), offset+2
|
||||
offset += 6 // Skip the searchRange, entrySelector and rangeShift.
|
||||
if len(ttf) < 16*n+offset {
|
||||
err = FormatError("TTF data is too short")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
f := new(Font)
|
||||
// Assign the table slices.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
x := 16*i + offset
|
||||
switch string(ttf[x : x+4]) {
|
||||
case "cmap":
|
||||
f.cmap, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "cvt ":
|
||||
f.cvt, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "fpgm":
|
||||
f.fpgm, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "glyf":
|
||||
f.glyf, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "hdmx":
|
||||
f.hdmx, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "head":
|
||||
f.head, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "hhea":
|
||||
f.hhea, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "hmtx":
|
||||
f.hmtx, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "kern":
|
||||
f.kern, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "loca":
|
||||
f.loca, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "maxp":
|
||||
f.maxp, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "name":
|
||||
f.name, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "OS/2":
|
||||
f.os2, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "prep":
|
||||
f.prep, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
case "vmtx":
|
||||
f.vmtx, err = readTable(ttf, ttf[x+8:x+16])
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Parse and sanity-check the TTF data.
|
||||
if err = f.parseHead(); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err = f.parseMaxp(); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err = f.parseCmap(); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err = f.parseKern(); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err = f.parseHhea(); err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
font = f
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
202
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/LICENSE
generated
vendored
202
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/LICENSE
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,202 +0,0 @@
|
|||
|
||||
Apache License
|
||||
Version 2.0, January 2004
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/
|
||||
|
||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
|
||||
|
||||
1. Definitions.
|
||||
|
||||
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
|
||||
and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
|
||||
the copyright owner that is granting the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
|
||||
other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
|
||||
control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
|
||||
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
|
||||
direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
|
||||
otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
|
||||
outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
|
||||
|
||||
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
exercising permissions granted by this License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
|
||||
including but not limited to software source code, documentation
|
||||
source, and configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
|
||||
transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
|
||||
not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
|
||||
and conversions to other media types.
|
||||
|
||||
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
|
||||
Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
|
||||
copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
|
||||
(an example is provided in the Appendix below).
|
||||
|
||||
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
|
||||
form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
|
||||
editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
|
||||
represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
|
||||
of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
|
||||
separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
|
||||
the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
|
||||
|
||||
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
|
||||
the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
|
||||
to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
|
||||
submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
|
||||
or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
|
||||
the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
|
||||
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
|
||||
to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
|
||||
communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
|
||||
and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
|
||||
Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
|
||||
excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
|
||||
designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
|
||||
|
||||
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
|
||||
subsequently incorporated within the Work.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
|
||||
publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
|
||||
Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
|
||||
use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
|
||||
where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
|
||||
by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
|
||||
Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
|
||||
with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
|
||||
institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
|
||||
cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
|
||||
or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
|
||||
or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
|
||||
granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
|
||||
as of the date such litigation is filed.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
|
||||
Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
|
||||
modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
|
||||
meet the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
|
||||
Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
|
||||
|
||||
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
|
||||
stating that You changed the files; and
|
||||
|
||||
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
|
||||
that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
|
||||
attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
|
||||
excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
|
||||
the Derivative Works; and
|
||||
|
||||
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
|
||||
distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
|
||||
include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
|
||||
within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
|
||||
pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
|
||||
of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
|
||||
as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
|
||||
documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
|
||||
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
|
||||
wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
|
||||
of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
|
||||
do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
|
||||
notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
|
||||
or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
|
||||
that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
|
||||
as modifying the License.
|
||||
|
||||
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
|
||||
may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
|
||||
for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
|
||||
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
|
||||
reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
|
||||
the conditions stated in this License.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
|
||||
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
|
||||
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
|
||||
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
|
||||
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
|
||||
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
|
||||
names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
|
||||
except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
|
||||
origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
|
||||
agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
|
||||
Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
|
||||
implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
|
||||
of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
|
||||
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
|
||||
appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
|
||||
risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
|
||||
whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
|
||||
unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
|
||||
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
|
||||
liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
|
||||
incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
|
||||
result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
|
||||
Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
|
||||
work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
|
||||
other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
|
||||
has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
|
||||
the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
|
||||
and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
|
||||
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
|
||||
License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
|
||||
on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
|
||||
of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
|
||||
defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
|
||||
incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
|
||||
of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
|
||||
|
||||
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
||||
|
||||
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
|
||||
|
||||
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
|
||||
boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
|
||||
replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
|
||||
the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
|
||||
comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
|
||||
file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
|
||||
same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
|
||||
identification within third-party archives.
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r1/doc.go
generated
vendored
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r1/doc.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package r1 implements types and functions for working with geometry in ℝ¹.
|
||||
|
||||
See ../s2 for a more detailed overview.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package r1
|
||||
159
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r1/interval.go
generated
vendored
159
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r1/interval.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,159 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package r1
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Interval represents a closed interval on ℝ.
|
||||
// Zero-length intervals (where Lo == Hi) represent single points.
|
||||
// If Lo > Hi then the interval is empty.
|
||||
type Interval struct {
|
||||
Lo, Hi float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EmptyInterval returns an empty interval.
|
||||
func EmptyInterval() Interval { return Interval{1, 0} }
|
||||
|
||||
// IntervalFromPoint returns an interval representing a single point.
|
||||
func IntervalFromPoint(p float64) Interval { return Interval{p, p} }
|
||||
|
||||
// IsEmpty reports whether the interval is empty.
|
||||
func (i Interval) IsEmpty() bool { return i.Lo > i.Hi }
|
||||
|
||||
// Equal returns true iff the interval contains the same points as oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Equal(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
return i == oi || i.IsEmpty() && oi.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Center returns the midpoint of the interval.
|
||||
// It is undefined for empty intervals.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Center() float64 { return 0.5 * (i.Lo + i.Hi) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Length returns the length of the interval.
|
||||
// The length of an empty interval is negative.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Length() float64 { return i.Hi - i.Lo }
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains returns true iff the interval contains p.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Contains(p float64) bool { return i.Lo <= p && p <= i.Hi }
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsInterval returns true iff the interval contains oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) ContainsInterval(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if oi.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i.Lo <= oi.Lo && oi.Hi <= i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContains returns true iff the the interval strictly contains p.
|
||||
func (i Interval) InteriorContains(p float64) bool {
|
||||
return i.Lo < p && p < i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContainsInterval returns true iff the interval strictly contains oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) InteriorContainsInterval(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if oi.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i.Lo < oi.Lo && oi.Hi < i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersects returns true iff the interval contains any points in common with oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Intersects(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if i.Lo <= oi.Lo {
|
||||
return oi.Lo <= i.Hi && oi.Lo <= oi.Hi // oi.Lo ∈ i and oi is not empty
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i.Lo <= oi.Hi && i.Lo <= i.Hi // i.Lo ∈ oi and i is not empty
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorIntersects returns true iff the interior of the interval contains any points in common with oi, including the latter's boundary.
|
||||
func (i Interval) InteriorIntersects(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
return oi.Lo < i.Hi && i.Lo < oi.Hi && i.Lo < i.Hi && oi.Lo <= oi.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersection returns the interval containing all points common to i and j.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Intersection(j Interval) Interval {
|
||||
// Empty intervals do not need to be special-cased.
|
||||
return Interval{
|
||||
Lo: math.Max(i.Lo, j.Lo),
|
||||
Hi: math.Min(i.Hi, j.Hi),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPoint returns the interval expanded so that it contains the given point.
|
||||
func (i Interval) AddPoint(p float64) Interval {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return Interval{p, p}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p < i.Lo {
|
||||
return Interval{p, i.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p > i.Hi {
|
||||
return Interval{i.Lo, p}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClampPoint returns the closest point in the interval to the given point "p".
|
||||
// The interval must be non-empty.
|
||||
func (i Interval) ClampPoint(p float64) float64 {
|
||||
return math.Max(i.Lo, math.Min(i.Hi, p))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Expanded returns an interval that has been expanded on each side by margin.
|
||||
// If margin is negative, then the function shrinks the interval on
|
||||
// each side by margin instead. The resulting interval may be empty. Any
|
||||
// expansion of an empty interval remains empty.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Expanded(margin float64) Interval {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{i.Lo - margin, i.Hi + margin}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Union returns the smallest interval that contains this interval and the given interval.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Union(other Interval) Interval {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return other
|
||||
}
|
||||
if other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{math.Min(i.Lo, other.Lo), math.Max(i.Hi, other.Hi)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i Interval) String() string { return fmt.Sprintf("[%.7f, %.7f]", i.Lo, i.Hi) }
|
||||
|
||||
// epsilon is a small number that represents a reasonable level of noise between two
|
||||
// values that can be considered to be equal.
|
||||
const epsilon = 1e-14
|
||||
|
||||
// ApproxEqual reports whether the interval can be transformed into the
|
||||
// given interval by moving each endpoint a small distance.
|
||||
// The empty interval is considered to be positioned arbitrarily on the
|
||||
// real line, so any interval with a small enough length will match
|
||||
// the empty interval.
|
||||
func (i Interval) ApproxEqual(other Interval) bool {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return other.Length() <= 2*epsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
if other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return i.Length() <= 2*epsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
return math.Abs(other.Lo-i.Lo) <= epsilon &&
|
||||
math.Abs(other.Hi-i.Hi) <= epsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r2/doc.go
generated
vendored
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r2/doc.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package r2 implements types and functions for working with geometry in ℝ².
|
||||
|
||||
See package s2 for a more detailed overview.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package r2
|
||||
255
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r2/rect.go
generated
vendored
255
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r2/rect.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,255 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package r2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Point represents a point in ℝ².
|
||||
type Point struct {
|
||||
X, Y float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add returns the sum of p and op.
|
||||
func (p Point) Add(op Point) Point { return Point{p.X + op.X, p.Y + op.Y} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Sub returns the difference of p and op.
|
||||
func (p Point) Sub(op Point) Point { return Point{p.X - op.X, p.Y - op.Y} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Mul returns the scalar product of p and m.
|
||||
func (p Point) Mul(m float64) Point { return Point{m * p.X, m * p.Y} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Ortho returns a counterclockwise orthogonal point with the same norm.
|
||||
func (p Point) Ortho() Point { return Point{-p.Y, p.X} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Dot returns the dot product between p and op.
|
||||
func (p Point) Dot(op Point) float64 { return p.X*op.X + p.Y*op.Y }
|
||||
|
||||
// Cross returns the cross product of p and op.
|
||||
func (p Point) Cross(op Point) float64 { return p.X*op.Y - p.Y*op.X }
|
||||
|
||||
// Norm returns the vector's norm.
|
||||
func (p Point) Norm() float64 { return math.Hypot(p.X, p.Y) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Normalize returns a unit point in the same direction as p.
|
||||
func (p Point) Normalize() Point {
|
||||
if p.X == 0 && p.Y == 0 {
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p.Mul(1 / p.Norm())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p Point) String() string { return fmt.Sprintf("(%.12f, %.12f)", p.X, p.Y) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Rect represents a closed axis-aligned rectangle in the (x,y) plane.
|
||||
type Rect struct {
|
||||
X, Y r1.Interval
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RectFromPoints constructs a rect that contains the given points.
|
||||
func RectFromPoints(pts ...Point) Rect {
|
||||
// Because the default value on interval is 0,0, we need to manually
|
||||
// define the interval from the first point passed in as our starting
|
||||
// interval, otherwise we end up with the case of passing in
|
||||
// Point{0.2, 0.3} and getting the starting Rect of {0, 0.2}, {0, 0.3}
|
||||
// instead of the Rect {0.2, 0.2}, {0.3, 0.3} which is not correct.
|
||||
if len(pts) == 0 {
|
||||
return Rect{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r := Rect{
|
||||
X: r1.Interval{Lo: pts[0].X, Hi: pts[0].X},
|
||||
Y: r1.Interval{Lo: pts[0].Y, Hi: pts[0].Y},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, p := range pts[1:] {
|
||||
r = r.AddPoint(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RectFromCenterSize constructs a rectangle with the given center and size.
|
||||
// Both dimensions of size must be non-negative.
|
||||
func RectFromCenterSize(center, size Point) Rect {
|
||||
return Rect{
|
||||
r1.Interval{Lo: center.X - size.X/2, Hi: center.X + size.X/2},
|
||||
r1.Interval{Lo: center.Y - size.Y/2, Hi: center.Y + size.Y/2},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EmptyRect constructs the canonical empty rectangle. Use IsEmpty() to test
|
||||
// for empty rectangles, since they have more than one representation. A Rect{}
|
||||
// is not the same as the EmptyRect.
|
||||
func EmptyRect() Rect {
|
||||
return Rect{r1.EmptyInterval(), r1.EmptyInterval()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsValid reports whether the rectangle is valid.
|
||||
// This requires the width to be empty iff the height is empty.
|
||||
func (r Rect) IsValid() bool {
|
||||
return r.X.IsEmpty() == r.Y.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsEmpty reports whether the rectangle is empty.
|
||||
func (r Rect) IsEmpty() bool {
|
||||
return r.X.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Vertices returns all four vertices of the rectangle. Vertices are returned in
|
||||
// CCW direction starting with the lower left corner.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Vertices() [4]Point {
|
||||
return [4]Point{
|
||||
{r.X.Lo, r.Y.Lo},
|
||||
{r.X.Hi, r.Y.Lo},
|
||||
{r.X.Hi, r.Y.Hi},
|
||||
{r.X.Lo, r.Y.Hi},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VertexIJ returns the vertex in direction i along the X-axis (0=left, 1=right) and
|
||||
// direction j along the Y-axis (0=down, 1=up).
|
||||
func (r Rect) VertexIJ(i, j int) Point {
|
||||
x := r.X.Lo
|
||||
if i == 1 {
|
||||
x = r.X.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
y := r.Y.Lo
|
||||
if j == 1 {
|
||||
y = r.Y.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Point{x, y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Lo returns the low corner of the rect.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Lo() Point {
|
||||
return Point{r.X.Lo, r.Y.Lo}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Hi returns the high corner of the rect.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Hi() Point {
|
||||
return Point{r.X.Hi, r.Y.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Center returns the center of the rectangle in (x,y)-space
|
||||
func (r Rect) Center() Point {
|
||||
return Point{r.X.Center(), r.Y.Center()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Size returns the width and height of this rectangle in (x,y)-space. Empty
|
||||
// rectangles have a negative width and height.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Size() Point {
|
||||
return Point{r.X.Length(), r.Y.Length()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsPoint reports whether the rectangle contains the given point.
|
||||
// Rectangles are closed regions, i.e. they contain their boundary.
|
||||
func (r Rect) ContainsPoint(p Point) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.Contains(p.X) && r.Y.Contains(p.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContainsPoint returns true iff the given point is contained in the interior
|
||||
// of the region (i.e. the region excluding its boundary).
|
||||
func (r Rect) InteriorContainsPoint(p Point) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.InteriorContains(p.X) && r.Y.InteriorContains(p.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains reports whether the rectangle contains the given rectangle.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Contains(other Rect) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.ContainsInterval(other.X) && r.Y.ContainsInterval(other.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContains reports whether the interior of this rectangle contains all of the
|
||||
// points of the given other rectangle (including its boundary).
|
||||
func (r Rect) InteriorContains(other Rect) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.InteriorContainsInterval(other.X) && r.Y.InteriorContainsInterval(other.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersects reports whether this rectangle and the other rectangle have any points in common.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Intersects(other Rect) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.Intersects(other.X) && r.Y.Intersects(other.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorIntersects reports whether the interior of this rectangle intersects
|
||||
// any point (including the boundary) of the given other rectangle.
|
||||
func (r Rect) InteriorIntersects(other Rect) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.InteriorIntersects(other.X) && r.Y.InteriorIntersects(other.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPoint expands the rectangle to include the given point. The rectangle is
|
||||
// expanded by the minimum amount possible.
|
||||
func (r Rect) AddPoint(p Point) Rect {
|
||||
return Rect{r.X.AddPoint(p.X), r.Y.AddPoint(p.Y)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddRect expands the rectangle to include the given rectangle. This is the
|
||||
// same as replacing the rectangle by the union of the two rectangles, but
|
||||
// is more efficient.
|
||||
func (r Rect) AddRect(other Rect) Rect {
|
||||
return Rect{r.X.Union(other.X), r.Y.Union(other.Y)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClampPoint returns the closest point in the rectangle to the given point.
|
||||
// The rectangle must be non-empty.
|
||||
func (r Rect) ClampPoint(p Point) Point {
|
||||
return Point{r.X.ClampPoint(p.X), r.Y.ClampPoint(p.Y)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Expanded returns a rectangle that has been expanded in the x-direction
|
||||
// by margin.X, and in y-direction by margin.Y. If either margin is empty,
|
||||
// then shrink the interval on the corresponding sides instead. The resulting
|
||||
// rectangle may be empty. Any expansion of an empty rectangle remains empty.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Expanded(margin Point) Rect {
|
||||
xx := r.X.Expanded(margin.X)
|
||||
yy := r.Y.Expanded(margin.Y)
|
||||
if xx.IsEmpty() || yy.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return EmptyRect()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Rect{xx, yy}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExpandedByMargin returns a Rect that has been expanded by the amount on all sides.
|
||||
func (r Rect) ExpandedByMargin(margin float64) Rect {
|
||||
return r.Expanded(Point{margin, margin})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Union returns the smallest rectangle containing the union of this rectangle and
|
||||
// the given rectangle.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Union(other Rect) Rect {
|
||||
return Rect{r.X.Union(other.X), r.Y.Union(other.Y)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersection returns the smallest rectangle containing the intersection of this
|
||||
// rectangle and the given rectangle.
|
||||
func (r Rect) Intersection(other Rect) Rect {
|
||||
xx := r.X.Intersection(other.X)
|
||||
yy := r.Y.Intersection(other.Y)
|
||||
if xx.IsEmpty() || yy.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return EmptyRect()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return Rect{xx, yy}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApproxEqual returns true if the x- and y-intervals of the two rectangles are
|
||||
// the same up to the given tolerance.
|
||||
func (r Rect) ApproxEqual(r2 Rect) bool {
|
||||
return r.X.ApproxEqual(r2.X) && r.Y.ApproxEqual(r2.Y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r Rect) String() string { return fmt.Sprintf("[Lo%s, Hi%s]", r.Lo(), r.Hi()) }
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r3/doc.go
generated
vendored
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r3/doc.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package r3 implements types and functions for working with geometry in ℝ³.
|
||||
|
||||
See ../s2 for a more detailed overview.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package r3
|
||||
198
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r3/precisevector.go
generated
vendored
198
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r3/precisevector.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,198 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2016 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package r3
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math/big"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// prec is the number of bits of precision to use for the Float values.
|
||||
// To keep things simple, we use the maximum allowable precision on big
|
||||
// values. This allows us to handle all values we expect in the s2 library.
|
||||
prec = big.MaxPrec
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// define some commonly referenced values.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
precise0 = precInt(0)
|
||||
precise1 = precInt(1)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// precStr wraps the conversion from a string into a big.Float. For results that
|
||||
// actually can be represented exactly, this should only be used on values that
|
||||
// are integer multiples of integer powers of 2.
|
||||
func precStr(s string) *big.Float {
|
||||
// Explicitly ignoring the bool return for this usage.
|
||||
f, _ := new(big.Float).SetPrec(prec).SetString(s)
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func precInt(i int64) *big.Float {
|
||||
return new(big.Float).SetPrec(prec).SetInt64(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func precFloat(f float64) *big.Float {
|
||||
return new(big.Float).SetPrec(prec).SetFloat64(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func precAdd(a, b *big.Float) *big.Float {
|
||||
return new(big.Float).SetPrec(prec).Add(a, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func precSub(a, b *big.Float) *big.Float {
|
||||
return new(big.Float).SetPrec(prec).Sub(a, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func precMul(a, b *big.Float) *big.Float {
|
||||
return new(big.Float).SetPrec(prec).Mul(a, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PreciseVector represents a point in ℝ³ using high-precision values.
|
||||
// Note that this is NOT a complete implementation because there are some
|
||||
// operations that Vector supports that are not feasible with arbitrary precision
|
||||
// math. (e.g., methods that need divison like Normalize, or methods needing a
|
||||
// square root operation such as Norm)
|
||||
type PreciseVector struct {
|
||||
X, Y, Z *big.Float
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PreciseVectorFromVector creates a high precision vector from the given Vector.
|
||||
func PreciseVectorFromVector(v Vector) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return NewPreciseVector(v.X, v.Y, v.Z)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewPreciseVector creates a high precision vector from the given floating point values.
|
||||
func NewPreciseVector(x, y, z float64) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return PreciseVector{
|
||||
X: precFloat(x),
|
||||
Y: precFloat(y),
|
||||
Z: precFloat(z),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Vector returns this precise vector converted to a Vector.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Vector() Vector {
|
||||
// The accuracy flag is ignored on these conversions back to float64.
|
||||
x, _ := v.X.Float64()
|
||||
y, _ := v.Y.Float64()
|
||||
z, _ := v.Z.Float64()
|
||||
return Vector{x, y, z}.Normalize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Equal reports whether v and ov are equal.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Equal(ov PreciseVector) bool {
|
||||
return v.X.Cmp(ov.X) == 0 && v.Y.Cmp(ov.Y) == 0 && v.Z.Cmp(ov.Z) == 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("(%10g, %10g, %10g)", v.X, v.Y, v.Z)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Norm2 returns the square of the norm.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Norm2() *big.Float { return v.Dot(v) }
|
||||
|
||||
// IsUnit reports whether this vector is of unit length.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) IsUnit() bool {
|
||||
return v.Norm2().Cmp(precise1) == 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Abs returns the vector with nonnegative components.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Abs() PreciseVector {
|
||||
return PreciseVector{
|
||||
X: new(big.Float).Abs(v.X),
|
||||
Y: new(big.Float).Abs(v.Y),
|
||||
Z: new(big.Float).Abs(v.Z),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add returns the standard vector sum of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Add(ov PreciseVector) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return PreciseVector{
|
||||
X: precAdd(v.X, ov.X),
|
||||
Y: precAdd(v.Y, ov.Y),
|
||||
Z: precAdd(v.Z, ov.Z),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sub returns the standard vector difference of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Sub(ov PreciseVector) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return PreciseVector{
|
||||
X: precSub(v.X, ov.X),
|
||||
Y: precSub(v.Y, ov.Y),
|
||||
Z: precSub(v.Z, ov.Z),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mul returns the standard scalar product of v and f.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Mul(f *big.Float) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return PreciseVector{
|
||||
X: precMul(v.X, f),
|
||||
Y: precMul(v.Y, f),
|
||||
Z: precMul(v.Z, f),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MulByFloat64 returns the standard scalar product of v and f.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) MulByFloat64(f float64) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return v.Mul(precFloat(f))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Dot returns the standard dot product of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Dot(ov PreciseVector) *big.Float {
|
||||
return precAdd(precMul(v.X, ov.X), precAdd(precMul(v.Y, ov.Y), precMul(v.Z, ov.Z)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cross returns the standard cross product of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) Cross(ov PreciseVector) PreciseVector {
|
||||
return PreciseVector{
|
||||
X: precSub(precMul(v.Y, ov.Z), precMul(v.Z, ov.Y)),
|
||||
Y: precSub(precMul(v.Z, ov.X), precMul(v.X, ov.Z)),
|
||||
Z: precSub(precMul(v.X, ov.Y), precMul(v.Y, ov.X)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LargestComponent returns the axis that represents the largest component in this vector.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) LargestComponent() Axis {
|
||||
t := v.Abs()
|
||||
|
||||
if t.X.Cmp(t.Y) > 0 {
|
||||
if t.X.Cmp(t.Z) > 0 {
|
||||
return XAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.Y.Cmp(t.Z) > 0 {
|
||||
return YAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SmallestComponent returns the axis that represents the smallest component in this vector.
|
||||
func (v PreciseVector) SmallestComponent() Axis {
|
||||
t := v.Abs()
|
||||
|
||||
if t.X.Cmp(t.Y) < 0 {
|
||||
if t.X.Cmp(t.Z) < 0 {
|
||||
return XAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.Y.Cmp(t.Z) < 0 {
|
||||
return YAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
183
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r3/vector.go
generated
vendored
183
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/r3/vector.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,183 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package r3
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Vector represents a point in ℝ³.
|
||||
type Vector struct {
|
||||
X, Y, Z float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApproxEqual reports whether v and ov are equal within a small epsilon.
|
||||
func (v Vector) ApproxEqual(ov Vector) bool {
|
||||
const epsilon = 1e-16
|
||||
return math.Abs(v.X-ov.X) < epsilon && math.Abs(v.Y-ov.Y) < epsilon && math.Abs(v.Z-ov.Z) < epsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v Vector) String() string { return fmt.Sprintf("(%0.24f, %0.24f, %0.24f)", v.X, v.Y, v.Z) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Norm returns the vector's norm.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Norm() float64 { return math.Sqrt(v.Dot(v)) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Norm2 returns the square of the norm.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Norm2() float64 { return v.Dot(v) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Normalize returns a unit vector in the same direction as v.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Normalize() Vector {
|
||||
n2 := v.Norm2()
|
||||
if n2 == 0 {
|
||||
return Vector{0, 0, 0}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v.Mul(1 / math.Sqrt(n2))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsUnit returns whether this vector is of approximately unit length.
|
||||
func (v Vector) IsUnit() bool {
|
||||
const epsilon = 5e-14
|
||||
return math.Abs(v.Norm2()-1) <= epsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Abs returns the vector with nonnegative components.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Abs() Vector { return Vector{math.Abs(v.X), math.Abs(v.Y), math.Abs(v.Z)} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Add returns the standard vector sum of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Add(ov Vector) Vector { return Vector{v.X + ov.X, v.Y + ov.Y, v.Z + ov.Z} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Sub returns the standard vector difference of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Sub(ov Vector) Vector { return Vector{v.X - ov.X, v.Y - ov.Y, v.Z - ov.Z} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Mul returns the standard scalar product of v and m.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Mul(m float64) Vector { return Vector{m * v.X, m * v.Y, m * v.Z} }
|
||||
|
||||
// Dot returns the standard dot product of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Dot(ov Vector) float64 { return v.X*ov.X + v.Y*ov.Y + v.Z*ov.Z }
|
||||
|
||||
// Cross returns the standard cross product of v and ov.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Cross(ov Vector) Vector {
|
||||
return Vector{
|
||||
v.Y*ov.Z - v.Z*ov.Y,
|
||||
v.Z*ov.X - v.X*ov.Z,
|
||||
v.X*ov.Y - v.Y*ov.X,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Distance returns the Euclidean distance between v and ov.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Distance(ov Vector) float64 { return v.Sub(ov).Norm() }
|
||||
|
||||
// Angle returns the angle between v and ov.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Angle(ov Vector) s1.Angle {
|
||||
return s1.Angle(math.Atan2(v.Cross(ov).Norm(), v.Dot(ov))) * s1.Radian
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Axis enumerates the 3 axes of ℝ³.
|
||||
type Axis int
|
||||
|
||||
// The three axes of ℝ³.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
XAxis Axis = iota
|
||||
YAxis
|
||||
ZAxis
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Ortho returns a unit vector that is orthogonal to v.
|
||||
// Ortho(-v) = -Ortho(v) for all v.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Ortho() Vector {
|
||||
ov := Vector{0.012, 0.0053, 0.00457}
|
||||
switch v.LargestComponent() {
|
||||
case XAxis:
|
||||
ov.Z = 1
|
||||
case YAxis:
|
||||
ov.X = 1
|
||||
default:
|
||||
ov.Y = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v.Cross(ov).Normalize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LargestComponent returns the axis that represents the largest component in this vector.
|
||||
func (v Vector) LargestComponent() Axis {
|
||||
t := v.Abs()
|
||||
|
||||
if t.X > t.Y {
|
||||
if t.X > t.Z {
|
||||
return XAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.Y > t.Z {
|
||||
return YAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SmallestComponent returns the axis that represents the smallest component in this vector.
|
||||
func (v Vector) SmallestComponent() Axis {
|
||||
t := v.Abs()
|
||||
|
||||
if t.X < t.Y {
|
||||
if t.X < t.Z {
|
||||
return XAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.Y < t.Z {
|
||||
return YAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ZAxis
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmp compares v and ov lexicographically and returns:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// -1 if v < ov
|
||||
// 0 if v == ov
|
||||
// +1 if v > ov
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method is based on C++'s std::lexicographical_compare. Two entities
|
||||
// are compared element by element with the given operator. The first mismatch
|
||||
// defines which is less (or greater) than the other. If both have equivalent
|
||||
// values they are lexicographically equal.
|
||||
func (v Vector) Cmp(ov Vector) int {
|
||||
if v.X < ov.X {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.X > ov.X {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// First elements were the same, try the next.
|
||||
if v.Y < ov.Y {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.Y > ov.Y {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Second elements were the same return the final compare.
|
||||
if v.Z < ov.Z {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.Z > ov.Z {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Both are equal
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
117
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/angle.go
generated
vendored
117
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/angle.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s1
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Angle represents a 1D angle. The internal representation is a double precision
|
||||
// value in radians, so conversion to and from radians is exact.
|
||||
// Conversions between E5, E6, E7, and Degrees are not always
|
||||
// exact. For example, Degrees(3.1) is different from E6(3100000) or E7(310000000).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The following conversions between degrees and radians are exact:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Degree*180 == Radian*math.Pi
|
||||
// Degree*(180/n) == Radian*(math.Pi/n) for n == 0..8
|
||||
//
|
||||
// These identities hold when the arguments are scaled up or down by any power
|
||||
// of 2. Some similar identities are also true, for example,
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Degree*60 == Radian*(math.Pi/3)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// But be aware that this type of identity does not hold in general. For example,
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Degree*3 != Radian*(math.Pi/60)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Similarly, the conversion to radians means that (Angle(x)*Degree).Degrees()
|
||||
// does not always equal x. For example,
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (Angle(45*n)*Degree).Degrees() == 45*n for n == 0..8
|
||||
//
|
||||
// but
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (60*Degree).Degrees() != 60
|
||||
//
|
||||
// When testing for equality, you should allow for numerical errors (floatApproxEq)
|
||||
// or convert to discrete E5/E6/E7 values first.
|
||||
type Angle float64
|
||||
|
||||
// Angle units.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Radian Angle = 1
|
||||
Degree = (math.Pi / 180) * Radian
|
||||
|
||||
E5 = 1e-5 * Degree
|
||||
E6 = 1e-6 * Degree
|
||||
E7 = 1e-7 * Degree
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Radians returns the angle in radians.
|
||||
func (a Angle) Radians() float64 { return float64(a) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Degrees returns the angle in degrees.
|
||||
func (a Angle) Degrees() float64 { return float64(a / Degree) }
|
||||
|
||||
// round returns the value rounded to nearest as an int32.
|
||||
// This does not match C++ exactly for the case of x.5.
|
||||
func round(val float64) int32 {
|
||||
if val < 0 {
|
||||
return int32(val - 0.5)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return int32(val + 0.5)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InfAngle returns an angle larger than any finite angle.
|
||||
func InfAngle() Angle {
|
||||
return Angle(math.Inf(1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isInf reports whether this Angle is infinite.
|
||||
func (a Angle) isInf() bool {
|
||||
return math.IsInf(float64(a), 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// E5 returns the angle in hundred thousandths of degrees.
|
||||
func (a Angle) E5() int32 { return round(a.Degrees() * 1e5) }
|
||||
|
||||
// E6 returns the angle in millionths of degrees.
|
||||
func (a Angle) E6() int32 { return round(a.Degrees() * 1e6) }
|
||||
|
||||
// E7 returns the angle in ten millionths of degrees.
|
||||
func (a Angle) E7() int32 { return round(a.Degrees() * 1e7) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Abs returns the absolute value of the angle.
|
||||
func (a Angle) Abs() Angle { return Angle(math.Abs(float64(a))) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Normalized returns an equivalent angle in [0, 2π).
|
||||
func (a Angle) Normalized() Angle {
|
||||
rad := math.Mod(float64(a), 2*math.Pi)
|
||||
if rad < 0 {
|
||||
rad += 2 * math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Angle(rad)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a Angle) String() string {
|
||||
return strconv.FormatFloat(a.Degrees(), 'f', 7, 64) // like "%.7f"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BUG(dsymonds): The major differences from the C++ version are:
|
||||
// - no unsigned E5/E6/E7 methods
|
||||
// - no S2Point or S2LatLng constructors
|
||||
// - no comparison or arithmetic operators
|
||||
245
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/chordangle.go
generated
vendored
245
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/chordangle.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,245 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2015 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s1
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ChordAngle represents the angle subtended by a chord (i.e., the straight
|
||||
// line segment connecting two points on the sphere). Its representation
|
||||
// makes it very efficient for computing and comparing distances, but unlike
|
||||
// Angle it is only capable of representing angles between 0 and π radians.
|
||||
// Generally, ChordAngle should only be used in loops where many angles need
|
||||
// to be calculated and compared. Otherwise it is simpler to use Angle.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ChordAngle loses some accuracy as the angle approaches π radians.
|
||||
// Specifically, the representation of (π - x) radians has an error of about
|
||||
// (1e-15 / x), with a maximum error of about 2e-8 radians (about 13cm on the
|
||||
// Earth's surface). For comparison, for angles up to π/2 radians (10000km)
|
||||
// the worst-case representation error is about 2e-16 radians (1 nanonmeter),
|
||||
// which is about the same as Angle.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ChordAngles are represented by the squared chord length, which can
|
||||
// range from 0 to 4. Positive infinity represents an infinite squared length.
|
||||
type ChordAngle float64
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// NegativeChordAngle represents a chord angle smaller than the zero angle.
|
||||
// The only valid operations on a NegativeChordAngle are comparisons,
|
||||
// Angle conversions, and Successor/Predecessor.
|
||||
NegativeChordAngle = ChordAngle(-1)
|
||||
|
||||
// RightChordAngle represents a chord angle of 90 degrees (a "right angle").
|
||||
RightChordAngle = ChordAngle(2)
|
||||
|
||||
// StraightChordAngle represents a chord angle of 180 degrees (a "straight angle").
|
||||
// This is the maximum finite chord angle.
|
||||
StraightChordAngle = ChordAngle(4)
|
||||
|
||||
// maxLength2 is the square of the maximum length allowed in a ChordAngle.
|
||||
maxLength2 = 4.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ChordAngleFromAngle returns a ChordAngle from the given Angle.
|
||||
func ChordAngleFromAngle(a Angle) ChordAngle {
|
||||
if a < 0 {
|
||||
return NegativeChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
if a.isInf() {
|
||||
return InfChordAngle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
l := 2 * math.Sin(0.5*math.Min(math.Pi, a.Radians()))
|
||||
return ChordAngle(l * l)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ChordAngleFromSquaredLength returns a ChordAngle from the squared chord length.
|
||||
// Note that the argument is automatically clamped to a maximum of 4 to
|
||||
// handle possible roundoff errors. The argument must be non-negative.
|
||||
func ChordAngleFromSquaredLength(length2 float64) ChordAngle {
|
||||
if length2 > maxLength2 {
|
||||
return StraightChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ChordAngle(length2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Expanded returns a new ChordAngle that has been adjusted by the given error
|
||||
// bound (which can be positive or negative). Error should be the value
|
||||
// returned by either MaxPointError or MaxAngleError. For example:
|
||||
// a := ChordAngleFromPoints(x, y)
|
||||
// a1 := a.Expanded(a.MaxPointError())
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Expanded(e float64) ChordAngle {
|
||||
// If the angle is special, don't change it. Otherwise clamp it to the valid range.
|
||||
if c.isSpecial() {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ChordAngle(math.Max(0.0, math.Min(maxLength2, float64(c)+e)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Angle converts this ChordAngle to an Angle.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Angle() Angle {
|
||||
if c < 0 {
|
||||
return -1 * Radian
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c.isInf() {
|
||||
return InfAngle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Angle(2 * math.Asin(0.5*math.Sqrt(float64(c))))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InfChordAngle returns a chord angle larger than any finite chord angle.
|
||||
// The only valid operations on an InfChordAngle are comparisons, Angle
|
||||
// conversions, and Successor/Predecessor.
|
||||
func InfChordAngle() ChordAngle {
|
||||
return ChordAngle(math.Inf(1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isInf reports whether this ChordAngle is infinite.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) isInf() bool {
|
||||
return math.IsInf(float64(c), 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isSpecial reports whether this ChordAngle is one of the special cases.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) isSpecial() bool {
|
||||
return c < 0 || c.isInf()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isValid reports whether this ChordAngle is valid or not.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) isValid() bool {
|
||||
return (c >= 0 && c <= maxLength2) || c.isSpecial()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Successor returns the smallest representable ChordAngle larger than this one.
|
||||
// This can be used to convert a "<" comparison to a "<=" comparison.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note the following special cases:
|
||||
// NegativeChordAngle.Successor == 0
|
||||
// StraightChordAngle.Successor == InfChordAngle
|
||||
// InfChordAngle.Successor == InfChordAngle
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Successor() ChordAngle {
|
||||
if c >= maxLength2 {
|
||||
return InfChordAngle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c < 0 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ChordAngle(math.Nextafter(float64(c), 10.0))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Predecessor returns the largest representable ChordAngle less than this one.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note the following special cases:
|
||||
// InfChordAngle.Predecessor == StraightChordAngle
|
||||
// ChordAngle(0).Predecessor == NegativeChordAngle
|
||||
// NegativeChordAngle.Predecessor == NegativeChordAngle
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Predecessor() ChordAngle {
|
||||
if c <= 0 {
|
||||
return NegativeChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c > maxLength2 {
|
||||
return StraightChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ChordAngle(math.Nextafter(float64(c), -10.0))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxPointError returns the maximum error size for a ChordAngle constructed
|
||||
// from 2 Points x and y, assuming that x and y are normalized to within the
|
||||
// bounds guaranteed by s2.Point.Normalize. The error is defined with respect to
|
||||
// the true distance after the points are projected to lie exactly on the sphere.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) MaxPointError() float64 {
|
||||
// There is a relative error of (2.5*dblEpsilon) when computing the squared
|
||||
// distance, plus a relative error of 2 * dblEpsilon, plus an absolute error
|
||||
// of (16 * dblEpsilon**2) because the lengths of the input points may differ
|
||||
// from 1 by up to (2*dblEpsilon) each. (This is the maximum error in Normalize).
|
||||
return 4.5*dblEpsilon*float64(c) + 16*dblEpsilon*dblEpsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxAngleError returns the maximum error for a ChordAngle constructed
|
||||
// as an Angle distance.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) MaxAngleError() float64 {
|
||||
return dblEpsilon * float64(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add adds the other ChordAngle to this one and returns the resulting value.
|
||||
// This method assumes the ChordAngles are not special.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Add(other ChordAngle) ChordAngle {
|
||||
// Note that this method (and Sub) is much more efficient than converting
|
||||
// the ChordAngle to an Angle and adding those and converting back. It
|
||||
// requires only one square root plus a few additions and multiplications.
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimization for the common case where b is an error tolerance
|
||||
// parameter that happens to be set to zero.
|
||||
if other == 0 {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clamp the angle sum to at most 180 degrees.
|
||||
if c+other >= maxLength2 {
|
||||
return StraightChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Let a and b be the (non-squared) chord lengths, and let c = a+b.
|
||||
// Let A, B, and C be the corresponding half-angles (a = 2*sin(A), etc).
|
||||
// Then the formula below can be derived from c = 2 * sin(A+B) and the
|
||||
// relationships sin(A+B) = sin(A)*cos(B) + sin(B)*cos(A)
|
||||
// cos(X) = sqrt(1 - sin^2(X))
|
||||
x := float64(c * (1 - 0.25*other))
|
||||
y := float64(other * (1 - 0.25*c))
|
||||
return ChordAngle(math.Min(maxLength2, x+y+2*math.Sqrt(x*y)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sub subtracts the other ChordAngle from this one and returns the resulting
|
||||
// value. This method assumes the ChordAngles are not special.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Sub(other ChordAngle) ChordAngle {
|
||||
if other == 0 {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c <= other {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
x := float64(c * (1 - 0.25*other))
|
||||
y := float64(other * (1 - 0.25*c))
|
||||
return ChordAngle(math.Max(0.0, x+y-2*math.Sqrt(x*y)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sin returns the sine of this chord angle. This method is more efficient
|
||||
// than converting to Angle and performing the computation.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Sin() float64 {
|
||||
return math.Sqrt(c.Sin2())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sin2 returns the square of the sine of this chord angle.
|
||||
// It is more efficient than Sin.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Sin2() float64 {
|
||||
// Let a be the (non-squared) chord length, and let A be the corresponding
|
||||
// half-angle (a = 2*sin(A)). The formula below can be derived from:
|
||||
// sin(2*A) = 2 * sin(A) * cos(A)
|
||||
// cos^2(A) = 1 - sin^2(A)
|
||||
// This is much faster than converting to an angle and computing its sine.
|
||||
return float64(c * (1 - 0.25*c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cos returns the cosine of this chord angle. This method is more efficient
|
||||
// than converting to Angle and performing the computation.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Cos() float64 {
|
||||
// cos(2*A) = cos^2(A) - sin^2(A) = 1 - 2*sin^2(A)
|
||||
return float64(1 - 0.5*c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tan returns the tangent of this chord angle.
|
||||
func (c ChordAngle) Tan() float64 {
|
||||
return c.Sin() / c.Cos()
|
||||
}
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/doc.go
generated
vendored
20
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/doc.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package s1 implements types and functions for working with geometry in S¹ (circular geometry).
|
||||
|
||||
See ../s2 for a more detailed overview.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package s1
|
||||
348
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/interval.go
generated
vendored
348
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s1/interval.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,348 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s1
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Interval represents a closed interval on a unit circle.
|
||||
// Zero-length intervals (where Lo == Hi) represent single points.
|
||||
// If Lo > Hi then the interval is "inverted".
|
||||
// The point at (-1, 0) on the unit circle has two valid representations,
|
||||
// [π,π] and [-π,-π]. We normalize the latter to the former in IntervalFromEndpoints.
|
||||
// There are two special intervals that take advantage of that:
|
||||
// - the full interval, [-π,π], and
|
||||
// - the empty interval, [π,-π].
|
||||
// Treat the exported fields as read-only.
|
||||
type Interval struct {
|
||||
Lo, Hi float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntervalFromEndpoints constructs a new interval from endpoints.
|
||||
// Both arguments must be in the range [-π,π]. This function allows inverted intervals
|
||||
// to be created.
|
||||
func IntervalFromEndpoints(lo, hi float64) Interval {
|
||||
i := Interval{lo, hi}
|
||||
if lo == -math.Pi && hi != math.Pi {
|
||||
i.Lo = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hi == -math.Pi && lo != math.Pi {
|
||||
i.Hi = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntervalFromPointPair returns the minimal interval containing the two given points.
|
||||
// Both arguments must be in [-π,π].
|
||||
func IntervalFromPointPair(a, b float64) Interval {
|
||||
if a == -math.Pi {
|
||||
a = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b == -math.Pi {
|
||||
b = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if positiveDistance(a, b) <= math.Pi {
|
||||
return Interval{a, b}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{b, a}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EmptyInterval returns an empty interval.
|
||||
func EmptyInterval() Interval { return Interval{math.Pi, -math.Pi} }
|
||||
|
||||
// FullInterval returns a full interval.
|
||||
func FullInterval() Interval { return Interval{-math.Pi, math.Pi} }
|
||||
|
||||
// IsValid reports whether the interval is valid.
|
||||
func (i Interval) IsValid() bool {
|
||||
return (math.Abs(i.Lo) <= math.Pi && math.Abs(i.Hi) <= math.Pi &&
|
||||
!(i.Lo == -math.Pi && i.Hi != math.Pi) &&
|
||||
!(i.Hi == -math.Pi && i.Lo != math.Pi))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsFull reports whether the interval is full.
|
||||
func (i Interval) IsFull() bool { return i.Lo == -math.Pi && i.Hi == math.Pi }
|
||||
|
||||
// IsEmpty reports whether the interval is empty.
|
||||
func (i Interval) IsEmpty() bool { return i.Lo == math.Pi && i.Hi == -math.Pi }
|
||||
|
||||
// IsInverted reports whether the interval is inverted; that is, whether Lo > Hi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) IsInverted() bool { return i.Lo > i.Hi }
|
||||
|
||||
// Invert returns the interval with endpoints swapped.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Invert() Interval {
|
||||
return Interval{i.Hi, i.Lo}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Center returns the midpoint of the interval.
|
||||
// It is undefined for full and empty intervals.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Center() float64 {
|
||||
c := 0.5 * (i.Lo + i.Hi)
|
||||
if !i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c <= 0 {
|
||||
return c + math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c - math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Length returns the length of the interval.
|
||||
// The length of an empty interval is negative.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Length() float64 {
|
||||
l := i.Hi - i.Lo
|
||||
if l >= 0 {
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
l += 2 * math.Pi
|
||||
if l > 0 {
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Assumes p ∈ (-π,π].
|
||||
func (i Interval) fastContains(p float64) bool {
|
||||
if i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return (p >= i.Lo || p <= i.Hi) && !i.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p >= i.Lo && p <= i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains returns true iff the interval contains p.
|
||||
// Assumes p ∈ [-π,π].
|
||||
func (i Interval) Contains(p float64) bool {
|
||||
if p == -math.Pi {
|
||||
p = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i.fastContains(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsInterval returns true iff the interval contains oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) ContainsInterval(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
if oi.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return oi.Lo >= i.Lo && oi.Hi <= i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (oi.Lo >= i.Lo || oi.Hi <= i.Hi) && !i.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oi.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return i.IsFull() || oi.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return oi.Lo >= i.Lo && oi.Hi <= i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContains returns true iff the interior of the interval contains p.
|
||||
// Assumes p ∈ [-π,π].
|
||||
func (i Interval) InteriorContains(p float64) bool {
|
||||
if p == -math.Pi {
|
||||
p = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return p > i.Lo || p < i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (p > i.Lo && p < i.Hi) || i.IsFull()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContainsInterval returns true iff the interior of the interval contains oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) InteriorContainsInterval(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
if oi.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return (oi.Lo > i.Lo && oi.Hi < i.Hi) || oi.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return oi.Lo > i.Lo || oi.Hi < i.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oi.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return i.IsFull() || oi.IsEmpty()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (oi.Lo > i.Lo && oi.Hi < i.Hi) || i.IsFull()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersects returns true iff the interval contains any points in common with oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Intersects(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() || oi.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return oi.IsInverted() || oi.Lo <= i.Hi || oi.Hi >= i.Lo
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oi.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return oi.Lo <= i.Hi || oi.Hi >= i.Lo
|
||||
}
|
||||
return oi.Lo <= i.Hi && oi.Hi >= i.Lo
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorIntersects returns true iff the interior of the interval contains any points in common with oi, including the latter's boundary.
|
||||
func (i Interval) InteriorIntersects(oi Interval) bool {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() || oi.IsEmpty() || i.Lo == i.Hi {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return oi.IsInverted() || oi.Lo < i.Hi || oi.Hi > i.Lo
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oi.IsInverted() {
|
||||
return oi.Lo < i.Hi || oi.Hi > i.Lo
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (oi.Lo < i.Hi && oi.Hi > i.Lo) || i.IsFull()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute distance from a to b in [0,2π], in a numerically stable way.
|
||||
func positiveDistance(a, b float64) float64 {
|
||||
d := b - a
|
||||
if d >= 0 {
|
||||
return d
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (b + math.Pi) - (a - math.Pi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Union returns the smallest interval that contains both the interval and oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Union(oi Interval) Interval {
|
||||
if oi.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.fastContains(oi.Lo) {
|
||||
if i.fastContains(oi.Hi) {
|
||||
// Either oi ⊂ i, or i ∪ oi is the full interval.
|
||||
if i.ContainsInterval(oi) {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return FullInterval()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{i.Lo, oi.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.fastContains(oi.Hi) {
|
||||
return Interval{oi.Lo, i.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Neither endpoint of oi is in i. Either i ⊂ oi, or i and oi are disjoint.
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() || oi.fastContains(i.Lo) {
|
||||
return oi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This is the only hard case where we need to find the closest pair of endpoints.
|
||||
if positiveDistance(oi.Hi, i.Lo) < positiveDistance(i.Hi, oi.Lo) {
|
||||
return Interval{oi.Lo, i.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{i.Lo, oi.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersection returns the smallest interval that contains the intersection of the interval and oi.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Intersection(oi Interval) Interval {
|
||||
if oi.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return EmptyInterval()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.fastContains(oi.Lo) {
|
||||
if i.fastContains(oi.Hi) {
|
||||
// Either oi ⊂ i, or i and oi intersect twice. Neither are empty.
|
||||
// In the first case we want to return i (which is shorter than oi).
|
||||
// In the second case one of them is inverted, and the smallest interval
|
||||
// that covers the two disjoint pieces is the shorter of i and oi.
|
||||
// We thus want to pick the shorter of i and oi in both cases.
|
||||
if oi.Length() < i.Length() {
|
||||
return oi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{oi.Lo, i.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.fastContains(oi.Hi) {
|
||||
return Interval{i.Lo, oi.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Neither endpoint of oi is in i. Either i ⊂ oi, or i and oi are disjoint.
|
||||
if oi.fastContains(i.Lo) {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return EmptyInterval()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPoint returns the interval expanded by the minimum amount necessary such
|
||||
// that it contains the given point "p" (an angle in the range [-Pi, Pi]).
|
||||
func (i Interval) AddPoint(p float64) Interval {
|
||||
if math.Abs(p) > math.Pi {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p == -math.Pi {
|
||||
p = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.fastContains(p) {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return Interval{p, p}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if positiveDistance(p, i.Lo) < positiveDistance(i.Hi, p) {
|
||||
return Interval{p, i.Hi}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Interval{i.Lo, p}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Define the maximum rounding error for arithmetic operations. Depending on the
|
||||
// platform the mantissa precision may be different than others, so we choose to
|
||||
// use specific values to be consistent across all.
|
||||
// The values come from the C++ implementation.
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// epsilon is a small number that represents a reasonable level of noise between two
|
||||
// values that can be considered to be equal.
|
||||
epsilon = 1e-15
|
||||
// dblEpsilon is a smaller number for values that require more precision.
|
||||
dblEpsilon = 2.220446049e-16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Expanded returns an interval that has been expanded on each side by margin.
|
||||
// If margin is negative, then the function shrinks the interval on
|
||||
// each side by margin instead. The resulting interval may be empty or
|
||||
// full. Any expansion (positive or negative) of a full interval remains
|
||||
// full, and any expansion of an empty interval remains empty.
|
||||
func (i Interval) Expanded(margin float64) Interval {
|
||||
if margin >= 0 {
|
||||
if i.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Check whether this interval will be full after expansion, allowing
|
||||
// for a rounding error when computing each endpoint.
|
||||
if i.Length()+2*margin+2*dblEpsilon >= 2*math.Pi {
|
||||
return FullInterval()
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if i.IsFull() {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Check whether this interval will be empty after expansion, allowing
|
||||
// for a rounding error when computing each endpoint.
|
||||
if i.Length()+2*margin-2*dblEpsilon <= 0 {
|
||||
return EmptyInterval()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
result := IntervalFromEndpoints(
|
||||
math.Remainder(i.Lo-margin, 2*math.Pi),
|
||||
math.Remainder(i.Hi+margin, 2*math.Pi),
|
||||
)
|
||||
if result.Lo <= -math.Pi {
|
||||
result.Lo = math.Pi
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i Interval) String() string {
|
||||
// like "[%.7f, %.7f]"
|
||||
return "[" + strconv.FormatFloat(i.Lo, 'f', 7, 64) + ", " + strconv.FormatFloat(i.Hi, 'f', 7, 64) + "]"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BUG(dsymonds): The major differences from the C++ version are:
|
||||
// - no validity checking on construction, etc. (not a bug?)
|
||||
// - a few operations
|
||||
53
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/bits_go18.go
generated
vendored
53
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/bits_go18.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2018 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
// This file is for the bit manipulation code pre-Go 1.9.
|
||||
|
||||
// findMSBSetNonZero64 returns the index (between 0 and 63) of the most
|
||||
// significant set bit. Passing zero to this function returns zero.
|
||||
func findMSBSetNonZero64(x uint64) int {
|
||||
val := []uint64{0x2, 0xC, 0xF0, 0xFF00, 0xFFFF0000, 0xFFFFFFFF00000000}
|
||||
shift := []uint64{1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32}
|
||||
var msbPos uint64
|
||||
for i := 5; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if x&val[i] != 0 {
|
||||
x >>= shift[i]
|
||||
msbPos |= shift[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return int(msbPos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const deBruijn64 = 0x03f79d71b4ca8b09
|
||||
const digitMask = uint64(1<<64 - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
var deBruijn64Lookup = []byte{
|
||||
0, 1, 56, 2, 57, 49, 28, 3, 61, 58, 42, 50, 38, 29, 17, 4,
|
||||
62, 47, 59, 36, 45, 43, 51, 22, 53, 39, 33, 30, 24, 18, 12, 5,
|
||||
63, 55, 48, 27, 60, 41, 37, 16, 46, 35, 44, 21, 52, 32, 23, 11,
|
||||
54, 26, 40, 15, 34, 20, 31, 10, 25, 14, 19, 9, 13, 8, 7, 6,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// findLSBSetNonZero64 returns the index (between 0 and 63) of the least
|
||||
// significant set bit. Passing zero to this function returns zero.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This code comes from trailingZeroBits in https://golang.org/src/math/big/nat.go
|
||||
// which references (Knuth, volume 4, section 7.3.1).
|
||||
func findLSBSetNonZero64(x uint64) int {
|
||||
return int(deBruijn64Lookup[((x&-x)*(deBruijn64&digitMask))>>58])
|
||||
}
|
||||
39
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/bits_go19.go
generated
vendored
39
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/bits_go19.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2018 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
// This file is for the bit manipulation code post-Go 1.9.
|
||||
|
||||
import "math/bits"
|
||||
|
||||
// findMSBSetNonZero64 returns the index (between 0 and 63) of the most
|
||||
// significant set bit. Passing zero to this function return zero.
|
||||
func findMSBSetNonZero64(x uint64) int {
|
||||
if x == 0 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 63 - bits.LeadingZeros64(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// findLSBSetNonZero64 returns the index (between 0 and 63) of the least
|
||||
// significant set bit. Passing zero to this function return zero.
|
||||
func findLSBSetNonZero64(x uint64) int {
|
||||
if x == 0 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bits.TrailingZeros64(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
519
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cap.go
generated
vendored
519
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cap.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,519 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r1"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// centerPoint is the default center for Caps
|
||||
centerPoint = PointFromCoords(1.0, 0, 0)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Cap represents a disc-shaped region defined by a center and radius.
|
||||
// Technically this shape is called a "spherical cap" (rather than disc)
|
||||
// because it is not planar; the cap represents a portion of the sphere that
|
||||
// has been cut off by a plane. The boundary of the cap is the circle defined
|
||||
// by the intersection of the sphere and the plane. For containment purposes,
|
||||
// the cap is a closed set, i.e. it contains its boundary.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the most part, you can use a spherical cap wherever you would use a
|
||||
// disc in planar geometry. The radius of the cap is measured along the
|
||||
// surface of the sphere (rather than the straight-line distance through the
|
||||
// interior). Thus a cap of radius π/2 is a hemisphere, and a cap of radius
|
||||
// π covers the entire sphere.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The center is a point on the surface of the unit sphere. (Hence the need for
|
||||
// it to be of unit length.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A cap can also be defined by its center point and height. The height is the
|
||||
// distance from the center point to the cutoff plane. There is also support for
|
||||
// "empty" and "full" caps, which contain no points and all points respectively.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Here are some useful relationships between the cap height (h), the cap
|
||||
// radius (r), the maximum chord length from the cap's center (d), and the
|
||||
// radius of cap's base (a).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// h = 1 - cos(r)
|
||||
// = 2 * sin^2(r/2)
|
||||
// d^2 = 2 * h
|
||||
// = a^2 + h^2
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The zero value of Cap is an invalid cap. Use EmptyCap to get a valid empty cap.
|
||||
type Cap struct {
|
||||
center Point
|
||||
radius s1.ChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapFromPoint constructs a cap containing a single point.
|
||||
func CapFromPoint(p Point) Cap {
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(p, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapFromCenterAngle constructs a cap with the given center and angle.
|
||||
func CapFromCenterAngle(center Point, angle s1.Angle) Cap {
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(center, s1.ChordAngleFromAngle(angle))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapFromCenterChordAngle constructs a cap where the angle is expressed as an
|
||||
// s1.ChordAngle. This constructor is more efficient than using an s1.Angle.
|
||||
func CapFromCenterChordAngle(center Point, radius s1.ChordAngle) Cap {
|
||||
return Cap{
|
||||
center: center,
|
||||
radius: radius,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapFromCenterHeight constructs a cap with the given center and height. A
|
||||
// negative height yields an empty cap; a height of 2 or more yields a full cap.
|
||||
// The center should be unit length.
|
||||
func CapFromCenterHeight(center Point, height float64) Cap {
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(center, s1.ChordAngleFromSquaredLength(2*height))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapFromCenterArea constructs a cap with the given center and surface area.
|
||||
// Note that the area can also be interpreted as the solid angle subtended by the
|
||||
// cap (because the sphere has unit radius). A negative area yields an empty cap;
|
||||
// an area of 4*π or more yields a full cap.
|
||||
func CapFromCenterArea(center Point, area float64) Cap {
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(center, s1.ChordAngleFromSquaredLength(area/math.Pi))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EmptyCap returns a cap that contains no points.
|
||||
func EmptyCap() Cap {
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(centerPoint, s1.NegativeChordAngle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FullCap returns a cap that contains all points.
|
||||
func FullCap() Cap {
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(centerPoint, s1.StraightChordAngle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsValid reports whether the Cap is considered valid.
|
||||
func (c Cap) IsValid() bool {
|
||||
return c.center.Vector.IsUnit() && c.radius <= s1.StraightChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsEmpty reports whether the cap is empty, i.e. it contains no points.
|
||||
func (c Cap) IsEmpty() bool {
|
||||
return c.radius < 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsFull reports whether the cap is full, i.e. it contains all points.
|
||||
func (c Cap) IsFull() bool {
|
||||
return c.radius == s1.StraightChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Center returns the cap's center point.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Center() Point {
|
||||
return c.center
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height returns the height of the cap. This is the distance from the center
|
||||
// point to the cutoff plane.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Height() float64 {
|
||||
return float64(0.5 * c.radius)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Radius returns the cap radius as an s1.Angle. (Note that the cap angle
|
||||
// is stored internally as a ChordAngle, so this method requires a trigonometric
|
||||
// operation and may yield a slightly different result than the value passed
|
||||
// to CapFromCenterAngle).
|
||||
func (c Cap) Radius() s1.Angle {
|
||||
return c.radius.Angle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Area returns the surface area of the Cap on the unit sphere.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Area() float64 {
|
||||
return 2.0 * math.Pi * math.Max(0, c.Height())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains reports whether this cap contains the other.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Contains(other Cap) bool {
|
||||
// In a set containment sense, every cap contains the empty cap.
|
||||
if c.IsFull() || other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c.radius >= ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, other.center).Add(other.radius)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersects reports whether this cap intersects the other cap.
|
||||
// i.e. whether they have any points in common.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Intersects(other Cap) bool {
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() || other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c.radius.Add(other.radius) >= ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, other.center)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorIntersects reports whether this caps interior intersects the other cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) InteriorIntersects(other Cap) bool {
|
||||
// Make sure this cap has an interior and the other cap is non-empty.
|
||||
if c.radius <= 0 || other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c.radius.Add(other.radius) > ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, other.center)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsPoint reports whether this cap contains the point.
|
||||
func (c Cap) ContainsPoint(p Point) bool {
|
||||
return ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, p) <= c.radius
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InteriorContainsPoint reports whether the point is within the interior of this cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) InteriorContainsPoint(p Point) bool {
|
||||
return c.IsFull() || ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, p) < c.radius
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Complement returns the complement of the interior of the cap. A cap and its
|
||||
// complement have the same boundary but do not share any interior points.
|
||||
// The complement operator is not a bijection because the complement of a
|
||||
// singleton cap (containing a single point) is the same as the complement
|
||||
// of an empty cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Complement() Cap {
|
||||
if c.IsFull() {
|
||||
return EmptyCap()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return FullCap()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(Point{c.center.Mul(-1)}, s1.StraightChordAngle.Sub(c.radius))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapBound returns a bounding spherical cap. This is not guaranteed to be exact.
|
||||
func (c Cap) CapBound() Cap {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RectBound returns a bounding latitude-longitude rectangle.
|
||||
// The bounds are not guaranteed to be tight.
|
||||
func (c Cap) RectBound() Rect {
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return EmptyRect()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
capAngle := c.Radius().Radians()
|
||||
allLongitudes := false
|
||||
lat := r1.Interval{
|
||||
Lo: latitude(c.center).Radians() - capAngle,
|
||||
Hi: latitude(c.center).Radians() + capAngle,
|
||||
}
|
||||
lng := s1.FullInterval()
|
||||
|
||||
// Check whether cap includes the south pole.
|
||||
if lat.Lo <= -math.Pi/2 {
|
||||
lat.Lo = -math.Pi / 2
|
||||
allLongitudes = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check whether cap includes the north pole.
|
||||
if lat.Hi >= math.Pi/2 {
|
||||
lat.Hi = math.Pi / 2
|
||||
allLongitudes = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !allLongitudes {
|
||||
// Compute the range of longitudes covered by the cap. We use the law
|
||||
// of sines for spherical triangles. Consider the triangle ABC where
|
||||
// A is the north pole, B is the center of the cap, and C is the point
|
||||
// of tangency between the cap boundary and a line of longitude. Then
|
||||
// C is a right angle, and letting a,b,c denote the sides opposite A,B,C,
|
||||
// we have sin(a)/sin(A) = sin(c)/sin(C), or sin(A) = sin(a)/sin(c).
|
||||
// Here "a" is the cap angle, and "c" is the colatitude (90 degrees
|
||||
// minus the latitude). This formula also works for negative latitudes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The formula for sin(a) follows from the relationship h = 1 - cos(a).
|
||||
sinA := c.radius.Sin()
|
||||
sinC := math.Cos(latitude(c.center).Radians())
|
||||
if sinA <= sinC {
|
||||
angleA := math.Asin(sinA / sinC)
|
||||
lng.Lo = math.Remainder(longitude(c.center).Radians()-angleA, math.Pi*2)
|
||||
lng.Hi = math.Remainder(longitude(c.center).Radians()+angleA, math.Pi*2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Rect{lat, lng}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Equal reports whether this cap is equal to the other cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Equal(other Cap) bool {
|
||||
return (c.radius == other.radius && c.center == other.center) ||
|
||||
(c.IsEmpty() && other.IsEmpty()) ||
|
||||
(c.IsFull() && other.IsFull())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApproxEqual reports whether this cap is equal to the other cap within the given tolerance.
|
||||
func (c Cap) ApproxEqual(other Cap) bool {
|
||||
const epsilon = 1e-14
|
||||
r2 := float64(c.radius)
|
||||
otherR2 := float64(other.radius)
|
||||
return c.center.ApproxEqual(other.center) &&
|
||||
math.Abs(r2-otherR2) <= epsilon ||
|
||||
c.IsEmpty() && otherR2 <= epsilon ||
|
||||
other.IsEmpty() && r2 <= epsilon ||
|
||||
c.IsFull() && otherR2 >= 2-epsilon ||
|
||||
other.IsFull() && r2 >= 2-epsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddPoint increases the cap if necessary to include the given point. If this cap is empty,
|
||||
// then the center is set to the point with a zero height. p must be unit-length.
|
||||
func (c Cap) AddPoint(p Point) Cap {
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
c.center = p
|
||||
c.radius = 0
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// After calling cap.AddPoint(p), cap.Contains(p) must be true. However
|
||||
// we don't need to do anything special to achieve this because Contains()
|
||||
// does exactly the same distance calculation that we do here.
|
||||
if newRad := ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, p); newRad > c.radius {
|
||||
c.radius = newRad
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddCap increases the cap height if necessary to include the other cap. If this cap is empty,
|
||||
// it is set to the other cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) AddCap(other Cap) Cap {
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return other
|
||||
}
|
||||
if other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We round up the distance to ensure that the cap is actually contained.
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): Do some error analysis in order to guarantee this.
|
||||
dist := ChordAngleBetweenPoints(c.center, other.center).Add(other.radius)
|
||||
if newRad := dist.Expanded(dblEpsilon * float64(dist)); newRad > c.radius {
|
||||
c.radius = newRad
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Expanded returns a new cap expanded by the given angle. If the cap is empty,
|
||||
// it returns an empty cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Expanded(distance s1.Angle) Cap {
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return EmptyCap()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return CapFromCenterChordAngle(c.center, c.radius.Add(s1.ChordAngleFromAngle(distance)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Cap) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("[Center=%v, Radius=%f]", c.center.Vector, c.Radius().Degrees())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// radiusToHeight converts an s1.Angle into the height of the cap.
|
||||
func radiusToHeight(r s1.Angle) float64 {
|
||||
if r.Radians() < 0 {
|
||||
return float64(s1.NegativeChordAngle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r.Radians() >= math.Pi {
|
||||
return float64(s1.RightChordAngle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return float64(0.5 * s1.ChordAngleFromAngle(r))
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsCell reports whether the cap contains the given cell.
|
||||
func (c Cap) ContainsCell(cell Cell) bool {
|
||||
// If the cap does not contain all cell vertices, return false.
|
||||
var vertices [4]Point
|
||||
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
|
||||
vertices[k] = cell.Vertex(k)
|
||||
if !c.ContainsPoint(vertices[k]) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Otherwise, return true if the complement of the cap does not intersect the cell.
|
||||
return !c.Complement().intersects(cell, vertices)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntersectsCell reports whether the cap intersects the cell.
|
||||
func (c Cap) IntersectsCell(cell Cell) bool {
|
||||
// If the cap contains any cell vertex, return true.
|
||||
var vertices [4]Point
|
||||
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
|
||||
vertices[k] = cell.Vertex(k)
|
||||
if c.ContainsPoint(vertices[k]) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c.intersects(cell, vertices)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersects reports whether the cap intersects any point of the cell excluding
|
||||
// its vertices (which are assumed to already have been checked).
|
||||
func (c Cap) intersects(cell Cell, vertices [4]Point) bool {
|
||||
// If the cap is a hemisphere or larger, the cell and the complement of the cap
|
||||
// are both convex. Therefore since no vertex of the cell is contained, no other
|
||||
// interior point of the cell is contained either.
|
||||
if c.radius >= s1.RightChordAngle {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We need to check for empty caps due to the center check just below.
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimization: return true if the cell contains the cap center. This allows half
|
||||
// of the edge checks below to be skipped.
|
||||
if cell.ContainsPoint(c.center) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// At this point we know that the cell does not contain the cap center, and the cap
|
||||
// does not contain any cell vertex. The only way that they can intersect is if the
|
||||
// cap intersects the interior of some edge.
|
||||
sin2Angle := c.radius.Sin2()
|
||||
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
|
||||
edge := cell.Edge(k).Vector
|
||||
dot := c.center.Vector.Dot(edge)
|
||||
if dot > 0 {
|
||||
// The center is in the interior half-space defined by the edge. We do not need
|
||||
// to consider these edges, since if the cap intersects this edge then it also
|
||||
// intersects the edge on the opposite side of the cell, because the center is
|
||||
// not contained with the cell.
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The Norm2() factor is necessary because "edge" is not normalized.
|
||||
if dot*dot > sin2Angle*edge.Norm2() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the great circle containing this edge intersects the interior of the cap. We just
|
||||
// need to check whether the point of closest approach occurs between the two edge endpoints.
|
||||
dir := edge.Cross(c.center.Vector)
|
||||
if dir.Dot(vertices[k].Vector) < 0 && dir.Dot(vertices[(k+1)&3].Vector) > 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionBound computes a covering of the Cap. In general the covering
|
||||
// consists of at most 4 cells except for very large caps, which may need
|
||||
// up to 6 cells. The output is not sorted.
|
||||
func (c Cap) CellUnionBound() []CellID {
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): The covering could be made quite a bit tighter by mapping
|
||||
// the cap to a rectangle in (i,j)-space and finding a covering for that.
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the maximum level such that the cap contains at most one cell vertex
|
||||
// and such that CellID.AppendVertexNeighbors() can be called.
|
||||
level := MinWidthMetric.MaxLevel(c.Radius().Radians()) - 1
|
||||
|
||||
// If level < 0, more than three face cells are required.
|
||||
if level < 0 {
|
||||
cellIDs := make([]CellID, 6)
|
||||
for face := 0; face < 6; face++ {
|
||||
cellIDs[face] = CellIDFromFace(face)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cellIDs
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The covering consists of the 4 cells at the given level that share the
|
||||
// cell vertex that is closest to the cap center.
|
||||
return cellIDFromPoint(c.center).VertexNeighbors(level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Centroid returns the true centroid of the cap multiplied by its surface area
|
||||
// The result lies on the ray from the origin through the cap's center, but it
|
||||
// is not unit length. Note that if you just want the "surface centroid", i.e.
|
||||
// the normalized result, then it is simpler to call Center.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The reason for multiplying the result by the cap area is to make it
|
||||
// easier to compute the centroid of more complicated shapes. The centroid
|
||||
// of a union of disjoint regions can be computed simply by adding their
|
||||
// Centroid() results. Caveat: for caps that contain a single point
|
||||
// (i.e., zero radius), this method always returns the origin (0, 0, 0).
|
||||
// This is because shapes with no area don't affect the centroid of a
|
||||
// union whose total area is positive.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Centroid() Point {
|
||||
// From symmetry, the centroid of the cap must be somewhere on the line
|
||||
// from the origin to the center of the cap on the surface of the sphere.
|
||||
// When a sphere is divided into slices of constant thickness by a set of
|
||||
// parallel planes, all slices have the same surface area. This implies
|
||||
// that the radial component of the centroid is simply the midpoint of the
|
||||
// range of radial distances spanned by the cap. That is easily computed
|
||||
// from the cap height.
|
||||
if c.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return Point{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
r := 1 - 0.5*c.Height()
|
||||
return Point{c.center.Mul(r * c.Area())}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Union returns the smallest cap which encloses this cap and other.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Union(other Cap) Cap {
|
||||
// If the other cap is larger, swap c and other for the rest of the computations.
|
||||
if c.radius < other.radius {
|
||||
c, other = other, c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c.IsFull() || other.IsEmpty() {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: This calculation would be more efficient using s1.ChordAngles.
|
||||
cRadius := c.Radius()
|
||||
otherRadius := other.Radius()
|
||||
distance := c.center.Distance(other.center)
|
||||
if cRadius >= distance+otherRadius {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
resRadius := 0.5 * (distance + cRadius + otherRadius)
|
||||
resCenter := InterpolateAtDistance(0.5*(distance-cRadius+otherRadius), c.center, other.center)
|
||||
return CapFromCenterAngle(resCenter, resRadius)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Encode encodes the Cap.
|
||||
func (c Cap) Encode(w io.Writer) error {
|
||||
e := &encoder{w: w}
|
||||
c.encode(e)
|
||||
return e.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Cap) encode(e *encoder) {
|
||||
e.writeFloat64(c.center.X)
|
||||
e.writeFloat64(c.center.Y)
|
||||
e.writeFloat64(c.center.Z)
|
||||
e.writeFloat64(float64(c.radius))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode decodes the Cap.
|
||||
func (c *Cap) Decode(r io.Reader) error {
|
||||
d := &decoder{r: asByteReader(r)}
|
||||
c.decode(d)
|
||||
return d.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *Cap) decode(d *decoder) {
|
||||
c.center.X = d.readFloat64()
|
||||
c.center.Y = d.readFloat64()
|
||||
c.center.Z = d.readFloat64()
|
||||
c.radius = s1.ChordAngle(d.readFloat64())
|
||||
}
|
||||
698
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cell.go
generated
vendored
698
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cell.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,698 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r1"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r2"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r3"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Cell is an S2 region object that represents a cell. Unlike CellIDs,
|
||||
// it supports efficient containment and intersection tests. However, it is
|
||||
// also a more expensive representation.
|
||||
type Cell struct {
|
||||
face int8
|
||||
level int8
|
||||
orientation int8
|
||||
id CellID
|
||||
uv r2.Rect
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellFromCellID constructs a Cell corresponding to the given CellID.
|
||||
func CellFromCellID(id CellID) Cell {
|
||||
c := Cell{}
|
||||
c.id = id
|
||||
f, i, j, o := c.id.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
c.face = int8(f)
|
||||
c.level = int8(c.id.Level())
|
||||
c.orientation = int8(o)
|
||||
c.uv = ijLevelToBoundUV(i, j, int(c.level))
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellFromPoint constructs a cell for the given Point.
|
||||
func CellFromPoint(p Point) Cell {
|
||||
return CellFromCellID(cellIDFromPoint(p))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellFromLatLng constructs a cell for the given LatLng.
|
||||
func CellFromLatLng(ll LatLng) Cell {
|
||||
return CellFromCellID(CellIDFromLatLng(ll))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Face returns the face this cell is on.
|
||||
func (c Cell) Face() int {
|
||||
return int(c.face)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// oppositeFace returns the face opposite the given face.
|
||||
func oppositeFace(face int) int {
|
||||
return (face + 3) % 6
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Level returns the level of this cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) Level() int {
|
||||
return int(c.level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ID returns the CellID this cell represents.
|
||||
func (c Cell) ID() CellID {
|
||||
return c.id
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsLeaf returns whether this Cell is a leaf or not.
|
||||
func (c Cell) IsLeaf() bool {
|
||||
return c.level == maxLevel
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SizeIJ returns the edge length of this cell in (i,j)-space.
|
||||
func (c Cell) SizeIJ() int {
|
||||
return sizeIJ(int(c.level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SizeST returns the edge length of this cell in (s,t)-space.
|
||||
func (c Cell) SizeST() float64 {
|
||||
return c.id.sizeST(int(c.level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Vertex returns the k-th vertex of the cell (k = 0,1,2,3) in CCW order
|
||||
// (lower left, lower right, upper right, upper left in the UV plane).
|
||||
func (c Cell) Vertex(k int) Point {
|
||||
return Point{faceUVToXYZ(int(c.face), c.uv.Vertices()[k].X, c.uv.Vertices()[k].Y).Normalize()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Edge returns the inward-facing normal of the great circle passing through
|
||||
// the CCW ordered edge from vertex k to vertex k+1 (mod 4) (for k = 0,1,2,3).
|
||||
func (c Cell) Edge(k int) Point {
|
||||
switch k {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return Point{vNorm(int(c.face), c.uv.Y.Lo).Normalize()} // Bottom
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
return Point{uNorm(int(c.face), c.uv.X.Hi).Normalize()} // Right
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
return Point{vNorm(int(c.face), c.uv.Y.Hi).Mul(-1.0).Normalize()} // Top
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return Point{uNorm(int(c.face), c.uv.X.Lo).Mul(-1.0).Normalize()} // Left
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BoundUV returns the bounds of this cell in (u,v)-space.
|
||||
func (c Cell) BoundUV() r2.Rect {
|
||||
return c.uv
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Center returns the direction vector corresponding to the center in
|
||||
// (s,t)-space of the given cell. This is the point at which the cell is
|
||||
// divided into four subcells; it is not necessarily the centroid of the
|
||||
// cell in (u,v)-space or (x,y,z)-space
|
||||
func (c Cell) Center() Point {
|
||||
return Point{c.id.rawPoint().Normalize()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Children returns the four direct children of this cell in traversal order
|
||||
// and returns true. If this is a leaf cell, or the children could not be created,
|
||||
// false is returned.
|
||||
// The C++ method is called Subdivide.
|
||||
func (c Cell) Children() ([4]Cell, bool) {
|
||||
var children [4]Cell
|
||||
|
||||
if c.id.IsLeaf() {
|
||||
return children, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the cell midpoint in uv-space.
|
||||
uvMid := c.id.centerUV()
|
||||
|
||||
// Create four children with the appropriate bounds.
|
||||
cid := c.id.ChildBegin()
|
||||
for pos := 0; pos < 4; pos++ {
|
||||
children[pos] = Cell{
|
||||
face: c.face,
|
||||
level: c.level + 1,
|
||||
orientation: c.orientation ^ int8(posToOrientation[pos]),
|
||||
id: cid,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We want to split the cell in half in u and v. To decide which
|
||||
// side to set equal to the midpoint value, we look at cell's (i,j)
|
||||
// position within its parent. The index for i is in bit 1 of ij.
|
||||
ij := posToIJ[c.orientation][pos]
|
||||
i := ij >> 1
|
||||
j := ij & 1
|
||||
if i == 1 {
|
||||
children[pos].uv.X.Hi = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
children[pos].uv.X.Lo = uvMid.X
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
children[pos].uv.X.Lo = c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
children[pos].uv.X.Hi = uvMid.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j == 1 {
|
||||
children[pos].uv.Y.Hi = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
children[pos].uv.Y.Lo = uvMid.Y
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
children[pos].uv.Y.Lo = c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
children[pos].uv.Y.Hi = uvMid.Y
|
||||
}
|
||||
cid = cid.Next()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return children, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExactArea returns the area of this cell as accurately as possible.
|
||||
func (c Cell) ExactArea() float64 {
|
||||
v0, v1, v2, v3 := c.Vertex(0), c.Vertex(1), c.Vertex(2), c.Vertex(3)
|
||||
return PointArea(v0, v1, v2) + PointArea(v0, v2, v3)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApproxArea returns the approximate area of this cell. This method is accurate
|
||||
// to within 3% percent for all cell sizes and accurate to within 0.1% for cells
|
||||
// at level 5 or higher (i.e. squares 350km to a side or smaller on the Earth's
|
||||
// surface). It is moderately cheap to compute.
|
||||
func (c Cell) ApproxArea() float64 {
|
||||
// All cells at the first two levels have the same area.
|
||||
if c.level < 2 {
|
||||
return c.AverageArea()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// First, compute the approximate area of the cell when projected
|
||||
// perpendicular to its normal. The cross product of its diagonals gives
|
||||
// the normal, and the length of the normal is twice the projected area.
|
||||
flatArea := 0.5 * (c.Vertex(2).Sub(c.Vertex(0).Vector).
|
||||
Cross(c.Vertex(3).Sub(c.Vertex(1).Vector)).Norm())
|
||||
|
||||
// Now, compensate for the curvature of the cell surface by pretending
|
||||
// that the cell is shaped like a spherical cap. The ratio of the
|
||||
// area of a spherical cap to the area of its projected disc turns out
|
||||
// to be 2 / (1 + sqrt(1 - r*r)) where r is the radius of the disc.
|
||||
// For example, when r=0 the ratio is 1, and when r=1 the ratio is 2.
|
||||
// Here we set Pi*r*r == flatArea to find the equivalent disc.
|
||||
return flatArea * 2 / (1 + math.Sqrt(1-math.Min(1/math.Pi*flatArea, 1)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AverageArea returns the average area of cells at the level of this cell.
|
||||
// This is accurate to within a factor of 1.7.
|
||||
func (c Cell) AverageArea() float64 {
|
||||
return AvgAreaMetric.Value(int(c.level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntersectsCell reports whether the intersection of this cell and the other cell is not nil.
|
||||
func (c Cell) IntersectsCell(oc Cell) bool {
|
||||
return c.id.Intersects(oc.id)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsCell reports whether this cell contains the other cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) ContainsCell(oc Cell) bool {
|
||||
return c.id.Contains(oc.id)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionBound computes a covering of the Cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) CellUnionBound() []CellID {
|
||||
return c.CapBound().CellUnionBound()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// latitude returns the latitude of the cell vertex in radians given by (i,j),
|
||||
// where i and j indicate the Hi (1) or Lo (0) corner.
|
||||
func (c Cell) latitude(i, j int) float64 {
|
||||
var u, v float64
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case i == 0 && j == 0:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
case i == 0 && j == 1:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
case i == 1 && j == 0:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
case i == 1 && j == 1:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("i and/or j is out of bounds")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return latitude(Point{faceUVToXYZ(int(c.face), u, v)}).Radians()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// longitude returns the longitude of the cell vertex in radians given by (i,j),
|
||||
// where i and j indicate the Hi (1) or Lo (0) corner.
|
||||
func (c Cell) longitude(i, j int) float64 {
|
||||
var u, v float64
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case i == 0 && j == 0:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
case i == 0 && j == 1:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
case i == 1 && j == 0:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
case i == 1 && j == 1:
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("i and/or j is out of bounds")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return longitude(Point{faceUVToXYZ(int(c.face), u, v)}).Radians()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
poleMinLat = math.Asin(math.Sqrt(1.0/3)) - 0.5*dblEpsilon
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RectBound returns the bounding rectangle of this cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) RectBound() Rect {
|
||||
if c.level > 0 {
|
||||
// Except for cells at level 0, the latitude and longitude extremes are
|
||||
// attained at the vertices. Furthermore, the latitude range is
|
||||
// determined by one pair of diagonally opposite vertices and the
|
||||
// longitude range is determined by the other pair.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We first determine which corner (i,j) of the cell has the largest
|
||||
// absolute latitude. To maximize latitude, we want to find the point in
|
||||
// the cell that has the largest absolute z-coordinate and the smallest
|
||||
// absolute x- and y-coordinates. To do this we look at each coordinate
|
||||
// (u and v), and determine whether we want to minimize or maximize that
|
||||
// coordinate based on the axis direction and the cell's (u,v) quadrant.
|
||||
u := c.uv.X.Lo + c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
v := c.uv.Y.Lo + c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
var i, j int
|
||||
if uAxis(int(c.face)).Z == 0 {
|
||||
if u < 0 {
|
||||
i = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if u > 0 {
|
||||
i = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if vAxis(int(c.face)).Z == 0 {
|
||||
if v < 0 {
|
||||
j = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if v > 0 {
|
||||
j = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
lat := r1.IntervalFromPoint(c.latitude(i, j)).AddPoint(c.latitude(1-i, 1-j))
|
||||
lng := s1.EmptyInterval().AddPoint(c.longitude(i, 1-j)).AddPoint(c.longitude(1-i, j))
|
||||
|
||||
// We grow the bounds slightly to make sure that the bounding rectangle
|
||||
// contains LatLngFromPoint(P) for any point P inside the loop L defined by the
|
||||
// four *normalized* vertices. Note that normalization of a vector can
|
||||
// change its direction by up to 0.5 * dblEpsilon radians, and it is not
|
||||
// enough just to add Normalize calls to the code above because the
|
||||
// latitude/longitude ranges are not necessarily determined by diagonally
|
||||
// opposite vertex pairs after normalization.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We would like to bound the amount by which the latitude/longitude of a
|
||||
// contained point P can exceed the bounds computed above. In the case of
|
||||
// longitude, the normalization error can change the direction of rounding
|
||||
// leading to a maximum difference in longitude of 2 * dblEpsilon. In
|
||||
// the case of latitude, the normalization error can shift the latitude by
|
||||
// up to 0.5 * dblEpsilon and the other sources of error can cause the
|
||||
// two latitudes to differ by up to another 1.5 * dblEpsilon, which also
|
||||
// leads to a maximum difference of 2 * dblEpsilon.
|
||||
return Rect{lat, lng}.expanded(LatLng{s1.Angle(2 * dblEpsilon), s1.Angle(2 * dblEpsilon)}).PolarClosure()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The 4 cells around the equator extend to +/-45 degrees latitude at the
|
||||
// midpoints of their top and bottom edges. The two cells covering the
|
||||
// poles extend down to +/-35.26 degrees at their vertices. The maximum
|
||||
// error in this calculation is 0.5 * dblEpsilon.
|
||||
var bound Rect
|
||||
switch c.face {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
bound = Rect{r1.Interval{-math.Pi / 4, math.Pi / 4}, s1.Interval{-math.Pi / 4, math.Pi / 4}}
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
bound = Rect{r1.Interval{-math.Pi / 4, math.Pi / 4}, s1.Interval{math.Pi / 4, 3 * math.Pi / 4}}
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
bound = Rect{r1.Interval{poleMinLat, math.Pi / 2}, s1.FullInterval()}
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
bound = Rect{r1.Interval{-math.Pi / 4, math.Pi / 4}, s1.Interval{3 * math.Pi / 4, -3 * math.Pi / 4}}
|
||||
case 4:
|
||||
bound = Rect{r1.Interval{-math.Pi / 4, math.Pi / 4}, s1.Interval{-3 * math.Pi / 4, -math.Pi / 4}}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
bound = Rect{r1.Interval{-math.Pi / 2, -poleMinLat}, s1.FullInterval()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Finally, we expand the bound to account for the error when a point P is
|
||||
// converted to an LatLng to test for containment. (The bound should be
|
||||
// large enough so that it contains the computed LatLng of any contained
|
||||
// point, not just the infinite-precision version.) We don't need to expand
|
||||
// longitude because longitude is calculated via a single call to math.Atan2,
|
||||
// which is guaranteed to be semi-monotonic.
|
||||
return bound.expanded(LatLng{s1.Angle(dblEpsilon), s1.Angle(0)})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapBound returns the bounding cap of this cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) CapBound() Cap {
|
||||
// We use the cell center in (u,v)-space as the cap axis. This vector is very close
|
||||
// to GetCenter() and faster to compute. Neither one of these vectors yields the
|
||||
// bounding cap with minimal surface area, but they are both pretty close.
|
||||
cap := CapFromPoint(Point{faceUVToXYZ(int(c.face), c.uv.Center().X, c.uv.Center().Y).Normalize()})
|
||||
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
|
||||
cap = cap.AddPoint(c.Vertex(k))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsPoint reports whether this cell contains the given point. Note that
|
||||
// unlike Loop/Polygon, a Cell is considered to be a closed set. This means
|
||||
// that a point on a Cell's edge or vertex belong to the Cell and the relevant
|
||||
// adjacent Cells too.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you want every point to be contained by exactly one Cell,
|
||||
// you will need to convert the Cell to a Loop.
|
||||
func (c Cell) ContainsPoint(p Point) bool {
|
||||
var uv r2.Point
|
||||
var ok bool
|
||||
if uv.X, uv.Y, ok = faceXYZToUV(int(c.face), p); !ok {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Expand the (u,v) bound to ensure that
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CellFromPoint(p).ContainsPoint(p)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// is always true. To do this, we need to account for the error when
|
||||
// converting from (u,v) coordinates to (s,t) coordinates. In the
|
||||
// normal case the total error is at most dblEpsilon.
|
||||
return c.uv.ExpandedByMargin(dblEpsilon).ContainsPoint(uv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Encode encodes the Cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) Encode(w io.Writer) error {
|
||||
e := &encoder{w: w}
|
||||
c.encode(e)
|
||||
return e.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Cell) encode(e *encoder) {
|
||||
c.id.encode(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode decodes the Cell.
|
||||
func (c *Cell) Decode(r io.Reader) error {
|
||||
d := &decoder{r: asByteReader(r)}
|
||||
c.decode(d)
|
||||
return d.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *Cell) decode(d *decoder) {
|
||||
c.id.decode(d)
|
||||
*c = CellFromCellID(c.id)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// vertexChordDist2 returns the squared chord distance from point P to the
|
||||
// given corner vertex specified by the Hi or Lo values of each.
|
||||
func (c Cell) vertexChordDist2(p Point, xHi, yHi bool) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
x := c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
y := c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
if xHi {
|
||||
x = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
if yHi {
|
||||
y = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ChordAngleBetweenPoints(p, PointFromCoords(x, y, 1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// uEdgeIsClosest reports whether a point P is closer to the interior of the specified
|
||||
// Cell edge (either the lower or upper edge of the Cell) or to the endpoints.
|
||||
func (c Cell) uEdgeIsClosest(p Point, vHi bool) bool {
|
||||
u0 := c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
u1 := c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
v := c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
if vHi {
|
||||
v = c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
// These are the normals to the planes that are perpendicular to the edge
|
||||
// and pass through one of its two endpoints.
|
||||
dir0 := r3.Vector{v*v + 1, -u0 * v, -u0}
|
||||
dir1 := r3.Vector{v*v + 1, -u1 * v, -u1}
|
||||
return p.Dot(dir0) > 0 && p.Dot(dir1) < 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// vEdgeIsClosest reports whether a point P is closer to the interior of the specified
|
||||
// Cell edge (either the right or left edge of the Cell) or to the endpoints.
|
||||
func (c Cell) vEdgeIsClosest(p Point, uHi bool) bool {
|
||||
v0 := c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
v1 := c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
u := c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
if uHi {
|
||||
u = c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
}
|
||||
dir0 := r3.Vector{-u * v0, u*u + 1, -v0}
|
||||
dir1 := r3.Vector{-u * v1, u*u + 1, -v1}
|
||||
return p.Dot(dir0) > 0 && p.Dot(dir1) < 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// edgeDistance reports the distance from a Point P to a given Cell edge. The point
|
||||
// P is given by its dot product, and the uv edge by its normal in the
|
||||
// given coordinate value.
|
||||
func edgeDistance(ij, uv float64) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// Let P by the target point and let R be the closest point on the given
|
||||
// edge AB. The desired distance PR can be expressed as PR^2 = PQ^2 + QR^2
|
||||
// where Q is the point P projected onto the plane through the great circle
|
||||
// through AB. We can compute the distance PQ^2 perpendicular to the plane
|
||||
// from "dirIJ" (the dot product of the target point P with the edge
|
||||
// normal) and the squared length the edge normal (1 + uv**2).
|
||||
pq2 := (ij * ij) / (1 + uv*uv)
|
||||
|
||||
// We can compute the distance QR as (1 - OQ) where O is the sphere origin,
|
||||
// and we can compute OQ^2 = 1 - PQ^2 using the Pythagorean theorem.
|
||||
// (This calculation loses accuracy as angle POQ approaches Pi/2.)
|
||||
qr := 1 - math.Sqrt(1-pq2)
|
||||
return s1.ChordAngleFromSquaredLength(pq2 + qr*qr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// distanceInternal reports the distance from the given point to the interior of
|
||||
// the cell if toInterior is true or to the boundary of the cell otherwise.
|
||||
func (c Cell) distanceInternal(targetXYZ Point, toInterior bool) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// All calculations are done in the (u,v,w) coordinates of this cell's face.
|
||||
target := faceXYZtoUVW(int(c.face), targetXYZ)
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute dot products with all four upward or rightward-facing edge
|
||||
// normals. dirIJ is the dot product for the edge corresponding to axis
|
||||
// I, endpoint J. For example, dir01 is the right edge of the Cell
|
||||
// (corresponding to the upper endpoint of the u-axis).
|
||||
dir00 := target.X - target.Z*c.uv.X.Lo
|
||||
dir01 := target.X - target.Z*c.uv.X.Hi
|
||||
dir10 := target.Y - target.Z*c.uv.Y.Lo
|
||||
dir11 := target.Y - target.Z*c.uv.Y.Hi
|
||||
inside := true
|
||||
if dir00 < 0 {
|
||||
inside = false // Target is to the left of the cell
|
||||
if c.vEdgeIsClosest(target, false) {
|
||||
return edgeDistance(-dir00, c.uv.X.Lo)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dir01 > 0 {
|
||||
inside = false // Target is to the right of the cell
|
||||
if c.vEdgeIsClosest(target, true) {
|
||||
return edgeDistance(dir01, c.uv.X.Hi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dir10 < 0 {
|
||||
inside = false // Target is below the cell
|
||||
if c.uEdgeIsClosest(target, false) {
|
||||
return edgeDistance(-dir10, c.uv.Y.Lo)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dir11 > 0 {
|
||||
inside = false // Target is above the cell
|
||||
if c.uEdgeIsClosest(target, true) {
|
||||
return edgeDistance(dir11, c.uv.Y.Hi)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if inside {
|
||||
if toInterior {
|
||||
return s1.ChordAngle(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Although you might think of Cells as rectangles, they are actually
|
||||
// arbitrary quadrilaterals after they are projected onto the sphere.
|
||||
// Therefore the simplest approach is just to find the minimum distance to
|
||||
// any of the four edges.
|
||||
return minChordAngle(edgeDistance(-dir00, c.uv.X.Lo),
|
||||
edgeDistance(dir01, c.uv.X.Hi),
|
||||
edgeDistance(-dir10, c.uv.Y.Lo),
|
||||
edgeDistance(dir11, c.uv.Y.Hi))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the closest point is one of the four cell vertices. Note that
|
||||
// it is *not* trivial to narrow down the candidates based on the edge sign
|
||||
// tests above, because (1) the edges don't meet at right angles and (2)
|
||||
// there are points on the far side of the sphere that are both above *and*
|
||||
// below the cell, etc.
|
||||
return minChordAngle(c.vertexChordDist2(target, false, false),
|
||||
c.vertexChordDist2(target, true, false),
|
||||
c.vertexChordDist2(target, false, true),
|
||||
c.vertexChordDist2(target, true, true))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Distance reports the distance from the cell to the given point. Returns zero if
|
||||
// the point is inside the cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) Distance(target Point) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
return c.distanceInternal(target, true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxDistance reports the maximum distance from the cell (including its interior) to the
|
||||
// given point.
|
||||
func (c Cell) MaxDistance(target Point) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// First check the 4 cell vertices. If all are within the hemisphere
|
||||
// centered around target, the max distance will be to one of these vertices.
|
||||
targetUVW := faceXYZtoUVW(int(c.face), target)
|
||||
maxDist := maxChordAngle(c.vertexChordDist2(targetUVW, false, false),
|
||||
c.vertexChordDist2(targetUVW, true, false),
|
||||
c.vertexChordDist2(targetUVW, false, true),
|
||||
c.vertexChordDist2(targetUVW, true, true))
|
||||
|
||||
if maxDist <= s1.RightChordAngle {
|
||||
return maxDist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, find the minimum distance dMin to the antipodal point and the
|
||||
// maximum distance will be pi - dMin.
|
||||
return s1.StraightChordAngle - c.BoundaryDistance(Point{target.Mul(-1)})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BoundaryDistance reports the distance from the cell boundary to the given point.
|
||||
func (c Cell) BoundaryDistance(target Point) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
return c.distanceInternal(target, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DistanceToEdge returns the minimum distance from the cell to the given edge AB. Returns
|
||||
// zero if the edge intersects the cell interior.
|
||||
func (c Cell) DistanceToEdge(a, b Point) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// Possible optimizations:
|
||||
// - Currently the (cell vertex, edge endpoint) distances are computed
|
||||
// twice each, and the length of AB is computed 4 times.
|
||||
// - To fix this, refactor GetDistance(target) so that it skips calculating
|
||||
// the distance to each cell vertex. Instead, compute the cell vertices
|
||||
// and distances in this function, and add a low-level UpdateMinDistance
|
||||
// that allows the XA, XB, and AB distances to be passed in.
|
||||
// - It might also be more efficient to do all calculations in UVW-space,
|
||||
// since this would involve transforming 2 points rather than 4.
|
||||
|
||||
// First, check the minimum distance to the edge endpoints A and B.
|
||||
// (This also detects whether either endpoint is inside the cell.)
|
||||
minDist := minChordAngle(c.Distance(a), c.Distance(b))
|
||||
if minDist == 0 {
|
||||
return minDist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, check whether the edge crosses the cell boundary.
|
||||
crosser := NewChainEdgeCrosser(a, b, c.Vertex(3))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
if crosser.ChainCrossingSign(c.Vertex(i)) != DoNotCross {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Finally, check whether the minimum distance occurs between a cell vertex
|
||||
// and the interior of the edge AB. (Some of this work is redundant, since
|
||||
// it also checks the distance to the endpoints A and B again.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that we don't need to check the distance from the interior of AB to
|
||||
// the interior of a cell edge, because the only way that this distance can
|
||||
// be minimal is if the two edges cross (already checked above).
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
minDist, _ = UpdateMinDistance(c.Vertex(i), a, b, minDist)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return minDist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxDistanceToEdge returns the maximum distance from the cell (including its interior)
|
||||
// to the given edge AB.
|
||||
func (c Cell) MaxDistanceToEdge(a, b Point) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// If the maximum distance from both endpoints to the cell is less than π/2
|
||||
// then the maximum distance from the edge to the cell is the maximum of the
|
||||
// two endpoint distances.
|
||||
maxDist := maxChordAngle(c.MaxDistance(a), c.MaxDistance(b))
|
||||
if maxDist <= s1.RightChordAngle {
|
||||
return maxDist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return s1.StraightChordAngle - c.DistanceToEdge(Point{a.Mul(-1)}, Point{b.Mul(-1)})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DistanceToCell returns the minimum distance from this cell to the given cell.
|
||||
// It returns zero if one cell contains the other.
|
||||
func (c Cell) DistanceToCell(target Cell) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// If the cells intersect, the distance is zero. We use the (u,v) ranges
|
||||
// rather than CellID intersects so that cells that share a partial edge or
|
||||
// corner are considered to intersect.
|
||||
if c.face == target.face && c.uv.Intersects(target.uv) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the minimum distance always occurs between a vertex of one
|
||||
// cell and an edge of the other cell (including the edge endpoints). This
|
||||
// represents a total of 32 possible (vertex, edge) pairs.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): This could be optimized to be at least 5x faster by pruning
|
||||
// the set of possible closest vertex/edge pairs using the faces and (u,v)
|
||||
// ranges of both cells.
|
||||
var va, vb [4]Point
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
va[i] = c.Vertex(i)
|
||||
vb[i] = target.Vertex(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
minDist := s1.InfChordAngle()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
for j := 0; j < 4; j++ {
|
||||
minDist, _ = UpdateMinDistance(va[i], vb[j], vb[(j+1)&3], minDist)
|
||||
minDist, _ = UpdateMinDistance(vb[i], va[j], va[(j+1)&3], minDist)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return minDist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxDistanceToCell returns the maximum distance from the cell (including its
|
||||
// interior) to the given target cell.
|
||||
func (c Cell) MaxDistanceToCell(target Cell) s1.ChordAngle {
|
||||
// Need to check the antipodal target for intersection with the cell. If it
|
||||
// intersects, the distance is the straight ChordAngle.
|
||||
// antipodalUV is the transpose of the original UV, interpreted within the opposite face.
|
||||
antipodalUV := r2.Rect{target.uv.Y, target.uv.X}
|
||||
if int(c.face) == oppositeFace(int(target.face)) && c.uv.Intersects(antipodalUV) {
|
||||
return s1.StraightChordAngle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the maximum distance always occurs between a vertex of one
|
||||
// cell and an edge of the other cell (including the edge endpoints). This
|
||||
// represents a total of 32 possible (vertex, edge) pairs.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): When the maximum distance is at most π/2, the maximum is
|
||||
// always attained between a pair of vertices, and this could be made much
|
||||
// faster by testing each vertex pair once rather than the current 4 times.
|
||||
var va, vb [4]Point
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
va[i] = c.Vertex(i)
|
||||
vb[i] = target.Vertex(i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
maxDist := s1.NegativeChordAngle
|
||||
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
|
||||
for j := 0; j < 4; j++ {
|
||||
maxDist, _ = UpdateMaxDistance(va[i], vb[j], vb[(j+1)&3], maxDist)
|
||||
maxDist, _ = UpdateMaxDistance(vb[i], va[j], va[(j+1)&3], maxDist)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return maxDist
|
||||
}
|
||||
921
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cellid.go
generated
vendored
921
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cellid.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,921 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r1"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r2"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r3"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CellID uniquely identifies a cell in the S2 cell decomposition.
|
||||
// The most significant 3 bits encode the face number (0-5). The
|
||||
// remaining 61 bits encode the position of the center of this cell
|
||||
// along the Hilbert curve on that face. The zero value and the value
|
||||
// (1<<64)-1 are invalid cell IDs. The first compares less than any
|
||||
// valid cell ID, the second as greater than any valid cell ID.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Sequentially increasing cell IDs follow a continuous space-filling curve
|
||||
// over the entire sphere. They have the following properties:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - The ID of a cell at level k consists of a 3-bit face number followed
|
||||
// by k bit pairs that recursively select one of the four children of
|
||||
// each cell. The next bit is always 1, and all other bits are 0.
|
||||
// Therefore, the level of a cell is determined by the position of its
|
||||
// lowest-numbered bit that is turned on (for a cell at level k, this
|
||||
// position is 2 * (maxLevel - k)).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - The ID of a parent cell is at the midpoint of the range of IDs spanned
|
||||
// by its children (or by its descendants at any level).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Leaf cells are often used to represent points on the unit sphere, and
|
||||
// this type provides methods for converting directly between these two
|
||||
// representations. For cells that represent 2D regions rather than
|
||||
// discrete point, it is better to use Cells.
|
||||
type CellID uint64
|
||||
|
||||
// SentinelCellID is an invalid cell ID guaranteed to be larger than any
|
||||
// valid cell ID. It is used primarily by ShapeIndex. The value is also used
|
||||
// by some S2 types when encoding data.
|
||||
// Note that the sentinel's RangeMin == RangeMax == itself.
|
||||
const SentinelCellID = CellID(^uint64(0))
|
||||
|
||||
// sortCellIDs sorts the slice of CellIDs in place.
|
||||
func sortCellIDs(ci []CellID) {
|
||||
sort.Sort(cellIDs(ci))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cellIDs implements the Sort interface for slices of CellIDs.
|
||||
type cellIDs []CellID
|
||||
|
||||
func (c cellIDs) Len() int { return len(c) }
|
||||
func (c cellIDs) Swap(i, j int) { c[i], c[j] = c[j], c[i] }
|
||||
func (c cellIDs) Less(i, j int) bool { return c[i] < c[j] }
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(dsymonds): Some of these constants should probably be exported.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
faceBits = 3
|
||||
numFaces = 6
|
||||
|
||||
// This is the number of levels needed to specify a leaf cell.
|
||||
maxLevel = 30
|
||||
|
||||
// The extra position bit (61 rather than 60) lets us encode each cell as its
|
||||
// Hilbert curve position at the cell center (which is halfway along the
|
||||
// portion of the Hilbert curve that fills that cell).
|
||||
posBits = 2*maxLevel + 1
|
||||
|
||||
// The maximum index of a valid leaf cell plus one. The range of valid leaf
|
||||
// cell indices is [0..maxSize-1].
|
||||
maxSize = 1 << maxLevel
|
||||
|
||||
wrapOffset = uint64(numFaces) << posBits
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CellIDFromFacePosLevel returns a cell given its face in the range
|
||||
// [0,5], the 61-bit Hilbert curve position pos within that face, and
|
||||
// the level in the range [0,maxLevel]. The position in the cell ID
|
||||
// will be truncated to correspond to the Hilbert curve position at
|
||||
// the center of the returned cell.
|
||||
func CellIDFromFacePosLevel(face int, pos uint64, level int) CellID {
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(face)<<posBits + pos | 1).Parent(level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellIDFromFace returns the cell corresponding to a given S2 cube face.
|
||||
func CellIDFromFace(face int) CellID {
|
||||
return CellID((uint64(face) << posBits) + lsbForLevel(0))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellIDFromLatLng returns the leaf cell containing ll.
|
||||
func CellIDFromLatLng(ll LatLng) CellID {
|
||||
return cellIDFromPoint(PointFromLatLng(ll))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellIDFromToken returns a cell given a hex-encoded string of its uint64 ID.
|
||||
func CellIDFromToken(s string) CellID {
|
||||
if len(s) > 16 {
|
||||
return CellID(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, err := strconv.ParseUint(s, 16, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return CellID(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Equivalent to right-padding string with zeros to 16 characters.
|
||||
if len(s) < 16 {
|
||||
n = n << (4 * uint(16-len(s)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return CellID(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ToToken returns a hex-encoded string of the uint64 cell id, with leading
|
||||
// zeros included but trailing zeros stripped.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) ToToken() string {
|
||||
s := strings.TrimRight(fmt.Sprintf("%016x", uint64(ci)), "0")
|
||||
if len(s) == 0 {
|
||||
return "X"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsValid reports whether ci represents a valid cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) IsValid() bool {
|
||||
return ci.Face() < numFaces && (ci.lsb()&0x1555555555555555 != 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Face returns the cube face for this cell ID, in the range [0,5].
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Face() int { return int(uint64(ci) >> posBits) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Pos returns the position along the Hilbert curve of this cell ID, in the range [0,2^posBits-1].
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Pos() uint64 { return uint64(ci) & (^uint64(0) >> faceBits) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Level returns the subdivision level of this cell ID, in the range [0, maxLevel].
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Level() int {
|
||||
return maxLevel - findLSBSetNonZero64(uint64(ci))>>1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsLeaf returns whether this cell ID is at the deepest level;
|
||||
// that is, the level at which the cells are smallest.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) IsLeaf() bool { return uint64(ci)&1 != 0 }
|
||||
|
||||
// ChildPosition returns the child position (0..3) of this cell's
|
||||
// ancestor at the given level, relative to its parent. The argument
|
||||
// should be in the range 1..kMaxLevel. For example,
|
||||
// ChildPosition(1) returns the position of this cell's level-1
|
||||
// ancestor within its top-level face cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) ChildPosition(level int) int {
|
||||
return int(uint64(ci)>>uint64(2*(maxLevel-level)+1)) & 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lsbForLevel returns the lowest-numbered bit that is on for cells at the given level.
|
||||
func lsbForLevel(level int) uint64 { return 1 << uint64(2*(maxLevel-level)) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Parent returns the cell at the given level, which must be no greater than the current level.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Parent(level int) CellID {
|
||||
lsb := lsbForLevel(level)
|
||||
return CellID((uint64(ci) & -lsb) | lsb)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// immediateParent is cheaper than Parent, but assumes !ci.isFace().
|
||||
func (ci CellID) immediateParent() CellID {
|
||||
nlsb := CellID(ci.lsb() << 2)
|
||||
return (ci & -nlsb) | nlsb
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isFace returns whether this is a top-level (face) cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) isFace() bool { return uint64(ci)&(lsbForLevel(0)-1) == 0 }
|
||||
|
||||
// lsb returns the least significant bit that is set.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) lsb() uint64 { return uint64(ci) & -uint64(ci) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Children returns the four immediate children of this cell.
|
||||
// If ci is a leaf cell, it returns four identical cells that are not the children.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Children() [4]CellID {
|
||||
var ch [4]CellID
|
||||
lsb := CellID(ci.lsb())
|
||||
ch[0] = ci - lsb + lsb>>2
|
||||
lsb >>= 1
|
||||
ch[1] = ch[0] + lsb
|
||||
ch[2] = ch[1] + lsb
|
||||
ch[3] = ch[2] + lsb
|
||||
return ch
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func sizeIJ(level int) int {
|
||||
return 1 << uint(maxLevel-level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeNeighbors returns the four cells that are adjacent across the cell's four edges.
|
||||
// Edges 0, 1, 2, 3 are in the down, right, up, left directions in the face space.
|
||||
// All neighbors are guaranteed to be distinct.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) EdgeNeighbors() [4]CellID {
|
||||
level := ci.Level()
|
||||
size := sizeIJ(level)
|
||||
f, i, j, _ := ci.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
return [4]CellID{
|
||||
cellIDFromFaceIJWrap(f, i, j-size).Parent(level),
|
||||
cellIDFromFaceIJWrap(f, i+size, j).Parent(level),
|
||||
cellIDFromFaceIJWrap(f, i, j+size).Parent(level),
|
||||
cellIDFromFaceIJWrap(f, i-size, j).Parent(level),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VertexNeighbors returns the neighboring cellIDs with vertex closest to this cell at the given level.
|
||||
// (Normally there are four neighbors, but the closest vertex may only have three neighbors if it is one of
|
||||
// the 8 cube vertices.)
|
||||
func (ci CellID) VertexNeighbors(level int) []CellID {
|
||||
halfSize := sizeIJ(level + 1)
|
||||
size := halfSize << 1
|
||||
f, i, j, _ := ci.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
|
||||
var isame, jsame bool
|
||||
var ioffset, joffset int
|
||||
if i&halfSize != 0 {
|
||||
ioffset = size
|
||||
isame = (i + size) < maxSize
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ioffset = -size
|
||||
isame = (i - size) >= 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j&halfSize != 0 {
|
||||
joffset = size
|
||||
jsame = (j + size) < maxSize
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
joffset = -size
|
||||
jsame = (j - size) >= 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
results := []CellID{
|
||||
ci.Parent(level),
|
||||
cellIDFromFaceIJSame(f, i+ioffset, j, isame).Parent(level),
|
||||
cellIDFromFaceIJSame(f, i, j+joffset, jsame).Parent(level),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if isame || jsame {
|
||||
results = append(results, cellIDFromFaceIJSame(f, i+ioffset, j+joffset, isame && jsame).Parent(level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return results
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AllNeighbors returns all neighbors of this cell at the given level. Two
|
||||
// cells X and Y are neighbors if their boundaries intersect but their
|
||||
// interiors do not. In particular, two cells that intersect at a single
|
||||
// point are neighbors. Note that for cells adjacent to a face vertex, the
|
||||
// same neighbor may be returned more than once. There could be up to eight
|
||||
// neighbors including the diagonal ones that share the vertex.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This requires level >= ci.Level().
|
||||
func (ci CellID) AllNeighbors(level int) []CellID {
|
||||
var neighbors []CellID
|
||||
|
||||
face, i, j, _ := ci.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the coordinates of the lower left-hand leaf cell. We need to
|
||||
// normalize (i,j) to a known position within the cell because level
|
||||
// may be larger than this cell's level.
|
||||
size := sizeIJ(ci.Level())
|
||||
i &= -size
|
||||
j &= -size
|
||||
|
||||
nbrSize := sizeIJ(level)
|
||||
|
||||
// We compute the top-bottom, left-right, and diagonal neighbors in one
|
||||
// pass. The loop test is at the end of the loop to avoid 32-bit overflow.
|
||||
for k := -nbrSize; ; k += nbrSize {
|
||||
var sameFace bool
|
||||
if k < 0 {
|
||||
sameFace = (j+k >= 0)
|
||||
} else if k >= size {
|
||||
sameFace = (j+k < maxSize)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
sameFace = true
|
||||
// Top and bottom neighbors.
|
||||
neighbors = append(neighbors, cellIDFromFaceIJSame(face, i+k, j-nbrSize,
|
||||
j-size >= 0).Parent(level))
|
||||
neighbors = append(neighbors, cellIDFromFaceIJSame(face, i+k, j+size,
|
||||
j+size < maxSize).Parent(level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Left, right, and diagonal neighbors.
|
||||
neighbors = append(neighbors, cellIDFromFaceIJSame(face, i-nbrSize, j+k,
|
||||
sameFace && i-size >= 0).Parent(level))
|
||||
neighbors = append(neighbors, cellIDFromFaceIJSame(face, i+size, j+k,
|
||||
sameFace && i+size < maxSize).Parent(level))
|
||||
|
||||
if k >= size {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return neighbors
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RangeMin returns the minimum CellID that is contained within this cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) RangeMin() CellID { return CellID(uint64(ci) - (ci.lsb() - 1)) }
|
||||
|
||||
// RangeMax returns the maximum CellID that is contained within this cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) RangeMax() CellID { return CellID(uint64(ci) + (ci.lsb() - 1)) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains returns true iff the CellID contains oci.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Contains(oci CellID) bool {
|
||||
return uint64(ci.RangeMin()) <= uint64(oci) && uint64(oci) <= uint64(ci.RangeMax())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersects returns true iff the CellID intersects oci.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Intersects(oci CellID) bool {
|
||||
return uint64(oci.RangeMin()) <= uint64(ci.RangeMax()) && uint64(oci.RangeMax()) >= uint64(ci.RangeMin())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the cell ID in the form "1/3210".
|
||||
func (ci CellID) String() string {
|
||||
if !ci.IsValid() {
|
||||
return "Invalid: " + strconv.FormatInt(int64(ci), 16)
|
||||
}
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte("012345"[ci.Face()]) // values > 5 will have been picked off by !IsValid above
|
||||
b.WriteByte('/')
|
||||
for level := 1; level <= ci.Level(); level++ {
|
||||
b.WriteByte("0123"[ci.ChildPosition(level)])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Point returns the center of the s2 cell on the sphere as a Point.
|
||||
// The maximum directional error in Point (compared to the exact
|
||||
// mathematical result) is 1.5 * dblEpsilon radians, and the maximum length
|
||||
// error is 2 * dblEpsilon (the same as Normalize).
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Point() Point { return Point{ci.rawPoint().Normalize()} }
|
||||
|
||||
// LatLng returns the center of the s2 cell on the sphere as a LatLng.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) LatLng() LatLng { return LatLngFromPoint(Point{ci.rawPoint()}) }
|
||||
|
||||
// ChildBegin returns the first child in a traversal of the children of this cell, in Hilbert curve order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// for ci := c.ChildBegin(); ci != c.ChildEnd(); ci = ci.Next() {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func (ci CellID) ChildBegin() CellID {
|
||||
ol := ci.lsb()
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) - ol + ol>>2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ChildBeginAtLevel returns the first cell in a traversal of children a given level deeper than this cell, in
|
||||
// Hilbert curve order. The given level must be no smaller than the cell's level.
|
||||
// See ChildBegin for example use.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) ChildBeginAtLevel(level int) CellID {
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) - ci.lsb() + lsbForLevel(level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ChildEnd returns the first cell after a traversal of the children of this cell in Hilbert curve order.
|
||||
// The returned cell may be invalid.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) ChildEnd() CellID {
|
||||
ol := ci.lsb()
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) + ol + ol>>2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ChildEndAtLevel returns the first cell after the last child in a traversal of children a given level deeper
|
||||
// than this cell, in Hilbert curve order.
|
||||
// The given level must be no smaller than the cell's level.
|
||||
// The returned cell may be invalid.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) ChildEndAtLevel(level int) CellID {
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) + ci.lsb() + lsbForLevel(level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Next returns the next cell along the Hilbert curve.
|
||||
// This is expected to be used with ChildBegin and ChildEnd,
|
||||
// or ChildBeginAtLevel and ChildEndAtLevel.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Next() CellID {
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) + ci.lsb()<<1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Prev returns the previous cell along the Hilbert curve.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Prev() CellID {
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) - ci.lsb()<<1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NextWrap returns the next cell along the Hilbert curve, wrapping from last to
|
||||
// first as necessary. This should not be used with ChildBegin and ChildEnd.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) NextWrap() CellID {
|
||||
n := ci.Next()
|
||||
if uint64(n) < wrapOffset {
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(n) - wrapOffset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PrevWrap returns the previous cell along the Hilbert curve, wrapping around from
|
||||
// first to last as necessary. This should not be used with ChildBegin and ChildEnd.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) PrevWrap() CellID {
|
||||
p := ci.Prev()
|
||||
if uint64(p) < wrapOffset {
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(p) + wrapOffset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AdvanceWrap advances or retreats the indicated number of steps along the
|
||||
// Hilbert curve at the current level and returns the new position. The
|
||||
// position wraps between the first and last faces as necessary.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) AdvanceWrap(steps int64) CellID {
|
||||
if steps == 0 {
|
||||
return ci
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We clamp the number of steps if necessary to ensure that we do not
|
||||
// advance past the End() or before the Begin() of this level.
|
||||
shift := uint(2*(maxLevel-ci.Level()) + 1)
|
||||
if steps < 0 {
|
||||
if min := -int64(uint64(ci) >> shift); steps < min {
|
||||
wrap := int64(wrapOffset >> shift)
|
||||
steps %= wrap
|
||||
if steps < min {
|
||||
steps += wrap
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Unlike Advance(), we don't want to return End(level).
|
||||
if max := int64((wrapOffset - uint64(ci)) >> shift); steps > max {
|
||||
wrap := int64(wrapOffset >> shift)
|
||||
steps %= wrap
|
||||
if steps > max {
|
||||
steps -= wrap
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If steps is negative, then shifting it left has undefined behavior.
|
||||
// Cast to uint64 for a 2's complement answer.
|
||||
return CellID(uint64(ci) + (uint64(steps) << shift))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Encode encodes the CellID.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Encode(w io.Writer) error {
|
||||
e := &encoder{w: w}
|
||||
ci.encode(e)
|
||||
return e.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (ci CellID) encode(e *encoder) {
|
||||
e.writeUint64(uint64(ci))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode encodes the CellID.
|
||||
func (ci *CellID) Decode(r io.Reader) error {
|
||||
d := &decoder{r: asByteReader(r)}
|
||||
ci.decode(d)
|
||||
return d.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (ci *CellID) decode(d *decoder) {
|
||||
*ci = CellID(d.readUint64())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: the methods below are not exported yet. Settle on the entire API design
|
||||
// before doing this. Do we want to mirror the C++ one as closely as possible?
|
||||
|
||||
// distanceFromBegin returns the number of steps that this cell is from the first
|
||||
// node in the S2 hierarchy at our level. (i.e., FromFace(0).ChildBeginAtLevel(ci.Level())).
|
||||
// The return value is always non-negative.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) distanceFromBegin() int64 {
|
||||
return int64(ci >> uint64(2*(maxLevel-ci.Level())+1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// rawPoint returns an unnormalized r3 vector from the origin through the center
|
||||
// of the s2 cell on the sphere.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) rawPoint() r3.Vector {
|
||||
face, si, ti := ci.faceSiTi()
|
||||
return faceUVToXYZ(face, stToUV((0.5/maxSize)*float64(si)), stToUV((0.5/maxSize)*float64(ti)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// faceSiTi returns the Face/Si/Ti coordinates of the center of the cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) faceSiTi() (face int, si, ti uint32) {
|
||||
face, i, j, _ := ci.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
delta := 0
|
||||
if ci.IsLeaf() {
|
||||
delta = 1
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (i^(int(ci)>>2))&1 != 0 {
|
||||
delta = 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return face, uint32(2*i + delta), uint32(2*j + delta)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// faceIJOrientation uses the global lookupIJ table to unfiddle the bits of ci.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) faceIJOrientation() (f, i, j, orientation int) {
|
||||
f = ci.Face()
|
||||
orientation = f & swapMask
|
||||
nbits := maxLevel - 7*lookupBits // first iteration
|
||||
|
||||
// Each iteration maps 8 bits of the Hilbert curve position into
|
||||
// 4 bits of "i" and "j". The lookup table transforms a key of the
|
||||
// form "ppppppppoo" to a value of the form "iiiijjjjoo", where the
|
||||
// letters [ijpo] represents bits of "i", "j", the Hilbert curve
|
||||
// position, and the Hilbert curve orientation respectively.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// On the first iteration we need to be careful to clear out the bits
|
||||
// representing the cube face.
|
||||
for k := 7; k >= 0; k-- {
|
||||
orientation += (int(uint64(ci)>>uint64(k*2*lookupBits+1)) & ((1 << uint(2*nbits)) - 1)) << 2
|
||||
orientation = lookupIJ[orientation]
|
||||
i += (orientation >> (lookupBits + 2)) << uint(k*lookupBits)
|
||||
j += ((orientation >> 2) & ((1 << lookupBits) - 1)) << uint(k*lookupBits)
|
||||
orientation &= (swapMask | invertMask)
|
||||
nbits = lookupBits // following iterations
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The position of a non-leaf cell at level "n" consists of a prefix of
|
||||
// 2*n bits that identifies the cell, followed by a suffix of
|
||||
// 2*(maxLevel-n)+1 bits of the form 10*. If n==maxLevel, the suffix is
|
||||
// just "1" and has no effect. Otherwise, it consists of "10", followed
|
||||
// by (maxLevel-n-1) repetitions of "00", followed by "0". The "10" has
|
||||
// no effect, while each occurrence of "00" has the effect of reversing
|
||||
// the swapMask bit.
|
||||
if ci.lsb()&0x1111111111111110 != 0 {
|
||||
orientation ^= swapMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cellIDFromFaceIJ returns a leaf cell given its cube face (range 0..5) and IJ coordinates.
|
||||
func cellIDFromFaceIJ(f, i, j int) CellID {
|
||||
// Note that this value gets shifted one bit to the left at the end
|
||||
// of the function.
|
||||
n := uint64(f) << (posBits - 1)
|
||||
// Alternating faces have opposite Hilbert curve orientations; this
|
||||
// is necessary in order for all faces to have a right-handed
|
||||
// coordinate system.
|
||||
bits := f & swapMask
|
||||
// Each iteration maps 4 bits of "i" and "j" into 8 bits of the Hilbert
|
||||
// curve position. The lookup table transforms a 10-bit key of the form
|
||||
// "iiiijjjjoo" to a 10-bit value of the form "ppppppppoo", where the
|
||||
// letters [ijpo] denote bits of "i", "j", Hilbert curve position, and
|
||||
// Hilbert curve orientation respectively.
|
||||
for k := 7; k >= 0; k-- {
|
||||
mask := (1 << lookupBits) - 1
|
||||
bits += int((i>>uint(k*lookupBits))&mask) << (lookupBits + 2)
|
||||
bits += int((j>>uint(k*lookupBits))&mask) << 2
|
||||
bits = lookupPos[bits]
|
||||
n |= uint64(bits>>2) << (uint(k) * 2 * lookupBits)
|
||||
bits &= (swapMask | invertMask)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return CellID(n*2 + 1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func cellIDFromFaceIJWrap(f, i, j int) CellID {
|
||||
// Convert i and j to the coordinates of a leaf cell just beyond the
|
||||
// boundary of this face. This prevents 32-bit overflow in the case
|
||||
// of finding the neighbors of a face cell.
|
||||
i = clampInt(i, -1, maxSize)
|
||||
j = clampInt(j, -1, maxSize)
|
||||
|
||||
// We want to wrap these coordinates onto the appropriate adjacent face.
|
||||
// The easiest way to do this is to convert the (i,j) coordinates to (x,y,z)
|
||||
// (which yields a point outside the normal face boundary), and then call
|
||||
// xyzToFaceUV to project back onto the correct face.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The code below converts (i,j) to (si,ti), and then (si,ti) to (u,v) using
|
||||
// the linear projection (u=2*s-1 and v=2*t-1). (The code further below
|
||||
// converts back using the inverse projection, s=0.5*(u+1) and t=0.5*(v+1).
|
||||
// Any projection would work here, so we use the simplest.) We also clamp
|
||||
// the (u,v) coordinates so that the point is barely outside the
|
||||
// [-1,1]x[-1,1] face rectangle, since otherwise the reprojection step
|
||||
// (which divides by the new z coordinate) might change the other
|
||||
// coordinates enough so that we end up in the wrong leaf cell.
|
||||
const scale = 1.0 / maxSize
|
||||
limit := math.Nextafter(1, 2)
|
||||
u := math.Max(-limit, math.Min(limit, scale*float64((i<<1)+1-maxSize)))
|
||||
v := math.Max(-limit, math.Min(limit, scale*float64((j<<1)+1-maxSize)))
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the leaf cell coordinates on the adjacent face, and convert
|
||||
// them to a cell id at the appropriate level.
|
||||
f, u, v = xyzToFaceUV(faceUVToXYZ(f, u, v))
|
||||
return cellIDFromFaceIJ(f, stToIJ(0.5*(u+1)), stToIJ(0.5*(v+1)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func cellIDFromFaceIJSame(f, i, j int, sameFace bool) CellID {
|
||||
if sameFace {
|
||||
return cellIDFromFaceIJ(f, i, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cellIDFromFaceIJWrap(f, i, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ijToSTMin converts the i- or j-index of a leaf cell to the minimum corresponding
|
||||
// s- or t-value contained by that cell. The argument must be in the range
|
||||
// [0..2**30], i.e. up to one position beyond the normal range of valid leaf
|
||||
// cell indices.
|
||||
func ijToSTMin(i int) float64 {
|
||||
return float64(i) / float64(maxSize)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stToIJ converts value in ST coordinates to a value in IJ coordinates.
|
||||
func stToIJ(s float64) int {
|
||||
return clampInt(int(math.Floor(maxSize*s)), 0, maxSize-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cellIDFromPoint returns a leaf cell containing point p. Usually there is
|
||||
// exactly one such cell, but for points along the edge of a cell, any
|
||||
// adjacent cell may be (deterministically) chosen. This is because
|
||||
// s2.CellIDs are considered to be closed sets. The returned cell will
|
||||
// always contain the given point, i.e.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CellFromPoint(p).ContainsPoint(p)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// is always true.
|
||||
func cellIDFromPoint(p Point) CellID {
|
||||
f, u, v := xyzToFaceUV(r3.Vector{p.X, p.Y, p.Z})
|
||||
i := stToIJ(uvToST(u))
|
||||
j := stToIJ(uvToST(v))
|
||||
return cellIDFromFaceIJ(f, i, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ijLevelToBoundUV returns the bounds in (u,v)-space for the cell at the given
|
||||
// level containing the leaf cell with the given (i,j)-coordinates.
|
||||
func ijLevelToBoundUV(i, j, level int) r2.Rect {
|
||||
cellSize := sizeIJ(level)
|
||||
xLo := i & -cellSize
|
||||
yLo := j & -cellSize
|
||||
|
||||
return r2.Rect{
|
||||
X: r1.Interval{
|
||||
Lo: stToUV(ijToSTMin(xLo)),
|
||||
Hi: stToUV(ijToSTMin(xLo + cellSize)),
|
||||
},
|
||||
Y: r1.Interval{
|
||||
Lo: stToUV(ijToSTMin(yLo)),
|
||||
Hi: stToUV(ijToSTMin(yLo + cellSize)),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Constants related to the bit mangling in the Cell ID.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
lookupBits = 4
|
||||
swapMask = 0x01
|
||||
invertMask = 0x02
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// The following lookup tables are used to convert efficiently between an
|
||||
// (i,j) cell index and the corresponding position along the Hilbert curve.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// lookupPos maps 4 bits of "i", 4 bits of "j", and 2 bits representing the
|
||||
// orientation of the current cell into 8 bits representing the order in which
|
||||
// that subcell is visited by the Hilbert curve, plus 2 bits indicating the
|
||||
// new orientation of the Hilbert curve within that subcell. (Cell
|
||||
// orientations are represented as combination of swapMask and invertMask.)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// lookupIJ is an inverted table used for mapping in the opposite
|
||||
// direction.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We also experimented with looking up 16 bits at a time (14 bits of position
|
||||
// plus 2 of orientation) but found that smaller lookup tables gave better
|
||||
// performance. (2KB fits easily in the primary cache.)
|
||||
var (
|
||||
ijToPos = [4][4]int{
|
||||
{0, 1, 3, 2}, // canonical order
|
||||
{0, 3, 1, 2}, // axes swapped
|
||||
{2, 3, 1, 0}, // bits inverted
|
||||
{2, 1, 3, 0}, // swapped & inverted
|
||||
}
|
||||
posToIJ = [4][4]int{
|
||||
{0, 1, 3, 2}, // canonical order: (0,0), (0,1), (1,1), (1,0)
|
||||
{0, 2, 3, 1}, // axes swapped: (0,0), (1,0), (1,1), (0,1)
|
||||
{3, 2, 0, 1}, // bits inverted: (1,1), (1,0), (0,0), (0,1)
|
||||
{3, 1, 0, 2}, // swapped & inverted: (1,1), (0,1), (0,0), (1,0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
posToOrientation = [4]int{swapMask, 0, 0, invertMask | swapMask}
|
||||
lookupIJ [1 << (2*lookupBits + 2)]int
|
||||
lookupPos [1 << (2*lookupBits + 2)]int
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
initLookupCell(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
|
||||
initLookupCell(0, 0, 0, swapMask, 0, swapMask)
|
||||
initLookupCell(0, 0, 0, invertMask, 0, invertMask)
|
||||
initLookupCell(0, 0, 0, swapMask|invertMask, 0, swapMask|invertMask)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// initLookupCell initializes the lookupIJ table at init time.
|
||||
func initLookupCell(level, i, j, origOrientation, pos, orientation int) {
|
||||
if level == lookupBits {
|
||||
ij := (i << lookupBits) + j
|
||||
lookupPos[(ij<<2)+origOrientation] = (pos << 2) + orientation
|
||||
lookupIJ[(pos<<2)+origOrientation] = (ij << 2) + orientation
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
level++
|
||||
i <<= 1
|
||||
j <<= 1
|
||||
pos <<= 2
|
||||
r := posToIJ[orientation]
|
||||
initLookupCell(level, i+(r[0]>>1), j+(r[0]&1), origOrientation, pos, orientation^posToOrientation[0])
|
||||
initLookupCell(level, i+(r[1]>>1), j+(r[1]&1), origOrientation, pos+1, orientation^posToOrientation[1])
|
||||
initLookupCell(level, i+(r[2]>>1), j+(r[2]&1), origOrientation, pos+2, orientation^posToOrientation[2])
|
||||
initLookupCell(level, i+(r[3]>>1), j+(r[3]&1), origOrientation, pos+3, orientation^posToOrientation[3])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CommonAncestorLevel returns the level of the common ancestor of the two S2 CellIDs.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) CommonAncestorLevel(other CellID) (level int, ok bool) {
|
||||
bits := uint64(ci ^ other)
|
||||
if bits < ci.lsb() {
|
||||
bits = ci.lsb()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bits < other.lsb() {
|
||||
bits = other.lsb()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
msbPos := findMSBSetNonZero64(bits)
|
||||
if msbPos > 60 {
|
||||
return 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (60 - msbPos) >> 1, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Advance advances or retreats the indicated number of steps along the
|
||||
// Hilbert curve at the current level, and returns the new position. The
|
||||
// position is never advanced past End() or before Begin().
|
||||
func (ci CellID) Advance(steps int64) CellID {
|
||||
if steps == 0 {
|
||||
return ci
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We clamp the number of steps if necessary to ensure that we do not
|
||||
// advance past the End() or before the Begin() of this level. Note that
|
||||
// minSteps and maxSteps always fit in a signed 64-bit integer.
|
||||
stepShift := uint(2*(maxLevel-ci.Level()) + 1)
|
||||
if steps < 0 {
|
||||
minSteps := -int64(uint64(ci) >> stepShift)
|
||||
if steps < minSteps {
|
||||
steps = minSteps
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
maxSteps := int64((wrapOffset + ci.lsb() - uint64(ci)) >> stepShift)
|
||||
if steps > maxSteps {
|
||||
steps = maxSteps
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ci + CellID(steps)<<stepShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// centerST return the center of the CellID in (s,t)-space.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) centerST() r2.Point {
|
||||
_, si, ti := ci.faceSiTi()
|
||||
return r2.Point{siTiToST(si), siTiToST(ti)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sizeST returns the edge length of this CellID in (s,t)-space at the given level.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) sizeST(level int) float64 {
|
||||
return ijToSTMin(sizeIJ(level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// boundST returns the bound of this CellID in (s,t)-space.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) boundST() r2.Rect {
|
||||
s := ci.sizeST(ci.Level())
|
||||
return r2.RectFromCenterSize(ci.centerST(), r2.Point{s, s})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// centerUV returns the center of this CellID in (u,v)-space. Note that
|
||||
// the center of the cell is defined as the point at which it is recursively
|
||||
// subdivided into four children; in general, it is not at the midpoint of
|
||||
// the (u,v) rectangle covered by the cell.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) centerUV() r2.Point {
|
||||
_, si, ti := ci.faceSiTi()
|
||||
return r2.Point{stToUV(siTiToST(si)), stToUV(siTiToST(ti))}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// boundUV returns the bound of this CellID in (u,v)-space.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) boundUV() r2.Rect {
|
||||
_, i, j, _ := ci.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
return ijLevelToBoundUV(i, j, ci.Level())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// expandEndpoint returns a new u-coordinate u' such that the distance from the
|
||||
// line u=u' to the given edge (u,v0)-(u,v1) is exactly the given distance
|
||||
// (which is specified as the sine of the angle corresponding to the distance).
|
||||
func expandEndpoint(u, maxV, sinDist float64) float64 {
|
||||
// This is based on solving a spherical right triangle, similar to the
|
||||
// calculation in Cap.RectBound.
|
||||
// Given an edge of the form (u,v0)-(u,v1), let maxV = max(abs(v0), abs(v1)).
|
||||
sinUShift := sinDist * math.Sqrt((1+u*u+maxV*maxV)/(1+u*u))
|
||||
cosUShift := math.Sqrt(1 - sinUShift*sinUShift)
|
||||
// The following is an expansion of tan(atan(u) + asin(sinUShift)).
|
||||
return (cosUShift*u + sinUShift) / (cosUShift - sinUShift*u)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// expandedByDistanceUV returns a rectangle expanded in (u,v)-space so that it
|
||||
// contains all points within the given distance of the boundary, and return the
|
||||
// smallest such rectangle. If the distance is negative, then instead shrink this
|
||||
// rectangle so that it excludes all points within the given absolute distance
|
||||
// of the boundary.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Distances are measured *on the sphere*, not in (u,v)-space. For example,
|
||||
// you can use this method to expand the (u,v)-bound of an CellID so that
|
||||
// it contains all points within 5km of the original cell. You can then
|
||||
// test whether a point lies within the expanded bounds like this:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if u, v, ok := faceXYZtoUV(face, point); ok && bound.ContainsPoint(r2.Point{u,v}) { ... }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Limitations:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - Because the rectangle is drawn on one of the six cube-face planes
|
||||
// (i.e., {x,y,z} = +/-1), it can cover at most one hemisphere. This
|
||||
// limits the maximum amount that a rectangle can be expanded. For
|
||||
// example, CellID bounds can be expanded safely by at most 45 degrees
|
||||
// (about 5000 km on the Earth's surface).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - The implementation is not exact for negative distances. The resulting
|
||||
// rectangle will exclude all points within the given distance of the
|
||||
// boundary but may be slightly smaller than necessary.
|
||||
func expandedByDistanceUV(uv r2.Rect, distance s1.Angle) r2.Rect {
|
||||
// Expand each of the four sides of the rectangle just enough to include all
|
||||
// points within the given distance of that side. (The rectangle may be
|
||||
// expanded by a different amount in (u,v)-space on each side.)
|
||||
maxU := math.Max(math.Abs(uv.X.Lo), math.Abs(uv.X.Hi))
|
||||
maxV := math.Max(math.Abs(uv.Y.Lo), math.Abs(uv.Y.Hi))
|
||||
sinDist := math.Sin(float64(distance))
|
||||
return r2.Rect{
|
||||
X: r1.Interval{expandEndpoint(uv.X.Lo, maxV, -sinDist),
|
||||
expandEndpoint(uv.X.Hi, maxV, sinDist)},
|
||||
Y: r1.Interval{expandEndpoint(uv.Y.Lo, maxU, -sinDist),
|
||||
expandEndpoint(uv.Y.Hi, maxU, sinDist)}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxTile returns the largest cell with the same RangeMin such that
|
||||
// RangeMax < limit.RangeMin. It returns limit if no such cell exists.
|
||||
// This method can be used to generate a small set of CellIDs that covers
|
||||
// a given range (a tiling). This example shows how to generate a tiling
|
||||
// for a semi-open range of leaf cells [start, limit):
|
||||
//
|
||||
// for id := start.MaxTile(limit); id != limit; id = id.Next().MaxTile(limit)) { ... }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that in general the cells in the tiling will be of different sizes;
|
||||
// they gradually get larger (near the middle of the range) and then
|
||||
// gradually get smaller as limit is approached.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) MaxTile(limit CellID) CellID {
|
||||
start := ci.RangeMin()
|
||||
if start >= limit.RangeMin() {
|
||||
return limit
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if ci.RangeMax() >= limit {
|
||||
// The cell is too large, shrink it. Note that when generating coverings
|
||||
// of CellID ranges, this loop usually executes only once. Also because
|
||||
// ci.RangeMin() < limit.RangeMin(), we will always exit the loop by the
|
||||
// time we reach a leaf cell.
|
||||
for {
|
||||
ci = ci.Children()[0]
|
||||
if ci.RangeMax() < limit {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ci
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The cell may be too small. Grow it if necessary. Note that generally
|
||||
// this loop only iterates once.
|
||||
for !ci.isFace() {
|
||||
parent := ci.immediateParent()
|
||||
if parent.RangeMin() != start || parent.RangeMax() >= limit {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
ci = parent
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ci
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// centerFaceSiTi returns the (face, si, ti) coordinates of the center of the cell.
|
||||
// Note that although (si,ti) coordinates span the range [0,2**31] in general,
|
||||
// the cell center coordinates are always in the range [1,2**31-1] and
|
||||
// therefore can be represented using a signed 32-bit integer.
|
||||
func (ci CellID) centerFaceSiTi() (face, si, ti int) {
|
||||
// First we compute the discrete (i,j) coordinates of a leaf cell contained
|
||||
// within the given cell. Given that cells are represented by the Hilbert
|
||||
// curve position corresponding at their center, it turns out that the cell
|
||||
// returned by faceIJOrientation is always one of two leaf cells closest
|
||||
// to the center of the cell (unless the given cell is a leaf cell itself,
|
||||
// in which case there is only one possibility).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Given a cell of size s >= 2 (i.e. not a leaf cell), and letting (imin,
|
||||
// jmin) be the coordinates of its lower left-hand corner, the leaf cell
|
||||
// returned by faceIJOrientation is either (imin + s/2, jmin + s/2)
|
||||
// (imin + s/2 - 1, jmin + s/2 - 1). The first case is the one we want.
|
||||
// We can distinguish these two cases by looking at the low bit of i or
|
||||
// j. In the second case the low bit is one, unless s == 2 (i.e. the
|
||||
// level just above leaf cells) in which case the low bit is zero.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In the code below, the expression ((i ^ (int(id) >> 2)) & 1) is true
|
||||
// if we are in the second case described above.
|
||||
face, i, j, _ := ci.faceIJOrientation()
|
||||
delta := 0
|
||||
if ci.IsLeaf() {
|
||||
delta = 1
|
||||
} else if (int64(i)^(int64(ci)>>2))&1 == 1 {
|
||||
delta = 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Note that (2 * {i,j} + delta) will never overflow a 32-bit integer.
|
||||
return face, 2*i + delta, 2*j + delta
|
||||
}
|
||||
590
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cellunion.go
generated
vendored
590
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/cellunion.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,590 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A CellUnion is a collection of CellIDs.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It is normalized if it is sorted, and does not contain redundancy.
|
||||
// Specifically, it may not contain the same CellID twice, nor a CellID that
|
||||
// is contained by another, nor the four sibling CellIDs that are children of
|
||||
// a single higher level CellID.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CellUnions are not required to be normalized, but certain operations will
|
||||
// return different results if they are not (e.g. Contains).
|
||||
type CellUnion []CellID
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionFromRange creates a CellUnion that covers the half-open range
|
||||
// of leaf cells [begin, end). If begin == end the resulting union is empty.
|
||||
// This requires that begin and end are both leaves, and begin <= end.
|
||||
// To create a closed-ended range, pass in end.Next().
|
||||
func CellUnionFromRange(begin, end CellID) CellUnion {
|
||||
// We repeatedly add the largest cell we can.
|
||||
var cu CellUnion
|
||||
for id := begin.MaxTile(end); id != end; id = id.Next().MaxTile(end) {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, id)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The output is normalized because the cells are added in order by the iteration.
|
||||
return cu
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionFromUnion creates a CellUnion from the union of the given CellUnions.
|
||||
func CellUnionFromUnion(cellUnions ...CellUnion) CellUnion {
|
||||
var cu CellUnion
|
||||
for _, cellUnion := range cellUnions {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, cellUnion...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
cu.Normalize()
|
||||
return cu
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionFromIntersection creates a CellUnion from the intersection of the given CellUnions.
|
||||
func CellUnionFromIntersection(x, y CellUnion) CellUnion {
|
||||
var cu CellUnion
|
||||
|
||||
// This is a fairly efficient calculation that uses binary search to skip
|
||||
// over sections of both input vectors. It takes constant time if all the
|
||||
// cells of x come before or after all the cells of y in CellID order.
|
||||
var i, j int
|
||||
for i < len(x) && j < len(y) {
|
||||
iMin := x[i].RangeMin()
|
||||
jMin := y[j].RangeMin()
|
||||
if iMin > jMin {
|
||||
// Either j.Contains(i) or the two cells are disjoint.
|
||||
if x[i] <= y[j].RangeMax() {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, x[i])
|
||||
i++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Advance j to the first cell possibly contained by x[i].
|
||||
j = y.lowerBound(j+1, len(y), iMin)
|
||||
// The previous cell y[j-1] may now contain x[i].
|
||||
if x[i] <= y[j-1].RangeMax() {
|
||||
j--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if jMin > iMin {
|
||||
// Identical to the code above with i and j reversed.
|
||||
if y[j] <= x[i].RangeMax() {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, y[j])
|
||||
j++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
i = x.lowerBound(i+1, len(x), jMin)
|
||||
if y[j] <= x[i-1].RangeMax() {
|
||||
i--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// i and j have the same RangeMin(), so one contains the other.
|
||||
if x[i] < y[j] {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, x[i])
|
||||
i++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, y[j])
|
||||
j++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The output is generated in sorted order.
|
||||
cu.Normalize()
|
||||
return cu
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionFromIntersectionWithCellID creates a CellUnion from the intersection
|
||||
// of a CellUnion with the given CellID. This can be useful for splitting a
|
||||
// CellUnion into chunks.
|
||||
func CellUnionFromIntersectionWithCellID(x CellUnion, id CellID) CellUnion {
|
||||
var cu CellUnion
|
||||
if x.ContainsCellID(id) {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, id)
|
||||
cu.Normalize()
|
||||
return cu
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
idmax := id.RangeMax()
|
||||
for i := x.lowerBound(0, len(x), id.RangeMin()); i < len(x) && x[i] <= idmax; i++ {
|
||||
cu = append(cu, x[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cu.Normalize()
|
||||
return cu
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionFromDifference creates a CellUnion from the difference (x - y)
|
||||
// of the given CellUnions.
|
||||
func CellUnionFromDifference(x, y CellUnion) CellUnion {
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): This is approximately O(N*log(N)), but could probably
|
||||
// use similar techniques as CellUnionFromIntersectionWithCellID to be more efficient.
|
||||
|
||||
var cu CellUnion
|
||||
for _, xid := range x {
|
||||
cu.cellUnionDifferenceInternal(xid, &y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The output is generated in sorted order, and there should not be any
|
||||
// cells that can be merged (provided that both inputs were normalized).
|
||||
return cu
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The C++ constructor methods FromNormalized and FromVerbatim are not necessary
|
||||
// since they don't call Normalize, and just set the CellIDs directly on the object,
|
||||
// so straight casting is sufficient in Go to replicate this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
// IsValid reports whether the cell union is valid, meaning that the CellIDs are
|
||||
// valid, non-overlapping, and sorted in increasing order.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) IsValid() bool {
|
||||
for i, cid := range *cu {
|
||||
if !cid.IsValid() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (*cu)[i-1].RangeMax() >= cid.RangeMin() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsNormalized reports whether the cell union is normalized, meaning that it is
|
||||
// satisfies IsValid and that no four cells have a common parent.
|
||||
// Certain operations such as Contains will return a different
|
||||
// result if the cell union is not normalized.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) IsNormalized() bool {
|
||||
for i, cid := range *cu {
|
||||
if !cid.IsValid() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (*cu)[i-1].RangeMax() >= cid.RangeMin() {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < 3 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if areSiblings((*cu)[i-3], (*cu)[i-2], (*cu)[i-1], cid) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Normalize normalizes the CellUnion.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) Normalize() {
|
||||
sortCellIDs(*cu)
|
||||
|
||||
output := make([]CellID, 0, len(*cu)) // the list of accepted cells
|
||||
// Loop invariant: output is a sorted list of cells with no redundancy.
|
||||
for _, ci := range *cu {
|
||||
// The first two passes here either ignore this new candidate,
|
||||
// or remove previously accepted cells that are covered by this candidate.
|
||||
|
||||
// Ignore this cell if it is contained by the previous one.
|
||||
// We only need to check the last accepted cell. The ordering of the
|
||||
// cells implies containment (but not the converse), and output has no redundancy,
|
||||
// so if this candidate is not contained by the last accepted cell
|
||||
// then it cannot be contained by any previously accepted cell.
|
||||
if len(output) > 0 && output[len(output)-1].Contains(ci) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Discard any previously accepted cells contained by this one.
|
||||
// This could be any contiguous trailing subsequence, but it can't be
|
||||
// a discontiguous subsequence because of the containment property of
|
||||
// sorted S2 cells mentioned above.
|
||||
j := len(output) - 1 // last index to keep
|
||||
for j >= 0 {
|
||||
if !ci.Contains(output[j]) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
j--
|
||||
}
|
||||
output = output[:j+1]
|
||||
|
||||
// See if the last three cells plus this one can be collapsed.
|
||||
// We loop because collapsing three accepted cells and adding a higher level cell
|
||||
// could cascade into previously accepted cells.
|
||||
for len(output) >= 3 && areSiblings(output[len(output)-3], output[len(output)-2], output[len(output)-1], ci) {
|
||||
// Replace four children by their parent cell.
|
||||
output = output[:len(output)-3]
|
||||
ci = ci.immediateParent() // checked !ci.isFace above
|
||||
}
|
||||
output = append(output, ci)
|
||||
}
|
||||
*cu = output
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntersectsCellID reports whether this CellUnion intersects the given cell ID.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) IntersectsCellID(id CellID) bool {
|
||||
// Find index of array item that occurs directly after our probe cell:
|
||||
i := sort.Search(len(*cu), func(i int) bool { return id < (*cu)[i] })
|
||||
|
||||
if i != len(*cu) && (*cu)[i].RangeMin() <= id.RangeMax() {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i != 0 && (*cu)[i-1].RangeMax() >= id.RangeMin()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsCellID reports whether the CellUnion contains the given cell ID.
|
||||
// Containment is defined with respect to regions, e.g. a cell contains its 4 children.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CAVEAT: If you have constructed a non-normalized CellUnion, note that groups
|
||||
// of 4 child cells are *not* considered to contain their parent cell. To get
|
||||
// this behavior you must use one of the call Normalize() explicitly.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ContainsCellID(id CellID) bool {
|
||||
// Find index of array item that occurs directly after our probe cell:
|
||||
i := sort.Search(len(*cu), func(i int) bool { return id < (*cu)[i] })
|
||||
|
||||
if i != len(*cu) && (*cu)[i].RangeMin() <= id {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return i != 0 && (*cu)[i-1].RangeMax() >= id
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Denormalize replaces this CellUnion with an expanded version of the
|
||||
// CellUnion where any cell whose level is less than minLevel or where
|
||||
// (level - minLevel) is not a multiple of levelMod is replaced by its
|
||||
// children, until either both of these conditions are satisfied or the
|
||||
// maximum level is reached.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) Denormalize(minLevel, levelMod int) {
|
||||
var denorm CellUnion
|
||||
for _, id := range *cu {
|
||||
level := id.Level()
|
||||
newLevel := level
|
||||
if newLevel < minLevel {
|
||||
newLevel = minLevel
|
||||
}
|
||||
if levelMod > 1 {
|
||||
newLevel += (maxLevel - (newLevel - minLevel)) % levelMod
|
||||
if newLevel > maxLevel {
|
||||
newLevel = maxLevel
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if newLevel == level {
|
||||
denorm = append(denorm, id)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
end := id.ChildEndAtLevel(newLevel)
|
||||
for ci := id.ChildBeginAtLevel(newLevel); ci != end; ci = ci.Next() {
|
||||
denorm = append(denorm, ci)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
*cu = denorm
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RectBound returns a Rect that bounds this entity.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) RectBound() Rect {
|
||||
bound := EmptyRect()
|
||||
for _, c := range *cu {
|
||||
bound = bound.Union(CellFromCellID(c).RectBound())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bound
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CapBound returns a Cap that bounds this entity.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) CapBound() Cap {
|
||||
if len(*cu) == 0 {
|
||||
return EmptyCap()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the approximate centroid of the region. This won't produce the
|
||||
// bounding cap of minimal area, but it should be close enough.
|
||||
var centroid Point
|
||||
|
||||
for _, ci := range *cu {
|
||||
area := AvgAreaMetric.Value(ci.Level())
|
||||
centroid = Point{centroid.Add(ci.Point().Mul(area))}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if zero := (Point{}); centroid == zero {
|
||||
centroid = PointFromCoords(1, 0, 0)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
centroid = Point{centroid.Normalize()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Use the centroid as the cap axis, and expand the cap angle so that it
|
||||
// contains the bounding caps of all the individual cells. Note that it is
|
||||
// *not* sufficient to just bound all the cell vertices because the bounding
|
||||
// cap may be concave (i.e. cover more than one hemisphere).
|
||||
c := CapFromPoint(centroid)
|
||||
for _, ci := range *cu {
|
||||
c = c.AddCap(CellFromCellID(ci).CapBound())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsCell reports whether this cell union contains the given cell.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ContainsCell(c Cell) bool {
|
||||
return cu.ContainsCellID(c.id)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntersectsCell reports whether this cell union intersects the given cell.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) IntersectsCell(c Cell) bool {
|
||||
return cu.IntersectsCellID(c.id)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsPoint reports whether this cell union contains the given point.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ContainsPoint(p Point) bool {
|
||||
return cu.ContainsCell(CellFromPoint(p))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CellUnionBound computes a covering of the CellUnion.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) CellUnionBound() []CellID {
|
||||
return cu.CapBound().CellUnionBound()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LeafCellsCovered reports the number of leaf cells covered by this cell union.
|
||||
// This will be no more than 6*2^60 for the whole sphere.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) LeafCellsCovered() int64 {
|
||||
var numLeaves int64
|
||||
for _, c := range *cu {
|
||||
numLeaves += 1 << uint64((maxLevel-int64(c.Level()))<<1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return numLeaves
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns true if the given four cells have a common parent.
|
||||
// This requires that the four CellIDs are distinct.
|
||||
func areSiblings(a, b, c, d CellID) bool {
|
||||
// A necessary (but not sufficient) condition is that the XOR of the
|
||||
// four cell IDs must be zero. This is also very fast to test.
|
||||
if (a ^ b ^ c) != d {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Now we do a slightly more expensive but exact test. First, compute a
|
||||
// mask that blocks out the two bits that encode the child position of
|
||||
// "id" with respect to its parent, then check that the other three
|
||||
// children all agree with "mask".
|
||||
mask := uint64(d.lsb() << 1)
|
||||
mask = ^(mask + (mask << 1))
|
||||
idMasked := (uint64(d) & mask)
|
||||
return ((uint64(a)&mask) == idMasked &&
|
||||
(uint64(b)&mask) == idMasked &&
|
||||
(uint64(c)&mask) == idMasked &&
|
||||
!d.isFace())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains reports whether this CellUnion contains all of the CellIDs of the given CellUnion.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) Contains(o CellUnion) bool {
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): Investigate alternatives such as divide-and-conquer
|
||||
// or alternating-skip-search that may be significantly faster in both
|
||||
// the average and worst case. This applies to Intersects as well.
|
||||
for _, id := range o {
|
||||
if !cu.ContainsCellID(id) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersects reports whether this CellUnion intersects any of the CellIDs of the given CellUnion.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) Intersects(o CellUnion) bool {
|
||||
for _, c := range *cu {
|
||||
if o.ContainsCellID(c) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lowerBound returns the index in this CellUnion to the first element whose value
|
||||
// is not considered to go before the given cell id. (i.e., either it is equivalent
|
||||
// or comes after the given id.) If there is no match, then end is returned.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) lowerBound(begin, end int, id CellID) int {
|
||||
for i := begin; i < end; i++ {
|
||||
if (*cu)[i] >= id {
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return end
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cellUnionDifferenceInternal adds the difference between the CellID and the union to
|
||||
// the result CellUnion. If they intersect but the difference is non-empty, it divides
|
||||
// and conquers.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) cellUnionDifferenceInternal(id CellID, other *CellUnion) {
|
||||
if !other.IntersectsCellID(id) {
|
||||
(*cu) = append((*cu), id)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !other.ContainsCellID(id) {
|
||||
for _, child := range id.Children() {
|
||||
cu.cellUnionDifferenceInternal(child, other)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExpandAtLevel expands this CellUnion by adding a rim of cells at expandLevel
|
||||
// around the unions boundary.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For each cell c in the union, we add all cells at level
|
||||
// expandLevel that abut c. There are typically eight of those
|
||||
// (four edge-abutting and four sharing a vertex). However, if c is
|
||||
// finer than expandLevel, we add all cells abutting
|
||||
// c.Parent(expandLevel) as well as c.Parent(expandLevel) itself,
|
||||
// as an expandLevel cell rarely abuts a smaller cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the size of the output is exponential in
|
||||
// expandLevel. For example, if expandLevel == 20 and the input
|
||||
// has a cell at level 10, there will be on the order of 4000
|
||||
// adjacent cells in the output. For most applications the
|
||||
// ExpandByRadius method below is easier to use.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ExpandAtLevel(level int) {
|
||||
var output CellUnion
|
||||
levelLsb := lsbForLevel(level)
|
||||
for i := len(*cu) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
id := (*cu)[i]
|
||||
if id.lsb() < levelLsb {
|
||||
id = id.Parent(level)
|
||||
// Optimization: skip over any cells contained by this one. This is
|
||||
// especially important when very small regions are being expanded.
|
||||
for i > 0 && id.Contains((*cu)[i-1]) {
|
||||
i--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output = append(output, id)
|
||||
output = append(output, id.AllNeighbors(level)...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
sortCellIDs(output)
|
||||
|
||||
*cu = output
|
||||
cu.Normalize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExpandByRadius expands this CellUnion such that it contains all points whose
|
||||
// distance to the CellUnion is at most minRadius, but do not use cells that
|
||||
// are more than maxLevelDiff levels higher than the largest cell in the input.
|
||||
// The second parameter controls the tradeoff between accuracy and output size
|
||||
// when a large region is being expanded by a small amount (e.g. expanding Canada
|
||||
// by 1km). For example, if maxLevelDiff == 4 the region will always be expanded
|
||||
// by approximately 1/16 the width of its largest cell. Note that in the worst case,
|
||||
// the number of cells in the output can be up to 4 * (1 + 2 ** maxLevelDiff) times
|
||||
// larger than the number of cells in the input.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ExpandByRadius(minRadius s1.Angle, maxLevelDiff int) {
|
||||
minLevel := maxLevel
|
||||
for _, cid := range *cu {
|
||||
minLevel = minInt(minLevel, cid.Level())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the maximum level such that all cells are at least "minRadius" wide.
|
||||
radiusLevel := MinWidthMetric.MaxLevel(minRadius.Radians())
|
||||
if radiusLevel == 0 && minRadius.Radians() > MinWidthMetric.Value(0) {
|
||||
// The requested expansion is greater than the width of a face cell.
|
||||
// The easiest way to handle this is to expand twice.
|
||||
cu.ExpandAtLevel(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
cu.ExpandAtLevel(minInt(minLevel+maxLevelDiff, radiusLevel))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Equal reports whether the two CellUnions are equal.
|
||||
func (cu CellUnion) Equal(o CellUnion) bool {
|
||||
if len(cu) != len(o) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(cu); i++ {
|
||||
if cu[i] != o[i] {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AverageArea returns the average area of this CellUnion.
|
||||
// This is accurate to within a factor of 1.7.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) AverageArea() float64 {
|
||||
return AvgAreaMetric.Value(maxLevel) * float64(cu.LeafCellsCovered())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApproxArea returns the approximate area of this CellUnion. This method is accurate
|
||||
// to within 3% percent for all cell sizes and accurate to within 0.1% for cells
|
||||
// at level 5 or higher within the union.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ApproxArea() float64 {
|
||||
var area float64
|
||||
for _, id := range *cu {
|
||||
area += CellFromCellID(id).ApproxArea()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return area
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExactArea returns the area of this CellUnion as accurately as possible.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) ExactArea() float64 {
|
||||
var area float64
|
||||
for _, id := range *cu {
|
||||
area += CellFromCellID(id).ExactArea()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return area
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Encode encodes the CellUnion.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) Encode(w io.Writer) error {
|
||||
e := &encoder{w: w}
|
||||
cu.encode(e)
|
||||
return e.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) encode(e *encoder) {
|
||||
e.writeInt8(encodingVersion)
|
||||
e.writeInt64(int64(len(*cu)))
|
||||
for _, ci := range *cu {
|
||||
ci.encode(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode decodes the CellUnion.
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) Decode(r io.Reader) error {
|
||||
d := &decoder{r: asByteReader(r)}
|
||||
cu.decode(d)
|
||||
return d.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (cu *CellUnion) decode(d *decoder) {
|
||||
version := d.readInt8()
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if version != encodingVersion {
|
||||
d.err = fmt.Errorf("only version %d is supported", encodingVersion)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := d.readInt64()
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
const maxCells = 1000000
|
||||
if n > maxCells {
|
||||
d.err = fmt.Errorf("too many cells (%d; max is %d)", n, maxCells)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
*cu = make([]CellID, n)
|
||||
for i := range *cu {
|
||||
(*cu)[i].decode(d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
133
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/centroids.go
generated
vendored
133
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/centroids.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,133 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2018 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r3"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// There are several notions of the "centroid" of a triangle. First, there
|
||||
// is the planar centroid, which is simply the centroid of the ordinary
|
||||
// (non-spherical) triangle defined by the three vertices. Second, there is
|
||||
// the surface centroid, which is defined as the intersection of the three
|
||||
// medians of the spherical triangle. It is possible to show that this
|
||||
// point is simply the planar centroid projected to the surface of the
|
||||
// sphere. Finally, there is the true centroid (mass centroid), which is
|
||||
// defined as the surface integral over the spherical triangle of (x,y,z)
|
||||
// divided by the triangle area. This is the point that the triangle would
|
||||
// rotate around if it was spinning in empty space.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The best centroid for most purposes is the true centroid. Unlike the
|
||||
// planar and surface centroids, the true centroid behaves linearly as
|
||||
// regions are added or subtracted. That is, if you split a triangle into
|
||||
// pieces and compute the average of their centroids (weighted by triangle
|
||||
// area), the result equals the centroid of the original triangle. This is
|
||||
// not true of the other centroids.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Also note that the surface centroid may be nowhere near the intuitive
|
||||
// "center" of a spherical triangle. For example, consider the triangle
|
||||
// with vertices A=(1,eps,0), B=(0,0,1), C=(-1,eps,0) (a quarter-sphere).
|
||||
// The surface centroid of this triangle is at S=(0, 2*eps, 1), which is
|
||||
// within a distance of 2*eps of the vertex B. Note that the median from A
|
||||
// (the segment connecting A to the midpoint of BC) passes through S, since
|
||||
// this is the shortest path connecting the two endpoints. On the other
|
||||
// hand, the true centroid is at M=(0, 0.5, 0.5), which when projected onto
|
||||
// the surface is a much more reasonable interpretation of the "center" of
|
||||
// this triangle.
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
// TrueCentroid returns the true centroid of the spherical triangle ABC
|
||||
// multiplied by the signed area of spherical triangle ABC. The reasons for
|
||||
// multiplying by the signed area are (1) this is the quantity that needs to be
|
||||
// summed to compute the centroid of a union or difference of triangles, and
|
||||
// (2) it's actually easier to calculate this way. All points must have unit length.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the result of this function is defined to be Point(0, 0, 0) if
|
||||
// the triangle is degenerate.
|
||||
func TrueCentroid(a, b, c Point) Point {
|
||||
// Use Distance to get accurate results for small triangles.
|
||||
ra := float64(1)
|
||||
if sa := float64(b.Distance(c)); sa != 0 {
|
||||
ra = sa / math.Sin(sa)
|
||||
}
|
||||
rb := float64(1)
|
||||
if sb := float64(c.Distance(a)); sb != 0 {
|
||||
rb = sb / math.Sin(sb)
|
||||
}
|
||||
rc := float64(1)
|
||||
if sc := float64(a.Distance(b)); sc != 0 {
|
||||
rc = sc / math.Sin(sc)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Now compute a point M such that:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// [Ax Ay Az] [Mx] [ra]
|
||||
// [Bx By Bz] [My] = 0.5 * det(A,B,C) * [rb]
|
||||
// [Cx Cy Cz] [Mz] [rc]
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To improve the numerical stability we subtract the first row (A) from the
|
||||
// other two rows; this reduces the cancellation error when A, B, and C are
|
||||
// very close together. Then we solve it using Cramer's rule.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The result is the true centroid of the triangle multiplied by the
|
||||
// triangle's area.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This code still isn't as numerically stable as it could be.
|
||||
// The biggest potential improvement is to compute B-A and C-A more
|
||||
// accurately so that (B-A)x(C-A) is always inside triangle ABC.
|
||||
x := r3.Vector{a.X, b.X - a.X, c.X - a.X}
|
||||
y := r3.Vector{a.Y, b.Y - a.Y, c.Y - a.Y}
|
||||
z := r3.Vector{a.Z, b.Z - a.Z, c.Z - a.Z}
|
||||
r := r3.Vector{ra, rb - ra, rc - ra}
|
||||
|
||||
return Point{r3.Vector{y.Cross(z).Dot(r), z.Cross(x).Dot(r), x.Cross(y).Dot(r)}.Mul(0.5)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeTrueCentroid returns the true centroid of the spherical geodesic edge AB
|
||||
// multiplied by the length of the edge AB. As with triangles, the true centroid
|
||||
// of a collection of line segments may be computed simply by summing the result
|
||||
// of this method for each segment.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the planar centroid of a line segment is simply 0.5 * (a + b),
|
||||
// while the surface centroid is (a + b).Normalize(). However neither of
|
||||
// these values is appropriate for computing the centroid of a collection of
|
||||
// edges (such as a polyline).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Also note that the result of this function is defined to be Point(0, 0, 0)
|
||||
// if the edge is degenerate.
|
||||
func EdgeTrueCentroid(a, b Point) Point {
|
||||
// The centroid (multiplied by length) is a vector toward the midpoint
|
||||
// of the edge, whose length is twice the sine of half the angle between
|
||||
// the two vertices. Defining theta to be this angle, we have:
|
||||
vDiff := a.Sub(b.Vector) // Length == 2*sin(theta)
|
||||
vSum := a.Add(b.Vector) // Length == 2*cos(theta)
|
||||
sin2 := vDiff.Norm2()
|
||||
cos2 := vSum.Norm2()
|
||||
if cos2 == 0 {
|
||||
return Point{} // Ignore antipodal edges.
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Point{vSum.Mul(math.Sqrt(sin2 / cos2))} // Length == 2*sin(theta)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlanarCentroid returns the centroid of the planar triangle ABC. This can be
|
||||
// normalized to unit length to obtain the "surface centroid" of the corresponding
|
||||
// spherical triangle, i.e. the intersection of the three medians. However, note
|
||||
// that for large spherical triangles the surface centroid may be nowhere near
|
||||
// the intuitive "center".
|
||||
func PlanarCentroid(a, b, c Point) Point {
|
||||
return Point{a.Add(b.Vector).Add(c.Vector).Mul(1. / 3)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
157
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/contains_point_query.go
generated
vendored
157
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/contains_point_query.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,157 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2018 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
// VertexModel defines whether shapes are considered to contain their vertices.
|
||||
// Note that these definitions differ from the ones used by BooleanOperation.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that points other than vertices are never contained by polylines.
|
||||
// If you want need this behavior, use ClosestEdgeQuery's IsDistanceLess
|
||||
// with a suitable distance threshold instead.
|
||||
type VertexModel int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// VertexModelOpen means no shapes contain their vertices (not even
|
||||
// points). Therefore Contains(Point) returns true if and only if the
|
||||
// point is in the interior of some polygon.
|
||||
VertexModelOpen VertexModel = iota
|
||||
|
||||
// VertexModelSemiOpen means that polygon point containment is defined
|
||||
// such that if several polygons tile the region around a vertex, then
|
||||
// exactly one of those polygons contains that vertex. Points and
|
||||
// polylines still do not contain any vertices.
|
||||
VertexModelSemiOpen
|
||||
|
||||
// VertexModelClosed means all shapes contain their vertices (including
|
||||
// points and polylines).
|
||||
VertexModelClosed
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsPointQuery determines whether one or more shapes in a ShapeIndex
|
||||
// contain a given Point. The ShapeIndex may contain any number of points,
|
||||
// polylines, and/or polygons (possibly overlapping). Shape boundaries may be
|
||||
// modeled as Open, SemiOpen, or Closed (this affects whether or not shapes are
|
||||
// considered to contain their vertices).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that if you need to do a large number of point containment
|
||||
// tests, it is more efficient to re-use the query rather than creating a new
|
||||
// one each time.
|
||||
type ContainsPointQuery struct {
|
||||
model VertexModel
|
||||
index *ShapeIndex
|
||||
iter *ShapeIndexIterator
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContainsPointQuery creates a new instance of the ContainsPointQuery for the index
|
||||
// and given vertex model choice.
|
||||
func NewContainsPointQuery(index *ShapeIndex, model VertexModel) *ContainsPointQuery {
|
||||
return &ContainsPointQuery{
|
||||
index: index,
|
||||
model: model,
|
||||
iter: index.Iterator(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains reports whether any shape in the queries index contains the point p
|
||||
// under the queries vertex model (Open, SemiOpen, or Closed).
|
||||
func (q *ContainsPointQuery) Contains(p Point) bool {
|
||||
if !q.iter.LocatePoint(p) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cell := q.iter.IndexCell()
|
||||
for _, clipped := range cell.shapes {
|
||||
if q.shapeContains(clipped, q.iter.Center(), p) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// shapeContains reports whether the clippedShape from the iterator's center position contains
|
||||
// the given point.
|
||||
func (q *ContainsPointQuery) shapeContains(clipped *clippedShape, center, p Point) bool {
|
||||
inside := clipped.containsCenter
|
||||
numEdges := clipped.numEdges()
|
||||
if numEdges <= 0 {
|
||||
return inside
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
shape := q.index.Shape(clipped.shapeID)
|
||||
if !shape.HasInterior() {
|
||||
// Points and polylines can be ignored unless the vertex model is Closed.
|
||||
if q.model != VertexModelClosed {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the point is contained if and only if it matches a vertex.
|
||||
for _, edgeID := range clipped.edges {
|
||||
edge := shape.Edge(edgeID)
|
||||
if edge.V0 == p || edge.V1 == p {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Test containment by drawing a line segment from the cell center to the
|
||||
// given point and counting edge crossings.
|
||||
crosser := NewEdgeCrosser(center, p)
|
||||
for _, edgeID := range clipped.edges {
|
||||
edge := shape.Edge(edgeID)
|
||||
sign := crosser.CrossingSign(edge.V0, edge.V1)
|
||||
if sign == DoNotCross {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if sign == MaybeCross {
|
||||
// For the Open and Closed models, check whether p is a vertex.
|
||||
if q.model != VertexModelSemiOpen && (edge.V0 == p || edge.V1 == p) {
|
||||
return (q.model == VertexModelClosed)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// C++ plays fast and loose with the int <-> bool conversions here.
|
||||
if VertexCrossing(crosser.a, crosser.b, edge.V0, edge.V1) {
|
||||
sign = Cross
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
sign = DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
inside = inside != (sign == Cross)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return inside
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShapeContains reports whether the given shape contains the point under this
|
||||
// queries vertex model (Open, SemiOpen, or Closed).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This requires the shape belongs to this queries index.
|
||||
func (q *ContainsPointQuery) ShapeContains(shape Shape, p Point) bool {
|
||||
if !q.iter.LocatePoint(p) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
clipped := q.iter.IndexCell().findByShapeID(q.index.idForShape(shape))
|
||||
if clipped == nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return q.shapeContains(clipped, q.iter.Center(), p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): Remaining methods from C++
|
||||
// func (q *ContainsPointQuery) ContainingShapes(p Point) []Shape
|
||||
// type shapeVisitorFunc func(shape Shape) bool
|
||||
// func (q *ContainsPointQuery) VisitContainingShapes(p Point, v shapeVisitorFunc) bool
|
||||
// type edgeVisitorFunc func(shape ShapeEdge) bool
|
||||
// func (q *ContainsPointQuery) VisitIncidentEdges(p Point, v edgeVisitorFunc) bool
|
||||
63
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/contains_vertex_query.go
generated
vendored
63
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/contains_vertex_query.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsVertexQuery is used to track the edges entering and leaving the
|
||||
// given vertex of a Polygon in order to be able to determine if the point is
|
||||
// contained by the Polygon.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Point containment is defined according to the semi-open boundary model
|
||||
// which means that if several polygons tile the region around a vertex,
|
||||
// then exactly one of those polygons contains that vertex.
|
||||
type ContainsVertexQuery struct {
|
||||
target Point
|
||||
edgeMap map[Point]int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContainsVertexQuery returns a new query for the given vertex whose
|
||||
// containment will be determined.
|
||||
func NewContainsVertexQuery(target Point) *ContainsVertexQuery {
|
||||
return &ContainsVertexQuery{
|
||||
target: target,
|
||||
edgeMap: make(map[Point]int),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddEdge adds the edge between target and v with the given direction.
|
||||
// (+1 = outgoing, -1 = incoming, 0 = degenerate).
|
||||
func (q *ContainsVertexQuery) AddEdge(v Point, direction int) {
|
||||
q.edgeMap[v] += direction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ContainsVertex reports a +1 if the target vertex is contained, -1 if it is
|
||||
// not contained, and 0 if the incident edges consisted of matched sibling pairs.
|
||||
func (q *ContainsVertexQuery) ContainsVertex() int {
|
||||
// Find the unmatched edge that is immediately clockwise from Ortho(P).
|
||||
referenceDir := Point{q.target.Ortho()}
|
||||
|
||||
bestPoint := referenceDir
|
||||
bestDir := 0
|
||||
|
||||
for k, v := range q.edgeMap {
|
||||
if v == 0 {
|
||||
continue // This is a "matched" edge.
|
||||
}
|
||||
if OrderedCCW(referenceDir, bestPoint, k, q.target) {
|
||||
bestPoint = k
|
||||
bestDir = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bestDir
|
||||
}
|
||||
410
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/crossing_edge_query.go
generated
vendored
410
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/crossing_edge_query.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,410 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CrossingEdgeQuery is used to find the Edge IDs of Shapes that are crossed by
|
||||
// a given edge(s).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that if you need to query many edges, it is more efficient to declare
|
||||
// a single CrossingEdgeQuery instance and reuse it.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you want to find *all* the pairs of crossing edges, it is more efficient to
|
||||
// use the not yet implemented VisitCrossings in shapeutil.
|
||||
type CrossingEdgeQuery struct {
|
||||
index *ShapeIndex
|
||||
|
||||
// temporary values used while processing a query.
|
||||
a, b r2.Point
|
||||
iter *ShapeIndexIterator
|
||||
|
||||
// candidate cells generated when finding crossings.
|
||||
cells []*ShapeIndexCell
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewCrossingEdgeQuery creates a CrossingEdgeQuery for the given index.
|
||||
func NewCrossingEdgeQuery(index *ShapeIndex) *CrossingEdgeQuery {
|
||||
c := &CrossingEdgeQuery{
|
||||
index: index,
|
||||
iter: index.Iterator(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Crossings returns the set of edge of the shape S that intersect the given edge AB.
|
||||
// If the CrossingType is Interior, then only intersections at a point interior to both
|
||||
// edges are reported, while if it is CrossingTypeAll then edges that share a vertex
|
||||
// are also reported.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) Crossings(a, b Point, shape Shape, crossType CrossingType) []int {
|
||||
edges := c.candidates(a, b, shape)
|
||||
if len(edges) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
crosser := NewEdgeCrosser(a, b)
|
||||
out := 0
|
||||
n := len(edges)
|
||||
|
||||
for in := 0; in < n; in++ {
|
||||
b := shape.Edge(edges[in])
|
||||
sign := crosser.CrossingSign(b.V0, b.V1)
|
||||
if crossType == CrossingTypeAll && (sign == MaybeCross || sign == Cross) || crossType != CrossingTypeAll && sign == Cross {
|
||||
edges[out] = edges[in]
|
||||
out++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if out < n {
|
||||
edges = edges[0:out]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return edges
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeMap stores a sorted set of edge ids for each shape.
|
||||
type EdgeMap map[Shape][]int
|
||||
|
||||
// CrossingsEdgeMap returns the set of all edges in the index that intersect the given
|
||||
// edge AB. If crossType is CrossingTypeInterior, then only intersections at a
|
||||
// point interior to both edges are reported, while if it is CrossingTypeAll
|
||||
// then edges that share a vertex are also reported.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The edges are returned as a mapping from shape to the edges of that shape
|
||||
// that intersect AB. Every returned shape has at least one crossing edge.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) CrossingsEdgeMap(a, b Point, crossType CrossingType) EdgeMap {
|
||||
edgeMap := c.candidatesEdgeMap(a, b)
|
||||
if len(edgeMap) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
crosser := NewEdgeCrosser(a, b)
|
||||
for shape, edges := range edgeMap {
|
||||
out := 0
|
||||
n := len(edges)
|
||||
for in := 0; in < n; in++ {
|
||||
edge := shape.Edge(edges[in])
|
||||
sign := crosser.CrossingSign(edge.V0, edge.V1)
|
||||
if (crossType == CrossingTypeAll && (sign == MaybeCross || sign == Cross)) || (crossType != CrossingTypeAll && sign == Cross) {
|
||||
edgeMap[shape][out] = edges[in]
|
||||
out++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if out == 0 {
|
||||
delete(edgeMap, shape)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if out < n {
|
||||
edgeMap[shape] = edgeMap[shape][0:out]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return edgeMap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// candidates returns a superset of the edges of the given shape that intersect
|
||||
// the edge AB.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) candidates(a, b Point, shape Shape) []int {
|
||||
var edges []int
|
||||
|
||||
// For small loops it is faster to use brute force. The threshold below was
|
||||
// determined using benchmarks.
|
||||
const maxBruteForceEdges = 27
|
||||
maxEdges := shape.NumEdges()
|
||||
if maxEdges <= maxBruteForceEdges {
|
||||
edges = make([]int, maxEdges)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < maxEdges; i++ {
|
||||
edges[i] = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return edges
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the set of index cells intersected by the query edge.
|
||||
c.getCellsForEdge(a, b)
|
||||
if len(c.cells) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Gather all the edges that intersect those cells and sort them.
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): Shapes don't track their ID, so we need to range over
|
||||
// the index to find the ID manually.
|
||||
var shapeID int32
|
||||
for k, v := range c.index.shapes {
|
||||
if v == shape {
|
||||
shapeID = k
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, cell := range c.cells {
|
||||
if cell == nil {
|
||||
}
|
||||
clipped := cell.findByShapeID(shapeID)
|
||||
if clipped == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, j := range clipped.edges {
|
||||
edges = append(edges, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c.cells) > 1 {
|
||||
edges = uniqueInts(edges)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return edges
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// uniqueInts returns the sorted uniqued values from the given input.
|
||||
func uniqueInts(in []int) []int {
|
||||
var edges []int
|
||||
m := make(map[int]bool)
|
||||
for _, i := range in {
|
||||
if m[i] {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
m[i] = true
|
||||
edges = append(edges, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort.Ints(edges)
|
||||
return edges
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// candidatesEdgeMap returns a map from shapes to the superse of edges for that
|
||||
// shape that intersect the edge AB.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CAVEAT: This method may return shapes that have an empty set of candidate edges.
|
||||
// However the return value is non-empty only if at least one shape has a candidate edge.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) candidatesEdgeMap(a, b Point) EdgeMap {
|
||||
edgeMap := make(EdgeMap, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
// If there are only a few edges then it's faster to use brute force. We
|
||||
// only bother with this optimization when there is a single shape.
|
||||
if len(c.index.shapes) == 1 {
|
||||
// Typically this method is called many times, so it is worth checking
|
||||
// whether the edge map is empty or already consists of a single entry for
|
||||
// this shape, and skip clearing edge map in that case.
|
||||
shape := c.index.Shape(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Note that we leave the edge map non-empty even if there are no candidates
|
||||
// (i.e., there is a single entry with an empty set of edges).
|
||||
edgeMap[shape] = c.candidates(a, b, shape)
|
||||
return edgeMap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the set of index cells intersected by the query edge.
|
||||
c.getCellsForEdge(a, b)
|
||||
if len(c.cells) == 0 {
|
||||
return edgeMap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Gather all the edges that intersect those cells and sort them.
|
||||
for _, cell := range c.cells {
|
||||
for _, clipped := range cell.shapes {
|
||||
s := c.index.Shape(clipped.shapeID)
|
||||
for j := 0; j < clipped.numEdges(); j++ {
|
||||
edgeMap[s] = append(edgeMap[s], clipped.edges[j])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c.cells) > 1 {
|
||||
for s, edges := range edgeMap {
|
||||
edgeMap[s] = uniqueInts(edges)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return edgeMap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getCells returns the set of ShapeIndexCells that might contain edges intersecting
|
||||
// the edge AB in the given cell root. This method is used primarly by loop and shapeutil.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) getCells(a, b Point, root *PaddedCell) []*ShapeIndexCell {
|
||||
aUV, bUV, ok := ClipToFace(a, b, root.id.Face())
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
c.a = aUV
|
||||
c.b = bUV
|
||||
edgeBound := r2.RectFromPoints(c.a, c.b)
|
||||
if root.Bound().Intersects(edgeBound) {
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(root, edgeBound)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(c.cells) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c.cells
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getCellsForEdge populates the cells field to the set of index cells intersected by an edge AB.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) getCellsForEdge(a, b Point) {
|
||||
c.cells = nil
|
||||
|
||||
segments := FaceSegments(a, b)
|
||||
for _, segment := range segments {
|
||||
c.a = segment.a
|
||||
c.b = segment.b
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimization: rather than always starting the recursive subdivision at
|
||||
// the top level face cell, instead we start at the smallest S2CellId that
|
||||
// contains the edge (the edge root cell). This typically lets us skip
|
||||
// quite a few levels of recursion since most edges are short.
|
||||
edgeBound := r2.RectFromPoints(c.a, c.b)
|
||||
pcell := PaddedCellFromCellID(CellIDFromFace(segment.face), 0)
|
||||
edgeRoot := pcell.ShrinkToFit(edgeBound)
|
||||
|
||||
// Now we need to determine how the edge root cell is related to the cells
|
||||
// in the spatial index (cellMap). There are three cases:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1. edgeRoot is an index cell or is contained within an index cell.
|
||||
// In this case we only need to look at the contents of that cell.
|
||||
// 2. edgeRoot is subdivided into one or more index cells. In this case
|
||||
// we recursively subdivide to find the cells intersected by AB.
|
||||
// 3. edgeRoot does not intersect any index cells. In this case there
|
||||
// is nothing to do.
|
||||
relation := c.iter.LocateCellID(edgeRoot)
|
||||
if relation == Indexed {
|
||||
// edgeRoot is an index cell or is contained by an index cell (case 1).
|
||||
c.cells = append(c.cells, c.iter.IndexCell())
|
||||
} else if relation == Subdivided {
|
||||
// edgeRoot is subdivided into one or more index cells (case 2). We
|
||||
// find the cells intersected by AB using recursive subdivision.
|
||||
if !edgeRoot.isFace() {
|
||||
pcell = PaddedCellFromCellID(edgeRoot, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(pcell, edgeBound)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// computeCellsIntersected computes the index cells intersected by the current
|
||||
// edge that are descendants of pcell and adds them to this queries set of cells.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) computeCellsIntersected(pcell *PaddedCell, edgeBound r2.Rect) {
|
||||
|
||||
c.iter.seek(pcell.id.RangeMin())
|
||||
if c.iter.Done() || c.iter.CellID() > pcell.id.RangeMax() {
|
||||
// The index does not contain pcell or any of its descendants.
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c.iter.CellID() == pcell.id {
|
||||
// The index contains this cell exactly.
|
||||
c.cells = append(c.cells, c.iter.IndexCell())
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, split the edge among the four children of pcell.
|
||||
center := pcell.Middle().Lo()
|
||||
|
||||
if edgeBound.X.Hi < center.X {
|
||||
// Edge is entirely contained in the two left children.
|
||||
c.clipVAxis(edgeBound, center.Y, 0, pcell)
|
||||
return
|
||||
} else if edgeBound.X.Lo >= center.X {
|
||||
// Edge is entirely contained in the two right children.
|
||||
c.clipVAxis(edgeBound, center.Y, 1, pcell)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
childBounds := c.splitUBound(edgeBound, center.X)
|
||||
if edgeBound.Y.Hi < center.Y {
|
||||
// Edge is entirely contained in the two lower children.
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, 0, 0), childBounds[0])
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, 1, 0), childBounds[1])
|
||||
} else if edgeBound.Y.Lo >= center.Y {
|
||||
// Edge is entirely contained in the two upper children.
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, 0, 1), childBounds[0])
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, 1, 1), childBounds[1])
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// The edge bound spans all four children. The edge itself intersects
|
||||
// at most three children (since no padding is being used).
|
||||
c.clipVAxis(childBounds[0], center.Y, 0, pcell)
|
||||
c.clipVAxis(childBounds[1], center.Y, 1, pcell)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clipVAxis computes the intersected cells recursively for a given padded cell.
|
||||
// Given either the left (i=0) or right (i=1) side of a padded cell pcell,
|
||||
// determine whether the current edge intersects the lower child, upper child,
|
||||
// or both children, and call c.computeCellsIntersected recursively on those children.
|
||||
// The center is the v-coordinate at the center of pcell.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) clipVAxis(edgeBound r2.Rect, center float64, i int, pcell *PaddedCell) {
|
||||
if edgeBound.Y.Hi < center {
|
||||
// Edge is entirely contained in the lower child.
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, i, 0), edgeBound)
|
||||
} else if edgeBound.Y.Lo >= center {
|
||||
// Edge is entirely contained in the upper child.
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, i, 1), edgeBound)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// The edge intersects both children.
|
||||
childBounds := c.splitVBound(edgeBound, center)
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, i, 0), childBounds[0])
|
||||
c.computeCellsIntersected(PaddedCellFromParentIJ(pcell, i, 1), childBounds[1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// splitUBound returns the bound for two children as a result of spliting the
|
||||
// current edge at the given value U.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) splitUBound(edgeBound r2.Rect, u float64) [2]r2.Rect {
|
||||
v := edgeBound.Y.ClampPoint(interpolateFloat64(u, c.a.X, c.b.X, c.a.Y, c.b.Y))
|
||||
// diag indicates which diagonal of the bounding box is spanned by AB:
|
||||
// it is 0 if AB has positive slope, and 1 if AB has negative slope.
|
||||
var diag int
|
||||
if (c.a.X > c.b.X) != (c.a.Y > c.b.Y) {
|
||||
diag = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return splitBound(edgeBound, 0, diag, u, v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// splitVBound returns the bound for two children as a result of spliting the
|
||||
// current edge into two child edges at the given value V.
|
||||
func (c *CrossingEdgeQuery) splitVBound(edgeBound r2.Rect, v float64) [2]r2.Rect {
|
||||
u := edgeBound.X.ClampPoint(interpolateFloat64(v, c.a.Y, c.b.Y, c.a.X, c.b.X))
|
||||
var diag int
|
||||
if (c.a.X > c.b.X) != (c.a.Y > c.b.Y) {
|
||||
diag = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return splitBound(edgeBound, diag, 0, u, v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// splitBound returns the bounds for the two childrenn as a result of spliting
|
||||
// the current edge into two child edges at the given point (u,v). uEnd and vEnd
|
||||
// indicate which bound endpoints of the first child will be updated.
|
||||
func splitBound(edgeBound r2.Rect, uEnd, vEnd int, u, v float64) [2]r2.Rect {
|
||||
var childBounds = [2]r2.Rect{
|
||||
edgeBound,
|
||||
edgeBound,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if uEnd == 1 {
|
||||
childBounds[0].X.Lo = u
|
||||
childBounds[1].X.Hi = u
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
childBounds[0].X.Hi = u
|
||||
childBounds[1].X.Lo = u
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if vEnd == 1 {
|
||||
childBounds[0].Y.Lo = v
|
||||
childBounds[1].Y.Hi = v
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
childBounds[0].Y.Hi = v
|
||||
childBounds[1].Y.Lo = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return childBounds
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/doc.go
generated
vendored
29
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/doc.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2014 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package s2 implements types and functions for working with geometry in S² (spherical geometry).
|
||||
|
||||
Its related packages, parallel to this one, are s1 (operates on S¹), r1 (operates on ℝ¹)
|
||||
and r3 (operates on ℝ³).
|
||||
|
||||
This package provides types and functions for the S2 cell hierarchy and coordinate systems.
|
||||
The S2 cell hierarchy is a hierarchical decomposition of the surface of a unit sphere (S²)
|
||||
into ``cells''; it is highly efficient, scales from continental size to under 1 cm²
|
||||
and preserves spatial locality (nearby cells have close IDs).
|
||||
|
||||
A presentation that gives an overview of S2 is
|
||||
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1Hl4KapfAENAOf4gv-pSngKwvS_jwNVHRPZTTDzXXn6Q/view.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
672
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_clipping.go
generated
vendored
672
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_clipping.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,672 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
// This file contains a collection of methods for:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (1) Robustly clipping geodesic edges to the faces of the S2 biunit cube
|
||||
// (see s2stuv), and
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (2) Robustly clipping 2D edges against 2D rectangles.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// These functions can be used to efficiently find the set of CellIDs that
|
||||
// are intersected by a geodesic edge (e.g., see CrossingEdgeQuery).
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r1"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r2"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r3"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// edgeClipErrorUVCoord is the maximum error in a u- or v-coordinate
|
||||
// compared to the exact result, assuming that the points A and B are in
|
||||
// the rectangle [-1,1]x[1,1] or slightly outside it (by 1e-10 or less).
|
||||
edgeClipErrorUVCoord = 2.25 * dblEpsilon
|
||||
|
||||
// edgeClipErrorUVDist is the maximum distance from a clipped point to
|
||||
// the corresponding exact result. It is equal to the error in a single
|
||||
// coordinate because at most one coordinate is subject to error.
|
||||
edgeClipErrorUVDist = 2.25 * dblEpsilon
|
||||
|
||||
// faceClipErrorRadians is the maximum angle between a returned vertex
|
||||
// and the nearest point on the exact edge AB. It is equal to the
|
||||
// maximum directional error in PointCross, plus the error when
|
||||
// projecting points onto a cube face.
|
||||
faceClipErrorRadians = 3 * dblEpsilon
|
||||
|
||||
// faceClipErrorDist is the same angle expressed as a maximum distance
|
||||
// in (u,v)-space. In other words, a returned vertex is at most this far
|
||||
// from the exact edge AB projected into (u,v)-space.
|
||||
faceClipErrorUVDist = 9 * dblEpsilon
|
||||
|
||||
// faceClipErrorUVCoord is the maximum angle between a returned vertex
|
||||
// and the nearest point on the exact edge AB expressed as the maximum error
|
||||
// in an individual u- or v-coordinate. In other words, for each
|
||||
// returned vertex there is a point on the exact edge AB whose u- and
|
||||
// v-coordinates differ from the vertex by at most this amount.
|
||||
faceClipErrorUVCoord = 9.0 * (1.0 / math.Sqrt2) * dblEpsilon
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectsRectErrorUVDist is the maximum error when computing if a point
|
||||
// intersects with a given Rect. If some point of AB is inside the
|
||||
// rectangle by at least this distance, the result is guaranteed to be true;
|
||||
// if all points of AB are outside the rectangle by at least this distance,
|
||||
// the result is guaranteed to be false. This bound assumes that rect is
|
||||
// a subset of the rectangle [-1,1]x[-1,1] or extends slightly outside it
|
||||
// (e.g., by 1e-10 or less).
|
||||
intersectsRectErrorUVDist = 3 * math.Sqrt2 * dblEpsilon
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ClipToFace returns the (u,v) coordinates for the portion of the edge AB that
|
||||
// intersects the given face, or false if the edge AB does not intersect.
|
||||
// This method guarantees that the clipped vertices lie within the [-1,1]x[-1,1]
|
||||
// cube face rectangle and are within faceClipErrorUVDist of the line AB, but
|
||||
// the results may differ from those produced by FaceSegments.
|
||||
func ClipToFace(a, b Point, face int) (aUV, bUV r2.Point, intersects bool) {
|
||||
return ClipToPaddedFace(a, b, face, 0.0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClipToPaddedFace returns the (u,v) coordinates for the portion of the edge AB that
|
||||
// intersects the given face, but rather than clipping to the square [-1,1]x[-1,1]
|
||||
// in (u,v) space, this method clips to [-R,R]x[-R,R] where R=(1+padding).
|
||||
// Padding must be non-negative.
|
||||
func ClipToPaddedFace(a, b Point, f int, padding float64) (aUV, bUV r2.Point, intersects bool) {
|
||||
// Fast path: both endpoints are on the given face.
|
||||
if face(a.Vector) == f && face(b.Vector) == f {
|
||||
au, av := validFaceXYZToUV(f, a.Vector)
|
||||
bu, bv := validFaceXYZToUV(f, b.Vector)
|
||||
return r2.Point{au, av}, r2.Point{bu, bv}, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert everything into the (u,v,w) coordinates of the given face. Note
|
||||
// that the cross product *must* be computed in the original (x,y,z)
|
||||
// coordinate system because PointCross (unlike the mathematical cross
|
||||
// product) can produce different results in different coordinate systems
|
||||
// when one argument is a linear multiple of the other, due to the use of
|
||||
// symbolic perturbations.
|
||||
normUVW := pointUVW(faceXYZtoUVW(f, a.PointCross(b)))
|
||||
aUVW := pointUVW(faceXYZtoUVW(f, a))
|
||||
bUVW := pointUVW(faceXYZtoUVW(f, b))
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding is handled by scaling the u- and v-components of the normal.
|
||||
// Letting R=1+padding, this means that when we compute the dot product of
|
||||
// the normal with a cube face vertex (such as (-1,-1,1)), we will actually
|
||||
// compute the dot product with the scaled vertex (-R,-R,1). This allows
|
||||
// methods such as intersectsFace, exitAxis, etc, to handle padding
|
||||
// with no further modifications.
|
||||
scaleUV := 1 + padding
|
||||
scaledN := pointUVW{r3.Vector{X: scaleUV * normUVW.X, Y: scaleUV * normUVW.Y, Z: normUVW.Z}}
|
||||
if !scaledN.intersectsFace() {
|
||||
return aUV, bUV, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): This is a workaround for extremely small vectors where some
|
||||
// loss of precision can occur in Normalize causing underflow. When PointCross
|
||||
// is updated to work around this, this can be removed.
|
||||
if math.Max(math.Abs(normUVW.X), math.Max(math.Abs(normUVW.Y), math.Abs(normUVW.Z))) < math.Ldexp(1, -511) {
|
||||
normUVW = pointUVW{normUVW.Mul(math.Ldexp(1, 563))}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
normUVW = pointUVW{normUVW.Normalize()}
|
||||
|
||||
aTan := pointUVW{normUVW.Cross(aUVW.Vector)}
|
||||
bTan := pointUVW{bUVW.Cross(normUVW.Vector)}
|
||||
|
||||
// As described in clipDestination, if the sum of the scores from clipping the two
|
||||
// endpoints is 3 or more, then the segment does not intersect this face.
|
||||
aUV, aScore := clipDestination(bUVW, aUVW, pointUVW{scaledN.Mul(-1)}, bTan, aTan, scaleUV)
|
||||
bUV, bScore := clipDestination(aUVW, bUVW, scaledN, aTan, bTan, scaleUV)
|
||||
|
||||
return aUV, bUV, aScore+bScore < 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClipEdge returns the portion of the edge defined by AB that is contained by the
|
||||
// given rectangle. If there is no intersection, false is returned and aClip and bClip
|
||||
// are undefined.
|
||||
func ClipEdge(a, b r2.Point, clip r2.Rect) (aClip, bClip r2.Point, intersects bool) {
|
||||
// Compute the bounding rectangle of AB, clip it, and then extract the new
|
||||
// endpoints from the clipped bound.
|
||||
bound := r2.RectFromPoints(a, b)
|
||||
if bound, intersects = clipEdgeBound(a, b, clip, bound); !intersects {
|
||||
return aClip, bClip, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
ai := 0
|
||||
if a.X > b.X {
|
||||
ai = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
aj := 0
|
||||
if a.Y > b.Y {
|
||||
aj = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return bound.VertexIJ(ai, aj), bound.VertexIJ(1-ai, 1-aj), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The three functions below (sumEqual, intersectsFace, intersectsOppositeEdges)
|
||||
// all compare a sum (u + v) to a third value w. They are implemented in such a
|
||||
// way that they produce an exact result even though all calculations are done
|
||||
// with ordinary floating-point operations. Here are the principles on which these
|
||||
// functions are based:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A. If u + v < w in floating-point, then u + v < w in exact arithmetic.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// B. If u + v < w in exact arithmetic, then at least one of the following
|
||||
// expressions is true in floating-point:
|
||||
// u + v < w
|
||||
// u < w - v
|
||||
// v < w - u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Proof: By rearranging terms and substituting ">" for "<", we can assume
|
||||
// that all values are non-negative. Now clearly "w" is not the smallest
|
||||
// value, so assume WLOG that "u" is the smallest. We want to show that
|
||||
// u < w - v in floating-point. If v >= w/2, the calculation of w - v is
|
||||
// exact since the result is smaller in magnitude than either input value,
|
||||
// so the result holds. Otherwise we have u <= v < w/2 and w - v >= w/2
|
||||
// (even in floating point), so the result also holds.
|
||||
|
||||
// sumEqual reports whether u + v == w exactly.
|
||||
func sumEqual(u, v, w float64) bool {
|
||||
return (u+v == w) && (u == w-v) && (v == w-u)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pointUVW represents a Point in (u,v,w) coordinate space of a cube face.
|
||||
type pointUVW Point
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectsFace reports whether a given directed line L intersects the cube face F.
|
||||
// The line L is defined by its normal N in the (u,v,w) coordinates of F.
|
||||
func (p pointUVW) intersectsFace() bool {
|
||||
// L intersects the [-1,1]x[-1,1] square in (u,v) if and only if the dot
|
||||
// products of N with the four corner vertices (-1,-1,1), (1,-1,1), (1,1,1),
|
||||
// and (-1,1,1) do not all have the same sign. This is true exactly when
|
||||
// |Nu| + |Nv| >= |Nw|. The code below evaluates this expression exactly.
|
||||
u := math.Abs(p.X)
|
||||
v := math.Abs(p.Y)
|
||||
w := math.Abs(p.Z)
|
||||
|
||||
// We only need to consider the cases where u or v is the smallest value,
|
||||
// since if w is the smallest then both expressions below will have a
|
||||
// positive LHS and a negative RHS.
|
||||
return (v >= w-u) && (u >= w-v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectsOppositeEdges reports whether a directed line L intersects two
|
||||
// opposite edges of a cube face F. This includs the case where L passes
|
||||
// exactly through a corner vertex of F. The directed line L is defined
|
||||
// by its normal N in the (u,v,w) coordinates of F.
|
||||
func (p pointUVW) intersectsOppositeEdges() bool {
|
||||
// The line L intersects opposite edges of the [-1,1]x[-1,1] (u,v) square if
|
||||
// and only exactly two of the corner vertices lie on each side of L. This
|
||||
// is true exactly when ||Nu| - |Nv|| >= |Nw|. The code below evaluates this
|
||||
// expression exactly.
|
||||
u := math.Abs(p.X)
|
||||
v := math.Abs(p.Y)
|
||||
w := math.Abs(p.Z)
|
||||
|
||||
// If w is the smallest, the following line returns an exact result.
|
||||
if math.Abs(u-v) != w {
|
||||
return math.Abs(u-v) >= w
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise u - v = w exactly, or w is not the smallest value. In either
|
||||
// case the following returns the correct result.
|
||||
if u >= v {
|
||||
return u-w >= v
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v-w >= u
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// axis represents the possible results of exitAxis.
|
||||
type axis int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
axisU axis = iota
|
||||
axisV
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// exitAxis reports which axis the directed line L exits the cube face F on.
|
||||
// The directed line L is represented by its CCW normal N in the (u,v,w) coordinates
|
||||
// of F. It returns axisU if L exits through the u=-1 or u=+1 edge, and axisV if L exits
|
||||
// through the v=-1 or v=+1 edge. Either result is acceptable if L exits exactly
|
||||
// through a corner vertex of the cube face.
|
||||
func (p pointUVW) exitAxis() axis {
|
||||
if p.intersectsOppositeEdges() {
|
||||
// The line passes through through opposite edges of the face.
|
||||
// It exits through the v=+1 or v=-1 edge if the u-component of N has a
|
||||
// larger absolute magnitude than the v-component.
|
||||
if math.Abs(p.X) >= math.Abs(p.Y) {
|
||||
return axisV
|
||||
}
|
||||
return axisU
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The line passes through through two adjacent edges of the face.
|
||||
// It exits the v=+1 or v=-1 edge if an even number of the components of N
|
||||
// are negative. We test this using signbit() rather than multiplication
|
||||
// to avoid the possibility of underflow.
|
||||
var x, y, z int
|
||||
if math.Signbit(p.X) {
|
||||
x = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if math.Signbit(p.Y) {
|
||||
y = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if math.Signbit(p.Z) {
|
||||
z = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if x^y^z == 0 {
|
||||
return axisV
|
||||
}
|
||||
return axisU
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// exitPoint returns the UV coordinates of the point where a directed line L (represented
|
||||
// by the CCW normal of this point), exits the cube face this point is derived from along
|
||||
// the given axis.
|
||||
func (p pointUVW) exitPoint(a axis) r2.Point {
|
||||
if a == axisU {
|
||||
u := -1.0
|
||||
if p.Y > 0 {
|
||||
u = 1.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r2.Point{u, (-u*p.X - p.Z) / p.Y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
v := -1.0
|
||||
if p.X < 0 {
|
||||
v = 1.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r2.Point{(-v*p.Y - p.Z) / p.X, v}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clipDestination returns a score which is used to indicate if the clipped edge AB
|
||||
// on the given face intersects the face at all. This function returns the score for
|
||||
// the given endpoint, which is an integer ranging from 0 to 3. If the sum of the scores
|
||||
// from both of the endpoints is 3 or more, then edge AB does not intersect this face.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// First, it clips the line segment AB to find the clipped destination B' on a given
|
||||
// face. (The face is specified implicitly by expressing *all arguments* in the (u,v,w)
|
||||
// coordinates of that face.) Second, it partially computes whether the segment AB
|
||||
// intersects this face at all. The actual condition is fairly complicated, but it
|
||||
// turns out that it can be expressed as a "score" that can be computed independently
|
||||
// when clipping the two endpoints A and B.
|
||||
func clipDestination(a, b, scaledN, aTan, bTan pointUVW, scaleUV float64) (r2.Point, int) {
|
||||
var uv r2.Point
|
||||
|
||||
// Optimization: if B is within the safe region of the face, use it.
|
||||
maxSafeUVCoord := 1 - faceClipErrorUVCoord
|
||||
if b.Z > 0 {
|
||||
uv = r2.Point{b.X / b.Z, b.Y / b.Z}
|
||||
if math.Max(math.Abs(uv.X), math.Abs(uv.Y)) <= maxSafeUVCoord {
|
||||
return uv, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise find the point B' where the line AB exits the face.
|
||||
uv = scaledN.exitPoint(scaledN.exitAxis()).Mul(scaleUV)
|
||||
|
||||
p := pointUVW(Point{r3.Vector{uv.X, uv.Y, 1.0}})
|
||||
|
||||
// Determine if the exit point B' is contained within the segment. We do this
|
||||
// by computing the dot products with two inward-facing tangent vectors at A
|
||||
// and B. If either dot product is negative, we say that B' is on the "wrong
|
||||
// side" of that point. As the point B' moves around the great circle AB past
|
||||
// the segment endpoint B, it is initially on the wrong side of B only; as it
|
||||
// moves further it is on the wrong side of both endpoints; and then it is on
|
||||
// the wrong side of A only. If the exit point B' is on the wrong side of
|
||||
// either endpoint, we can't use it; instead the segment is clipped at the
|
||||
// original endpoint B.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We reject the segment if the sum of the scores of the two endpoints is 3
|
||||
// or more. Here is what that rule encodes:
|
||||
// - If B' is on the wrong side of A, then the other clipped endpoint A'
|
||||
// must be in the interior of AB (otherwise AB' would go the wrong way
|
||||
// around the circle). There is a similar rule for A'.
|
||||
// - If B' is on the wrong side of either endpoint (and therefore we must
|
||||
// use the original endpoint B instead), then it must be possible to
|
||||
// project B onto this face (i.e., its w-coordinate must be positive).
|
||||
// This rule is only necessary to handle certain zero-length edges (A=B).
|
||||
score := 0
|
||||
if p.Sub(a.Vector).Dot(aTan.Vector) < 0 {
|
||||
score = 2 // B' is on wrong side of A.
|
||||
} else if p.Sub(b.Vector).Dot(bTan.Vector) < 0 {
|
||||
score = 1 // B' is on wrong side of B.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if score > 0 { // B' is not in the interior of AB.
|
||||
if b.Z <= 0 {
|
||||
score = 3 // B cannot be projected onto this face.
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
uv = r2.Point{b.X / b.Z, b.Y / b.Z}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return uv, score
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// updateEndpoint returns the interval with the specified endpoint updated to
|
||||
// the given value. If the value lies beyond the opposite endpoint, nothing is
|
||||
// changed and false is returned.
|
||||
func updateEndpoint(bound r1.Interval, highEndpoint bool, value float64) (r1.Interval, bool) {
|
||||
if !highEndpoint {
|
||||
if bound.Hi < value {
|
||||
return bound, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bound.Lo < value {
|
||||
bound.Lo = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bound, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bound.Lo > value {
|
||||
return bound, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bound.Hi > value {
|
||||
bound.Hi = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bound, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clipBoundAxis returns the clipped versions of the bounding intervals for the given
|
||||
// axes for the line segment from (a0,a1) to (b0,b1) so that neither extends beyond the
|
||||
// given clip interval. negSlope is a precomputed helper variable that indicates which
|
||||
// diagonal of the bounding box is spanned by AB; it is false if AB has positive slope,
|
||||
// and true if AB has negative slope. If the clipping interval doesn't overlap the bounds,
|
||||
// false is returned.
|
||||
func clipBoundAxis(a0, b0 float64, bound0 r1.Interval, a1, b1 float64, bound1 r1.Interval,
|
||||
negSlope bool, clip r1.Interval) (bound0c, bound1c r1.Interval, updated bool) {
|
||||
|
||||
if bound0.Lo < clip.Lo {
|
||||
// If the upper bound is below the clips lower bound, there is nothing to do.
|
||||
if bound0.Hi < clip.Lo {
|
||||
return bound0, bound1, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
// narrow the intervals lower bound to the clip bound.
|
||||
bound0.Lo = clip.Lo
|
||||
if bound1, updated = updateEndpoint(bound1, negSlope, interpolateFloat64(clip.Lo, a0, b0, a1, b1)); !updated {
|
||||
return bound0, bound1, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bound0.Hi > clip.Hi {
|
||||
// If the lower bound is above the clips upper bound, there is nothing to do.
|
||||
if bound0.Lo > clip.Hi {
|
||||
return bound0, bound1, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
// narrow the intervals upper bound to the clip bound.
|
||||
bound0.Hi = clip.Hi
|
||||
if bound1, updated = updateEndpoint(bound1, !negSlope, interpolateFloat64(clip.Hi, a0, b0, a1, b1)); !updated {
|
||||
return bound0, bound1, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return bound0, bound1, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// edgeIntersectsRect reports whether the edge defined by AB intersects the
|
||||
// given closed rectangle to within the error bound.
|
||||
func edgeIntersectsRect(a, b r2.Point, r r2.Rect) bool {
|
||||
// First check whether the bounds of a Rect around AB intersects the given rect.
|
||||
if !r.Intersects(r2.RectFromPoints(a, b)) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise AB intersects the rect if and only if all four vertices of rect
|
||||
// do not lie on the same side of the extended line AB. We test this by finding
|
||||
// the two vertices of rect with minimum and maximum projections onto the normal
|
||||
// of AB, and computing their dot products with the edge normal.
|
||||
n := b.Sub(a).Ortho()
|
||||
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
if n.X >= 0 {
|
||||
i = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
if n.Y >= 0 {
|
||||
j = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
max := n.Dot(r.VertexIJ(i, j).Sub(a))
|
||||
min := n.Dot(r.VertexIJ(1-i, 1-j).Sub(a))
|
||||
|
||||
return (max >= 0) && (min <= 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clippedEdgeBound returns the bounding rectangle of the portion of the edge defined
|
||||
// by AB intersected by clip. The resulting bound may be empty. This is a convenience
|
||||
// function built on top of clipEdgeBound.
|
||||
func clippedEdgeBound(a, b r2.Point, clip r2.Rect) r2.Rect {
|
||||
bound := r2.RectFromPoints(a, b)
|
||||
if b1, intersects := clipEdgeBound(a, b, clip, bound); intersects {
|
||||
return b1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r2.EmptyRect()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clipEdgeBound clips an edge AB to sequence of rectangles efficiently.
|
||||
// It represents the clipped edges by their bounding boxes rather than as a pair of
|
||||
// endpoints. Specifically, let A'B' be some portion of an edge AB, and let bound be
|
||||
// a tight bound of A'B'. This function returns the bound that is a tight bound
|
||||
// of A'B' intersected with a given rectangle. If A'B' does not intersect clip,
|
||||
// it returns false and the original bound.
|
||||
func clipEdgeBound(a, b r2.Point, clip, bound r2.Rect) (r2.Rect, bool) {
|
||||
// negSlope indicates which diagonal of the bounding box is spanned by AB: it
|
||||
// is false if AB has positive slope, and true if AB has negative slope. This is
|
||||
// used to determine which interval endpoints need to be updated each time
|
||||
// the edge is clipped.
|
||||
negSlope := (a.X > b.X) != (a.Y > b.Y)
|
||||
|
||||
b0x, b0y, up1 := clipBoundAxis(a.X, b.X, bound.X, a.Y, b.Y, bound.Y, negSlope, clip.X)
|
||||
if !up1 {
|
||||
return bound, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
b1y, b1x, up2 := clipBoundAxis(a.Y, b.Y, b0y, a.X, b.X, b0x, negSlope, clip.Y)
|
||||
if !up2 {
|
||||
return r2.Rect{b0x, b0y}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r2.Rect{X: b1x, Y: b1y}, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// interpolateFloat64 returns a value with the same combination of a1 and b1 as the
|
||||
// given value x is of a and b. This function makes the following guarantees:
|
||||
// - If x == a, then x1 = a1 (exactly).
|
||||
// - If x == b, then x1 = b1 (exactly).
|
||||
// - If a <= x <= b, then a1 <= x1 <= b1 (even if a1 == b1).
|
||||
// This requires a != b.
|
||||
func interpolateFloat64(x, a, b, a1, b1 float64) float64 {
|
||||
// To get results that are accurate near both A and B, we interpolate
|
||||
// starting from the closer of the two points.
|
||||
if math.Abs(a-x) <= math.Abs(b-x) {
|
||||
return a1 + (b1-a1)*(x-a)/(b-a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b1 + (a1-b1)*(x-b)/(a-b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FaceSegment represents an edge AB clipped to an S2 cube face. It is
|
||||
// represented by a face index and a pair of (u,v) coordinates.
|
||||
type FaceSegment struct {
|
||||
face int
|
||||
a, b r2.Point
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FaceSegments subdivides the given edge AB at every point where it crosses the
|
||||
// boundary between two S2 cube faces and returns the corresponding FaceSegments.
|
||||
// The segments are returned in order from A toward B. The input points must be
|
||||
// unit length.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function guarantees that the returned segments form a continuous path
|
||||
// from A to B, and that all vertices are within faceClipErrorUVDist of the
|
||||
// line AB. All vertices lie within the [-1,1]x[-1,1] cube face rectangles.
|
||||
// The results are consistent with Sign, i.e. the edge is well-defined even its
|
||||
// endpoints are antipodal.
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): Extend the implementation of PointCross so that this is true.
|
||||
func FaceSegments(a, b Point) []FaceSegment {
|
||||
var segment FaceSegment
|
||||
|
||||
// Fast path: both endpoints are on the same face.
|
||||
var aFace, bFace int
|
||||
aFace, segment.a.X, segment.a.Y = xyzToFaceUV(a.Vector)
|
||||
bFace, segment.b.X, segment.b.Y = xyzToFaceUV(b.Vector)
|
||||
if aFace == bFace {
|
||||
segment.face = aFace
|
||||
return []FaceSegment{segment}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Starting at A, we follow AB from face to face until we reach the face
|
||||
// containing B. The following code is designed to ensure that we always
|
||||
// reach B, even in the presence of numerical errors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// First we compute the normal to the plane containing A and B. This normal
|
||||
// becomes the ultimate definition of the line AB; it is used to resolve all
|
||||
// questions regarding where exactly the line goes. Unfortunately due to
|
||||
// numerical errors, the line may not quite intersect the faces containing
|
||||
// the original endpoints. We handle this by moving A and/or B slightly if
|
||||
// necessary so that they are on faces intersected by the line AB.
|
||||
ab := a.PointCross(b)
|
||||
|
||||
aFace, segment.a = moveOriginToValidFace(aFace, a, ab, segment.a)
|
||||
bFace, segment.b = moveOriginToValidFace(bFace, b, Point{ab.Mul(-1)}, segment.b)
|
||||
|
||||
// Now we simply follow AB from face to face until we reach B.
|
||||
var segments []FaceSegment
|
||||
segment.face = aFace
|
||||
bSaved := segment.b
|
||||
|
||||
for face := aFace; face != bFace; {
|
||||
// Complete the current segment by finding the point where AB
|
||||
// exits the current face.
|
||||
z := faceXYZtoUVW(face, ab)
|
||||
n := pointUVW{z.Vector}
|
||||
|
||||
exitAxis := n.exitAxis()
|
||||
segment.b = n.exitPoint(exitAxis)
|
||||
segments = append(segments, segment)
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the next face intersected by AB, and translate the exit
|
||||
// point of the current segment into the (u,v) coordinates of the
|
||||
// next face. This becomes the first point of the next segment.
|
||||
exitXyz := faceUVToXYZ(face, segment.b.X, segment.b.Y)
|
||||
face = nextFace(face, segment.b, exitAxis, n, bFace)
|
||||
exitUvw := faceXYZtoUVW(face, Point{exitXyz})
|
||||
segment.face = face
|
||||
segment.a = r2.Point{exitUvw.X, exitUvw.Y}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Finish the last segment.
|
||||
segment.b = bSaved
|
||||
return append(segments, segment)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// moveOriginToValidFace updates the origin point to a valid face if necessary.
|
||||
// Given a line segment AB whose origin A has been projected onto a given cube
|
||||
// face, determine whether it is necessary to project A onto a different face
|
||||
// instead. This can happen because the normal of the line AB is not computed
|
||||
// exactly, so that the line AB (defined as the set of points perpendicular to
|
||||
// the normal) may not intersect the cube face containing A. Even if it does
|
||||
// intersect the face, the exit point of the line from that face may be on
|
||||
// the wrong side of A (i.e., in the direction away from B). If this happens,
|
||||
// we reproject A onto the adjacent face where the line AB approaches A most
|
||||
// closely. This moves the origin by a small amount, but never more than the
|
||||
// error tolerances.
|
||||
func moveOriginToValidFace(face int, a, ab Point, aUV r2.Point) (int, r2.Point) {
|
||||
// Fast path: if the origin is sufficiently far inside the face, it is
|
||||
// always safe to use it.
|
||||
const maxSafeUVCoord = 1 - faceClipErrorUVCoord
|
||||
if math.Max(math.Abs((aUV).X), math.Abs((aUV).Y)) <= maxSafeUVCoord {
|
||||
return face, aUV
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise check whether the normal AB even intersects this face.
|
||||
z := faceXYZtoUVW(face, ab)
|
||||
n := pointUVW{z.Vector}
|
||||
if n.intersectsFace() {
|
||||
// Check whether the point where the line AB exits this face is on the
|
||||
// wrong side of A (by more than the acceptable error tolerance).
|
||||
uv := n.exitPoint(n.exitAxis())
|
||||
exit := faceUVToXYZ(face, uv.X, uv.Y)
|
||||
aTangent := ab.Normalize().Cross(a.Vector)
|
||||
|
||||
// We can use the given face.
|
||||
if exit.Sub(a.Vector).Dot(aTangent) >= -faceClipErrorRadians {
|
||||
return face, aUV
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise we reproject A to the nearest adjacent face. (If line AB does
|
||||
// not pass through a given face, it must pass through all adjacent faces.)
|
||||
var dir int
|
||||
if math.Abs((aUV).X) >= math.Abs((aUV).Y) {
|
||||
// U-axis
|
||||
if aUV.X > 0 {
|
||||
dir = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
face = uvwFace(face, 0, dir)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// V-axis
|
||||
if aUV.Y > 0 {
|
||||
dir = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
face = uvwFace(face, 1, dir)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
aUV.X, aUV.Y = validFaceXYZToUV(face, a.Vector)
|
||||
aUV.X = math.Max(-1.0, math.Min(1.0, aUV.X))
|
||||
aUV.Y = math.Max(-1.0, math.Min(1.0, aUV.Y))
|
||||
|
||||
return face, aUV
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// nextFace returns the next face that should be visited by FaceSegments, given that
|
||||
// we have just visited face and we are following the line AB (represented
|
||||
// by its normal N in the (u,v,w) coordinates of that face). The other
|
||||
// arguments include the point where AB exits face, the corresponding
|
||||
// exit axis, and the target face containing the destination point B.
|
||||
func nextFace(face int, exit r2.Point, axis axis, n pointUVW, targetFace int) int {
|
||||
// this bit is to work around C++ cleverly casting bools to ints for you.
|
||||
exitA := exit.X
|
||||
exit1MinusA := exit.Y
|
||||
|
||||
if axis == axisV {
|
||||
exitA = exit.Y
|
||||
exit1MinusA = exit.X
|
||||
}
|
||||
exitAPos := 0
|
||||
if exitA > 0 {
|
||||
exitAPos = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
exit1MinusAPos := 0
|
||||
if exit1MinusA > 0 {
|
||||
exit1MinusAPos = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We return the face that is adjacent to the exit point along the given
|
||||
// axis. If line AB exits *exactly* through a corner of the face, there are
|
||||
// two possible next faces. If one is the target face containing B, then
|
||||
// we guarantee that we advance to that face directly.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The three conditions below check that (1) AB exits approximately through
|
||||
// a corner, (2) the adjacent face along the non-exit axis is the target
|
||||
// face, and (3) AB exits *exactly* through the corner. (The sumEqual
|
||||
// code checks whether the dot product of (u,v,1) and n is exactly zero.)
|
||||
if math.Abs(exit1MinusA) == 1 &&
|
||||
uvwFace(face, int(1-axis), exit1MinusAPos) == targetFace &&
|
||||
sumEqual(exit.X*n.X, exit.Y*n.Y, -n.Z) {
|
||||
return targetFace
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise return the face that is adjacent to the exit point in the
|
||||
// direction of the exit axis.
|
||||
return uvwFace(face, int(axis), exitAPos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
227
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_crosser.go
generated
vendored
227
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_crosser.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,227 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeCrosser allows edges to be efficiently tested for intersection with a
|
||||
// given fixed edge AB. It is especially efficient when testing for
|
||||
// intersection with an edge chain connecting vertices v0, v1, v2, ...
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func CountIntersections(a, b Point, edges []Edge) int {
|
||||
// count := 0
|
||||
// crosser := NewEdgeCrosser(a, b)
|
||||
// for _, edge := range edges {
|
||||
// if crosser.CrossingSign(&edge.First, &edge.Second) != DoNotCross {
|
||||
// count++
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// return count
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
type EdgeCrosser struct {
|
||||
a Point
|
||||
b Point
|
||||
aXb Point
|
||||
|
||||
// To reduce the number of calls to expensiveSign, we compute an
|
||||
// outward-facing tangent at A and B if necessary. If the plane
|
||||
// perpendicular to one of these tangents separates AB from CD (i.e., one
|
||||
// edge on each side) then there is no intersection.
|
||||
aTangent Point // Outward-facing tangent at A.
|
||||
bTangent Point // Outward-facing tangent at B.
|
||||
|
||||
// The fields below are updated for each vertex in the chain.
|
||||
c Point // Previous vertex in the vertex chain.
|
||||
acb Direction // The orientation of triangle ACB.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewEdgeCrosser returns an EdgeCrosser with the fixed edge AB.
|
||||
func NewEdgeCrosser(a, b Point) *EdgeCrosser {
|
||||
norm := a.PointCross(b)
|
||||
return &EdgeCrosser{
|
||||
a: a,
|
||||
b: b,
|
||||
aXb: Point{a.Cross(b.Vector)},
|
||||
aTangent: Point{a.Cross(norm.Vector)},
|
||||
bTangent: Point{norm.Cross(b.Vector)},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CrossingSign reports whether the edge AB intersects the edge CD. If any two
|
||||
// vertices from different edges are the same, returns MaybeCross. If either edge
|
||||
// is degenerate (A == B or C == D), returns either DoNotCross or MaybeCross.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Properties of CrossingSign:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (1) CrossingSign(b,a,c,d) == CrossingSign(a,b,c,d)
|
||||
// (2) CrossingSign(c,d,a,b) == CrossingSign(a,b,c,d)
|
||||
// (3) CrossingSign(a,b,c,d) == MaybeCross if a==c, a==d, b==c, b==d
|
||||
// (3) CrossingSign(a,b,c,d) == DoNotCross or MaybeCross if a==b or c==d
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that if you want to check an edge against a chain of other edges,
|
||||
// it is slightly more efficient to use the single-argument version
|
||||
// ChainCrossingSign below.
|
||||
func (e *EdgeCrosser) CrossingSign(c, d Point) Crossing {
|
||||
if c != e.c {
|
||||
e.RestartAt(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return e.ChainCrossingSign(d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeOrVertexCrossing reports whether if CrossingSign(c, d) > 0, or AB and
|
||||
// CD share a vertex and VertexCrossing(a, b, c, d) is true.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method extends the concept of a "crossing" to the case where AB
|
||||
// and CD have a vertex in common. The two edges may or may not cross,
|
||||
// according to the rules defined in VertexCrossing above. The rules
|
||||
// are designed so that point containment tests can be implemented simply
|
||||
// by counting edge crossings. Similarly, determining whether one edge
|
||||
// chain crosses another edge chain can be implemented by counting.
|
||||
func (e *EdgeCrosser) EdgeOrVertexCrossing(c, d Point) bool {
|
||||
if c != e.c {
|
||||
e.RestartAt(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return e.EdgeOrVertexChainCrossing(d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewChainEdgeCrosser is a convenience constructor that uses AB as the fixed edge,
|
||||
// and C as the first vertex of the vertex chain (equivalent to calling RestartAt(c)).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// You don't need to use this or any of the chain functions unless you're trying to
|
||||
// squeeze out every last drop of performance. Essentially all you are saving is a test
|
||||
// whether the first vertex of the current edge is the same as the second vertex of the
|
||||
// previous edge.
|
||||
func NewChainEdgeCrosser(a, b, c Point) *EdgeCrosser {
|
||||
e := NewEdgeCrosser(a, b)
|
||||
e.RestartAt(c)
|
||||
return e
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RestartAt sets the current point of the edge crosser to be c.
|
||||
// Call this method when your chain 'jumps' to a new place.
|
||||
// The argument must point to a value that persists until the next call.
|
||||
func (e *EdgeCrosser) RestartAt(c Point) {
|
||||
e.c = c
|
||||
e.acb = -triageSign(e.a, e.b, e.c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ChainCrossingSign is like CrossingSign, but uses the last vertex passed to one of
|
||||
// the crossing methods (or RestartAt) as the first vertex of the current edge.
|
||||
func (e *EdgeCrosser) ChainCrossingSign(d Point) Crossing {
|
||||
// For there to be an edge crossing, the triangles ACB, CBD, BDA, DAC must
|
||||
// all be oriented the same way (CW or CCW). We keep the orientation of ACB
|
||||
// as part of our state. When each new point D arrives, we compute the
|
||||
// orientation of BDA and check whether it matches ACB. This checks whether
|
||||
// the points C and D are on opposite sides of the great circle through AB.
|
||||
|
||||
// Recall that triageSign is invariant with respect to rotating its
|
||||
// arguments, i.e. ABD has the same orientation as BDA.
|
||||
bda := triageSign(e.a, e.b, d)
|
||||
if e.acb == -bda && bda != Indeterminate {
|
||||
// The most common case -- triangles have opposite orientations. Save the
|
||||
// current vertex D as the next vertex C, and also save the orientation of
|
||||
// the new triangle ACB (which is opposite to the current triangle BDA).
|
||||
e.c = d
|
||||
e.acb = -bda
|
||||
return DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
return e.crossingSign(d, bda)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeOrVertexChainCrossing is like EdgeOrVertexCrossing, but uses the last vertex
|
||||
// passed to one of the crossing methods (or RestartAt) as the first vertex of the current edge.
|
||||
func (e *EdgeCrosser) EdgeOrVertexChainCrossing(d Point) bool {
|
||||
// We need to copy e.c since it is clobbered by ChainCrossingSign.
|
||||
c := e.c
|
||||
switch e.ChainCrossingSign(d) {
|
||||
case DoNotCross:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
case Cross:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return VertexCrossing(e.a, e.b, c, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// crossingSign handle the slow path of CrossingSign.
|
||||
func (e *EdgeCrosser) crossingSign(d Point, bda Direction) Crossing {
|
||||
// Compute the actual result, and then save the current vertex D as the next
|
||||
// vertex C, and save the orientation of the next triangle ACB (which is
|
||||
// opposite to the current triangle BDA).
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
e.c = d
|
||||
e.acb = -bda
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
// At this point, a very common situation is that A,B,C,D are four points on
|
||||
// a line such that AB does not overlap CD. (For example, this happens when
|
||||
// a line or curve is sampled finely, or when geometry is constructed by
|
||||
// computing the union of S2CellIds.) Most of the time, we can determine
|
||||
// that AB and CD do not intersect using the two outward-facing
|
||||
// tangents at A and B (parallel to AB) and testing whether AB and CD are on
|
||||
// opposite sides of the plane perpendicular to one of these tangents. This
|
||||
// is moderately expensive but still much cheaper than expensiveSign.
|
||||
|
||||
// The error in RobustCrossProd is insignificant. The maximum error in
|
||||
// the call to CrossProd (i.e., the maximum norm of the error vector) is
|
||||
// (0.5 + 1/sqrt(3)) * dblEpsilon. The maximum error in each call to
|
||||
// DotProd below is dblEpsilon. (There is also a small relative error
|
||||
// term that is insignificant because we are comparing the result against a
|
||||
// constant that is very close to zero.)
|
||||
maxError := (1.5 + 1/math.Sqrt(3)) * dblEpsilon
|
||||
if (e.c.Dot(e.aTangent.Vector) > maxError && d.Dot(e.aTangent.Vector) > maxError) || (e.c.Dot(e.bTangent.Vector) > maxError && d.Dot(e.bTangent.Vector) > maxError) {
|
||||
return DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, eliminate the cases where two vertices from different edges are
|
||||
// equal. (These cases could be handled in the code below, but we would rather
|
||||
// avoid calling ExpensiveSign if possible.)
|
||||
if e.a == e.c || e.a == d || e.b == e.c || e.b == d {
|
||||
return MaybeCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Eliminate the cases where an input edge is degenerate. (Note that in
|
||||
// most cases, if CD is degenerate then this method is not even called
|
||||
// because acb and bda have different signs.)
|
||||
if e.a == e.b || e.c == d {
|
||||
return DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise it's time to break out the big guns.
|
||||
if e.acb == Indeterminate {
|
||||
e.acb = -expensiveSign(e.a, e.b, e.c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bda == Indeterminate {
|
||||
bda = expensiveSign(e.a, e.b, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bda != e.acb {
|
||||
return DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cbd := -RobustSign(e.c, d, e.b)
|
||||
if cbd != e.acb {
|
||||
return DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
dac := RobustSign(e.c, d, e.a)
|
||||
if dac != e.acb {
|
||||
return DoNotCross
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Cross
|
||||
}
|
||||
394
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_crossings.go
generated
vendored
394
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_crossings.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,394 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/r3"
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// intersectionError can be set somewhat arbitrarily, because the algorithm
|
||||
// uses more precision if necessary in order to achieve the specified error.
|
||||
// The only strict requirement is that intersectionError >= dblEpsilon
|
||||
// radians. However, using a larger error tolerance makes the algorithm more
|
||||
// efficient because it reduces the number of cases where exact arithmetic is
|
||||
// needed.
|
||||
intersectionError = s1.Angle(8 * dblEpsilon)
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectionMergeRadius is used to ensure that intersection points that
|
||||
// are supposed to be coincident are merged back together into a single
|
||||
// vertex. This is required in order for various polygon operations (union,
|
||||
// intersection, etc) to work correctly. It is twice the intersection error
|
||||
// because two coincident intersection points might have errors in
|
||||
// opposite directions.
|
||||
intersectionMergeRadius = 2 * intersectionError
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// A Crossing indicates how edges cross.
|
||||
type Crossing int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Cross means the edges cross.
|
||||
Cross Crossing = iota
|
||||
// MaybeCross means two vertices from different edges are the same.
|
||||
MaybeCross
|
||||
// DoNotCross means the edges do not cross.
|
||||
DoNotCross
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Crossing) String() string {
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case Cross:
|
||||
return "Cross"
|
||||
case MaybeCross:
|
||||
return "MaybeCross"
|
||||
case DoNotCross:
|
||||
return "DoNotCross"
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("(BAD CROSSING %d)", c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CrossingSign reports whether the edge AB intersects the edge CD.
|
||||
// If AB crosses CD at a point that is interior to both edges, Cross is returned.
|
||||
// If any two vertices from different edges are the same it returns MaybeCross.
|
||||
// Otherwise it returns DoNotCross.
|
||||
// If either edge is degenerate (A == B or C == D), the return value is MaybeCross
|
||||
// if two vertices from different edges are the same and DoNotCross otherwise.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Properties of CrossingSign:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (1) CrossingSign(b,a,c,d) == CrossingSign(a,b,c,d)
|
||||
// (2) CrossingSign(c,d,a,b) == CrossingSign(a,b,c,d)
|
||||
// (3) CrossingSign(a,b,c,d) == MaybeCross if a==c, a==d, b==c, b==d
|
||||
// (3) CrossingSign(a,b,c,d) == DoNotCross or MaybeCross if a==b or c==d
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This method implements an exact, consistent perturbation model such
|
||||
// that no three points are ever considered to be collinear. This means
|
||||
// that even if you have 4 points A, B, C, D that lie exactly in a line
|
||||
// (say, around the equator), C and D will be treated as being slightly to
|
||||
// one side or the other of AB. This is done in a way such that the
|
||||
// results are always consistent (see RobustSign).
|
||||
func CrossingSign(a, b, c, d Point) Crossing {
|
||||
crosser := NewChainEdgeCrosser(a, b, c)
|
||||
return crosser.ChainCrossingSign(d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VertexCrossing reports whether two edges "cross" in such a way that point-in-polygon
|
||||
// containment tests can be implemented by counting the number of edge crossings.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Given two edges AB and CD where at least two vertices are identical
|
||||
// (i.e. CrossingSign(a,b,c,d) == 0), the basic rule is that a "crossing"
|
||||
// occurs if AB is encountered after CD during a CCW sweep around the shared
|
||||
// vertex starting from a fixed reference point.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that according to this rule, if AB crosses CD then in general CD
|
||||
// does not cross AB. However, this leads to the correct result when
|
||||
// counting polygon edge crossings. For example, suppose that A,B,C are
|
||||
// three consecutive vertices of a CCW polygon. If we now consider the edge
|
||||
// crossings of a segment BP as P sweeps around B, the crossing number
|
||||
// changes parity exactly when BP crosses BA or BC.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Useful properties of VertexCrossing (VC):
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (1) VC(a,a,c,d) == VC(a,b,c,c) == false
|
||||
// (2) VC(a,b,a,b) == VC(a,b,b,a) == true
|
||||
// (3) VC(a,b,c,d) == VC(a,b,d,c) == VC(b,a,c,d) == VC(b,a,d,c)
|
||||
// (3) If exactly one of a,b equals one of c,d, then exactly one of
|
||||
// VC(a,b,c,d) and VC(c,d,a,b) is true
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It is an error to call this method with 4 distinct vertices.
|
||||
func VertexCrossing(a, b, c, d Point) bool {
|
||||
// If A == B or C == D there is no intersection. We need to check this
|
||||
// case first in case 3 or more input points are identical.
|
||||
if a == b || c == d {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If any other pair of vertices is equal, there is a crossing if and only
|
||||
// if OrderedCCW indicates that the edge AB is further CCW around the
|
||||
// shared vertex O (either A or B) than the edge CD, starting from an
|
||||
// arbitrary fixed reference point.
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case a == d:
|
||||
return OrderedCCW(Point{a.Ortho()}, c, b, a)
|
||||
case b == c:
|
||||
return OrderedCCW(Point{b.Ortho()}, d, a, b)
|
||||
case a == c:
|
||||
return OrderedCCW(Point{a.Ortho()}, d, b, a)
|
||||
case b == d:
|
||||
return OrderedCCW(Point{b.Ortho()}, c, a, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgeOrVertexCrossing is a convenience function that calls CrossingSign to
|
||||
// handle cases where all four vertices are distinct, and VertexCrossing to
|
||||
// handle cases where two or more vertices are the same. This defines a crossing
|
||||
// function such that point-in-polygon containment tests can be implemented
|
||||
// by simply counting edge crossings.
|
||||
func EdgeOrVertexCrossing(a, b, c, d Point) bool {
|
||||
switch CrossingSign(a, b, c, d) {
|
||||
case DoNotCross:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
case Cross:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return VertexCrossing(a, b, c, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intersection returns the intersection point of two edges AB and CD that cross
|
||||
// (CrossingSign(a,b,c,d) == Crossing).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Useful properties of Intersection:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (1) Intersection(b,a,c,d) == Intersection(a,b,d,c) == Intersection(a,b,c,d)
|
||||
// (2) Intersection(c,d,a,b) == Intersection(a,b,c,d)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The returned intersection point X is guaranteed to be very close to the
|
||||
// true intersection point of AB and CD, even if the edges intersect at a
|
||||
// very small angle.
|
||||
func Intersection(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point) Point {
|
||||
// It is difficult to compute the intersection point of two edges accurately
|
||||
// when the angle between the edges is very small. Previously we handled
|
||||
// this by only guaranteeing that the returned intersection point is within
|
||||
// intersectionError of each edge. However, this means that when the edges
|
||||
// cross at a very small angle, the computed result may be very far from the
|
||||
// true intersection point.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Instead this function now guarantees that the result is always within
|
||||
// intersectionError of the true intersection. This requires using more
|
||||
// sophisticated techniques and in some cases extended precision.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - intersectionStable computes the intersection point using
|
||||
// projection and interpolation, taking care to minimize cancellation
|
||||
// error.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - intersectionExact computes the intersection point using precision
|
||||
// arithmetic and converts the final result back to an Point.
|
||||
pt, ok := intersectionStable(a0, a1, b0, b1)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
pt = intersectionExact(a0, a1, b0, b1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make sure the intersection point is on the correct side of the sphere.
|
||||
// Since all vertices are unit length, and edges are less than 180 degrees,
|
||||
// (a0 + a1) and (b0 + b1) both have positive dot product with the
|
||||
// intersection point. We use the sum of all vertices to make sure that the
|
||||
// result is unchanged when the edges are swapped or reversed.
|
||||
if pt.Dot((a0.Add(a1.Vector)).Add(b0.Add(b1.Vector))) < 0 {
|
||||
pt = Point{pt.Mul(-1)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return pt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes the cross product of two vectors, normalized to be unit length.
|
||||
// Also returns the length of the cross
|
||||
// product before normalization, which is useful for estimating the amount of
|
||||
// error in the result. For numerical stability, the vectors should both be
|
||||
// approximately unit length.
|
||||
func robustNormalWithLength(x, y r3.Vector) (r3.Vector, float64) {
|
||||
var pt r3.Vector
|
||||
// This computes 2 * (x.Cross(y)), but has much better numerical
|
||||
// stability when x and y are unit length.
|
||||
tmp := x.Sub(y).Cross(x.Add(y))
|
||||
length := tmp.Norm()
|
||||
if length != 0 {
|
||||
pt = tmp.Mul(1 / length)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pt, 0.5 * length // Since tmp == 2 * (x.Cross(y))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
// intersectionSimple is not used by the C++ so it is skipped here.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// projection returns the projection of aNorm onto X (x.Dot(aNorm)), and a bound
|
||||
// on the error in the result. aNorm is not necessarily unit length.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The remaining parameters (the length of aNorm (aNormLen) and the edge endpoints
|
||||
// a0 and a1) allow this dot product to be computed more accurately and efficiently.
|
||||
func projection(x, aNorm r3.Vector, aNormLen float64, a0, a1 Point) (proj, bound float64) {
|
||||
// The error in the dot product is proportional to the lengths of the input
|
||||
// vectors, so rather than using x itself (a unit-length vector) we use
|
||||
// the vectors from x to the closer of the two edge endpoints. This
|
||||
// typically reduces the error by a huge factor.
|
||||
x0 := x.Sub(a0.Vector)
|
||||
x1 := x.Sub(a1.Vector)
|
||||
x0Dist2 := x0.Norm2()
|
||||
x1Dist2 := x1.Norm2()
|
||||
|
||||
// If both distances are the same, we need to be careful to choose one
|
||||
// endpoint deterministically so that the result does not change if the
|
||||
// order of the endpoints is reversed.
|
||||
var dist float64
|
||||
if x0Dist2 < x1Dist2 || (x0Dist2 == x1Dist2 && x0.Cmp(x1) == -1) {
|
||||
dist = math.Sqrt(x0Dist2)
|
||||
proj = x0.Dot(aNorm)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dist = math.Sqrt(x1Dist2)
|
||||
proj = x1.Dot(aNorm)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This calculation bounds the error from all sources: the computation of
|
||||
// the normal, the subtraction of one endpoint, and the dot product itself.
|
||||
// dblEpsilon appears because the input points are assumed to be
|
||||
// normalized in double precision.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For reference, the bounds that went into this calculation are:
|
||||
// ||N'-N|| <= ((1 + 2 * sqrt(3))||N|| + 32 * sqrt(3) * dblEpsilon) * epsilon
|
||||
// |(A.B)'-(A.B)| <= (1.5 * (A.B) + 1.5 * ||A|| * ||B||) * epsilon
|
||||
// ||(X-Y)'-(X-Y)|| <= ||X-Y|| * epsilon
|
||||
bound = (((3.5+2*math.Sqrt(3))*aNormLen+32*math.Sqrt(3)*dblEpsilon)*dist + 1.5*math.Abs(proj)) * epsilon
|
||||
return proj, bound
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// compareEdges reports whether (a0,a1) is less than (b0,b1) with respect to a total
|
||||
// ordering on edges that is invariant under edge reversals.
|
||||
func compareEdges(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point) bool {
|
||||
if a0.Cmp(a1.Vector) != -1 {
|
||||
a0, a1 = a1, a0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b0.Cmp(b1.Vector) != -1 {
|
||||
b0, b1 = b1, b0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return a0.Cmp(b0.Vector) == -1 || (a0 == b0 && b0.Cmp(b1.Vector) == -1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectionStable returns the intersection point of the edges (a0,a1) and
|
||||
// (b0,b1) if it can be computed to within an error of at most intersectionError
|
||||
// by this function.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The intersection point is not guaranteed to have the correct sign because we
|
||||
// choose to use the longest of the two edges first. The sign is corrected by
|
||||
// Intersection.
|
||||
func intersectionStable(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point) (Point, bool) {
|
||||
// Sort the two edges so that (a0,a1) is longer, breaking ties in a
|
||||
// deterministic way that does not depend on the ordering of the endpoints.
|
||||
// This is desirable for two reasons:
|
||||
// - So that the result doesn't change when edges are swapped or reversed.
|
||||
// - It reduces error, since the first edge is used to compute the edge
|
||||
// normal (where a longer edge means less error), and the second edge
|
||||
// is used for interpolation (where a shorter edge means less error).
|
||||
aLen2 := a1.Sub(a0.Vector).Norm2()
|
||||
bLen2 := b1.Sub(b0.Vector).Norm2()
|
||||
if aLen2 < bLen2 || (aLen2 == bLen2 && compareEdges(a0, a1, b0, b1)) {
|
||||
return intersectionStableSorted(b0, b1, a0, a1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return intersectionStableSorted(a0, a1, b0, b1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectionStableSorted is a helper function for intersectionStable.
|
||||
// It expects that the edges (a0,a1) and (b0,b1) have been sorted so that
|
||||
// the first edge passed in is longer.
|
||||
func intersectionStableSorted(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point) (Point, bool) {
|
||||
var pt Point
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the normal of the plane through (a0, a1) in a stable way.
|
||||
aNorm := a0.Sub(a1.Vector).Cross(a0.Add(a1.Vector))
|
||||
aNormLen := aNorm.Norm()
|
||||
bLen := b1.Sub(b0.Vector).Norm()
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the projection (i.e., signed distance) of b0 and b1 onto the
|
||||
// plane through (a0, a1). Distances are scaled by the length of aNorm.
|
||||
b0Dist, b0Error := projection(b0.Vector, aNorm, aNormLen, a0, a1)
|
||||
b1Dist, b1Error := projection(b1.Vector, aNorm, aNormLen, a0, a1)
|
||||
|
||||
// The total distance from b0 to b1 measured perpendicularly to (a0,a1) is
|
||||
// |b0Dist - b1Dist|. Note that b0Dist and b1Dist generally have
|
||||
// opposite signs because b0 and b1 are on opposite sides of (a0, a1). The
|
||||
// code below finds the intersection point by interpolating along the edge
|
||||
// (b0, b1) to a fractional distance of b0Dist / (b0Dist - b1Dist).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It can be shown that the maximum error in the interpolation fraction is
|
||||
//
|
||||
// (b0Dist * b1Error - b1Dist * b0Error) / (distSum * (distSum - errorSum))
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We save ourselves some work by scaling the result and the error bound by
|
||||
// "distSum", since the result is normalized to be unit length anyway.
|
||||
distSum := math.Abs(b0Dist - b1Dist)
|
||||
errorSum := b0Error + b1Error
|
||||
if distSum <= errorSum {
|
||||
return pt, false // Error is unbounded in this case.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
x := b1.Mul(b0Dist).Sub(b0.Mul(b1Dist))
|
||||
err := bLen*math.Abs(b0Dist*b1Error-b1Dist*b0Error)/
|
||||
(distSum-errorSum) + 2*distSum*epsilon
|
||||
|
||||
// Finally we normalize the result, compute the corresponding error, and
|
||||
// check whether the total error is acceptable.
|
||||
xLen := x.Norm()
|
||||
maxError := intersectionError
|
||||
if err > (float64(maxError)-epsilon)*xLen {
|
||||
return pt, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return Point{x.Mul(1 / xLen)}, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// intersectionExact returns the intersection point of (a0, a1) and (b0, b1)
|
||||
// using precise arithmetic. Note that the result is not exact because it is
|
||||
// rounded down to double precision at the end. Also, the intersection point
|
||||
// is not guaranteed to have the correct sign (i.e., the return value may need
|
||||
// to be negated).
|
||||
func intersectionExact(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point) Point {
|
||||
// Since we are using presice arithmetic, we don't need to worry about
|
||||
// numerical stability.
|
||||
a0P := r3.PreciseVectorFromVector(a0.Vector)
|
||||
a1P := r3.PreciseVectorFromVector(a1.Vector)
|
||||
b0P := r3.PreciseVectorFromVector(b0.Vector)
|
||||
b1P := r3.PreciseVectorFromVector(b1.Vector)
|
||||
aNormP := a0P.Cross(a1P)
|
||||
bNormP := b0P.Cross(b1P)
|
||||
xP := aNormP.Cross(bNormP)
|
||||
|
||||
// The final Normalize() call is done in double precision, which creates a
|
||||
// directional error of up to 2*dblEpsilon. (Precise conversion and Normalize()
|
||||
// each contribute up to dblEpsilon of directional error.)
|
||||
x := xP.Vector()
|
||||
|
||||
if x == (r3.Vector{}) {
|
||||
// The two edges are exactly collinear, but we still consider them to be
|
||||
// "crossing" because of simulation of simplicity. Out of the four
|
||||
// endpoints, exactly two lie in the interior of the other edge. Of
|
||||
// those two we return the one that is lexicographically smallest.
|
||||
x = r3.Vector{10, 10, 10} // Greater than any valid S2Point
|
||||
|
||||
aNorm := Point{aNormP.Vector()}
|
||||
bNorm := Point{bNormP.Vector()}
|
||||
if OrderedCCW(b0, a0, b1, bNorm) && a0.Cmp(x) == -1 {
|
||||
return a0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if OrderedCCW(b0, a1, b1, bNorm) && a1.Cmp(x) == -1 {
|
||||
return a1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if OrderedCCW(a0, b0, a1, aNorm) && b0.Cmp(x) == -1 {
|
||||
return b0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if OrderedCCW(a0, b1, a1, aNorm) && b1.Cmp(x) == -1 {
|
||||
return b1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return Point{x}
|
||||
}
|
||||
378
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_distances.go
generated
vendored
378
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/edge_distances.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,378 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
// This file defines a collection of methods for computing the distance to an edge,
|
||||
// interpolating along an edge, projecting points onto edges, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/golang/geo/s1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DistanceFromSegment returns the distance of point X from line segment AB.
|
||||
// The points are expected to be normalized. The result is very accurate for small
|
||||
// distances but may have some numerical error if the distance is large
|
||||
// (approximately pi/2 or greater). The case A == B is handled correctly.
|
||||
func DistanceFromSegment(x, a, b Point) s1.Angle {
|
||||
var minDist s1.ChordAngle
|
||||
minDist, _ = updateMinDistance(x, a, b, minDist, true)
|
||||
return minDist.Angle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsDistanceLess reports whether the distance from X to the edge AB is less
|
||||
// than limit. This method is faster than DistanceFromSegment(). If you want to
|
||||
// compare against a fixed s1.Angle, you should convert it to an s1.ChordAngle
|
||||
// once and save the value, since this conversion is relatively expensive.
|
||||
func IsDistanceLess(x, a, b Point, limit s1.ChordAngle) bool {
|
||||
_, less := UpdateMinDistance(x, a, b, limit)
|
||||
return less
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UpdateMinDistance checks if the distance from X to the edge AB is less
|
||||
// than minDist, and if so, returns the updated value and true.
|
||||
// The case A == B is handled correctly.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use this method when you want to compute many distances and keep track of
|
||||
// the minimum. It is significantly faster than using DistanceFromSegment
|
||||
// because (1) using s1.ChordAngle is much faster than s1.Angle, and (2) it
|
||||
// can save a lot of work by not actually computing the distance when it is
|
||||
// obviously larger than the current minimum.
|
||||
func UpdateMinDistance(x, a, b Point, minDist s1.ChordAngle) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
return updateMinDistance(x, a, b, minDist, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UpdateMaxDistance checks if the distance from X to the edge AB is greater
|
||||
// than maxDist, and if so, returns the updated value and true.
|
||||
// Otherwise it returns false. The case A == B is handled correctly.
|
||||
func UpdateMaxDistance(x, a, b Point, maxDist s1.ChordAngle) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
dist := maxChordAngle(ChordAngleBetweenPoints(x, a), ChordAngleBetweenPoints(x, b))
|
||||
if dist > s1.RightChordAngle {
|
||||
dist, _ = updateMinDistance(Point{x.Mul(-1)}, a, b, dist, true)
|
||||
dist = s1.StraightChordAngle - dist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if maxDist < dist {
|
||||
return dist, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return maxDist, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsInteriorDistanceLess reports whether the minimum distance from X to the
|
||||
// edge AB is attained at an interior point of AB (i.e., not an endpoint), and
|
||||
// that distance is less than limit.
|
||||
func IsInteriorDistanceLess(x, a, b Point, limit s1.ChordAngle) bool {
|
||||
_, less := UpdateMinInteriorDistance(x, a, b, limit)
|
||||
return less
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UpdateMinInteriorDistance reports whether the minimum distance from X to AB
|
||||
// is attained at an interior point of AB (i.e., not an endpoint), and that distance
|
||||
// is less than minDist. If so, the value of minDist is updated and true is returned.
|
||||
// Otherwise it is unchanged and returns false.
|
||||
func UpdateMinInteriorDistance(x, a, b Point, minDist s1.ChordAngle) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
return interiorDist(x, a, b, minDist, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Project returns the point along the edge AB that is closest to the point X.
|
||||
// The fractional distance of this point along the edge AB can be obtained
|
||||
// using DistanceFraction.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This requires that all points are unit length.
|
||||
func Project(x, a, b Point) Point {
|
||||
aXb := a.PointCross(b)
|
||||
// Find the closest point to X along the great circle through AB.
|
||||
p := x.Sub(aXb.Mul(x.Dot(aXb.Vector) / aXb.Vector.Norm2()))
|
||||
|
||||
// If this point is on the edge AB, then it's the closest point.
|
||||
if Sign(aXb, a, Point{p}) && Sign(Point{p}, b, aXb) {
|
||||
return Point{p.Normalize()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the closest point is either A or B.
|
||||
if x.Sub(a.Vector).Norm2() <= x.Sub(b.Vector).Norm2() {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DistanceFraction returns the distance ratio of the point X along an edge AB.
|
||||
// If X is on the line segment AB, this is the fraction T such
|
||||
// that X == Interpolate(T, A, B).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This requires that A and B are distinct.
|
||||
func DistanceFraction(x, a, b Point) float64 {
|
||||
d0 := x.Angle(a.Vector)
|
||||
d1 := x.Angle(b.Vector)
|
||||
return float64(d0 / (d0 + d1))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Interpolate returns the point X along the line segment AB whose distance from A
|
||||
// is the given fraction "t" of the distance AB. Does NOT require that "t" be
|
||||
// between 0 and 1. Note that all distances are measured on the surface of
|
||||
// the sphere, so this is more complicated than just computing (1-t)*a + t*b
|
||||
// and normalizing the result.
|
||||
func Interpolate(t float64, a, b Point) Point {
|
||||
if t == 0 {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t == 1 {
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
ab := a.Angle(b.Vector)
|
||||
return InterpolateAtDistance(s1.Angle(t)*ab, a, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InterpolateAtDistance returns the point X along the line segment AB whose
|
||||
// distance from A is the angle ax.
|
||||
func InterpolateAtDistance(ax s1.Angle, a, b Point) Point {
|
||||
aRad := ax.Radians()
|
||||
|
||||
// Use PointCross to compute the tangent vector at A towards B. The
|
||||
// result is always perpendicular to A, even if A=B or A=-B, but it is not
|
||||
// necessarily unit length. (We effectively normalize it below.)
|
||||
normal := a.PointCross(b)
|
||||
tangent := normal.Vector.Cross(a.Vector)
|
||||
|
||||
// Now compute the appropriate linear combination of A and "tangent". With
|
||||
// infinite precision the result would always be unit length, but we
|
||||
// normalize it anyway to ensure that the error is within acceptable bounds.
|
||||
// (Otherwise errors can build up when the result of one interpolation is
|
||||
// fed into another interpolation.)
|
||||
return Point{(a.Mul(math.Cos(aRad)).Add(tangent.Mul(math.Sin(aRad) / tangent.Norm()))).Normalize()}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// minUpdateDistanceMaxError returns the maximum error in the result of
|
||||
// UpdateMinDistance (and the associated functions such as
|
||||
// UpdateMinInteriorDistance, IsDistanceLess, etc), assuming that all
|
||||
// input points are normalized to within the bounds guaranteed by r3.Vector's
|
||||
// Normalize. The error can be added or subtracted from an s1.ChordAngle
|
||||
// using its Expanded method.
|
||||
func minUpdateDistanceMaxError(dist s1.ChordAngle) float64 {
|
||||
// There are two cases for the maximum error in UpdateMinDistance(),
|
||||
// depending on whether the closest point is interior to the edge.
|
||||
return math.Max(minUpdateInteriorDistanceMaxError(dist), dist.MaxPointError())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// minUpdateInteriorDistanceMaxError returns the maximum error in the result of
|
||||
// UpdateMinInteriorDistance, assuming that all input points are normalized
|
||||
// to within the bounds guaranteed by Point's Normalize. The error can be added
|
||||
// or subtracted from an s1.ChordAngle using its Expanded method.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that accuracy goes down as the distance approaches 0 degrees or 180
|
||||
// degrees (for different reasons). Near 0 degrees the error is acceptable
|
||||
// for all practical purposes (about 1.2e-15 radians ~= 8 nanometers). For
|
||||
// exactly antipodal points the maximum error is quite high (0.5 meters),
|
||||
// but this error drops rapidly as the points move away from antipodality
|
||||
// (approximately 1 millimeter for points that are 50 meters from antipodal,
|
||||
// and 1 micrometer for points that are 50km from antipodal).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO(roberts): Currently the error bound does not hold for edges whose endpoints
|
||||
// are antipodal to within about 1e-15 radians (less than 1 micron). This could
|
||||
// be fixed by extending PointCross to use higher precision when necessary.
|
||||
func minUpdateInteriorDistanceMaxError(dist s1.ChordAngle) float64 {
|
||||
// If a point is more than 90 degrees from an edge, then the minimum
|
||||
// distance is always to one of the endpoints, not to the edge interior.
|
||||
if dist >= s1.RightChordAngle {
|
||||
return 0.0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This bound includes all source of error, assuming that the input points
|
||||
// are normalized. a and b are components of chord length that are
|
||||
// perpendicular and parallel to a plane containing the edge respectively.
|
||||
b := math.Min(1.0, 0.5*float64(dist)*float64(dist))
|
||||
a := math.Sqrt(b * (2 - b))
|
||||
return ((2.5+2*math.Sqrt(3)+8.5*a)*a +
|
||||
(2+2*math.Sqrt(3)/3+6.5*(1-b))*b +
|
||||
(23+16/math.Sqrt(3))*dblEpsilon) * dblEpsilon
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// updateMinDistance computes the distance from a point X to a line segment AB,
|
||||
// and if either the distance was less than the given minDist, or alwaysUpdate is
|
||||
// true, the value and whether it was updated are returned.
|
||||
func updateMinDistance(x, a, b Point, minDist s1.ChordAngle, alwaysUpdate bool) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
if d, ok := interiorDist(x, a, b, minDist, alwaysUpdate); ok {
|
||||
// Minimum distance is attained along the edge interior.
|
||||
return d, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise the minimum distance is to one of the endpoints.
|
||||
xa2, xb2 := (x.Sub(a.Vector)).Norm2(), x.Sub(b.Vector).Norm2()
|
||||
dist := s1.ChordAngle(math.Min(xa2, xb2))
|
||||
if !alwaysUpdate && dist >= minDist {
|
||||
return minDist, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return dist, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// interiorDist returns the shortest distance from point x to edge ab, assuming
|
||||
// that the closest point to X is interior to AB. If the closest point is not
|
||||
// interior to AB, interiorDist returns (minDist, false). If alwaysUpdate is set to
|
||||
// false, the distance is only updated when the value exceeds certain the given minDist.
|
||||
func interiorDist(x, a, b Point, minDist s1.ChordAngle, alwaysUpdate bool) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
// Chord distance of x to both end points a and b.
|
||||
xa2, xb2 := (x.Sub(a.Vector)).Norm2(), x.Sub(b.Vector).Norm2()
|
||||
|
||||
// The closest point on AB could either be one of the two vertices (the
|
||||
// vertex case) or in the interior (the interior case). Let C = A x B.
|
||||
// If X is in the spherical wedge extending from A to B around the axis
|
||||
// through C, then we are in the interior case. Otherwise we are in the
|
||||
// vertex case.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Check whether we might be in the interior case. For this to be true, XAB
|
||||
// and XBA must both be acute angles. Checking this condition exactly is
|
||||
// expensive, so instead we consider the planar triangle ABX (which passes
|
||||
// through the sphere's interior). The planar angles XAB and XBA are always
|
||||
// less than the corresponding spherical angles, so if we are in the
|
||||
// interior case then both of these angles must be acute.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We check this by computing the squared edge lengths of the planar
|
||||
// triangle ABX, and testing acuteness using the law of cosines:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// max(XA^2, XB^2) < min(XA^2, XB^2) + AB^2
|
||||
if math.Max(xa2, xb2) >= math.Min(xa2, xb2)+(a.Sub(b.Vector)).Norm2() {
|
||||
return minDist, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The minimum distance might be to a point on the edge interior. Let R
|
||||
// be closest point to X that lies on the great circle through AB. Rather
|
||||
// than computing the geodesic distance along the surface of the sphere,
|
||||
// instead we compute the "chord length" through the sphere's interior.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The squared chord length XR^2 can be expressed as XQ^2 + QR^2, where Q
|
||||
// is the point X projected onto the plane through the great circle AB.
|
||||
// The distance XQ^2 can be written as (X.C)^2 / |C|^2 where C = A x B.
|
||||
// We ignore the QR^2 term and instead use XQ^2 as a lower bound, since it
|
||||
// is faster and the corresponding distance on the Earth's surface is
|
||||
// accurate to within 1% for distances up to about 1800km.
|
||||
c := a.PointCross(b)
|
||||
c2 := c.Norm2()
|
||||
xDotC := x.Dot(c.Vector)
|
||||
xDotC2 := xDotC * xDotC
|
||||
if !alwaysUpdate && xDotC2 >= c2*float64(minDist) {
|
||||
// The closest point on the great circle AB is too far away.
|
||||
return minDist, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise we do the exact, more expensive test for the interior case.
|
||||
// This test is very likely to succeed because of the conservative planar
|
||||
// test we did initially.
|
||||
cx := c.Cross(x.Vector)
|
||||
if a.Dot(cx) >= 0 || b.Dot(cx) <= 0 {
|
||||
return minDist, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute the squared chord length XR^2 = XQ^2 + QR^2 (see above).
|
||||
// This calculation has good accuracy for all chord lengths since it
|
||||
// is based on both the dot product and cross product (rather than
|
||||
// deriving one from the other). However, note that the chord length
|
||||
// representation itself loses accuracy as the angle approaches π.
|
||||
qr := 1 - math.Sqrt(cx.Norm2()/c2)
|
||||
dist := s1.ChordAngle((xDotC2 / c2) + (qr * qr))
|
||||
|
||||
if !alwaysUpdate && dist >= minDist {
|
||||
return minDist, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return dist, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// updateEdgePairMinDistance computes the minimum distance between the given
|
||||
// pair of edges. If the two edges cross, the distance is zero. The cases
|
||||
// a0 == a1 and b0 == b1 are handled correctly.
|
||||
func updateEdgePairMinDistance(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point, minDist s1.ChordAngle) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
if minDist == 0 {
|
||||
return 0, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if CrossingSign(a0, a1, b0, b1) == Cross {
|
||||
minDist = 0
|
||||
return 0, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the minimum distance is achieved at an endpoint of at least
|
||||
// one of the two edges. We ensure that all four possibilities are always checked.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The calculation below computes each of the six vertex-vertex distances
|
||||
// twice (this could be optimized).
|
||||
var ok1, ok2, ok3, ok4 bool
|
||||
minDist, ok1 = UpdateMinDistance(a0, b0, b1, minDist)
|
||||
minDist, ok2 = UpdateMinDistance(a1, b0, b1, minDist)
|
||||
minDist, ok3 = UpdateMinDistance(b0, a0, a1, minDist)
|
||||
minDist, ok4 = UpdateMinDistance(b1, a0, a1, minDist)
|
||||
return minDist, ok1 || ok2 || ok3 || ok4
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// updateEdgePairMaxDistance reports the minimum distance between the given pair of edges.
|
||||
// If one edge crosses the antipodal reflection of the other, the distance is pi.
|
||||
func updateEdgePairMaxDistance(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point, maxDist s1.ChordAngle) (s1.ChordAngle, bool) {
|
||||
if maxDist == s1.StraightChordAngle {
|
||||
return s1.StraightChordAngle, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if CrossingSign(a0, a1, Point{b0.Mul(-1)}, Point{b1.Mul(-1)}) == Cross {
|
||||
return s1.StraightChordAngle, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the maximum distance is achieved at an endpoint of at least
|
||||
// one of the two edges. We ensure that all four possibilities are always checked.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The calculation below computes each of the six vertex-vertex distances
|
||||
// twice (this could be optimized).
|
||||
var ok1, ok2, ok3, ok4 bool
|
||||
maxDist, ok1 = UpdateMaxDistance(a0, b0, b1, maxDist)
|
||||
maxDist, ok2 = UpdateMaxDistance(a1, b0, b1, maxDist)
|
||||
maxDist, ok3 = UpdateMaxDistance(b0, a0, a1, maxDist)
|
||||
maxDist, ok4 = UpdateMaxDistance(b1, a0, a1, maxDist)
|
||||
return maxDist, ok1 || ok2 || ok3 || ok4
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EdgePairClosestPoints returns the pair of points (a, b) that achieves the
|
||||
// minimum distance between edges a0a1 and b0b1, where a is a point on a0a1 and
|
||||
// b is a point on b0b1. If the two edges intersect, a and b are both equal to
|
||||
// the intersection point. Handles a0 == a1 and b0 == b1 correctly.
|
||||
func EdgePairClosestPoints(a0, a1, b0, b1 Point) (Point, Point) {
|
||||
if CrossingSign(a0, a1, b0, b1) == Cross {
|
||||
x := Intersection(a0, a1, b0, b1)
|
||||
return x, x
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We save some work by first determining which vertex/edge pair achieves
|
||||
// the minimum distance, and then computing the closest point on that edge.
|
||||
var minDist s1.ChordAngle
|
||||
var ok bool
|
||||
|
||||
minDist, ok = updateMinDistance(a0, b0, b1, minDist, true)
|
||||
closestVertex := 0
|
||||
if minDist, ok = UpdateMinDistance(a1, b0, b1, minDist); ok {
|
||||
closestVertex = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if minDist, ok = UpdateMinDistance(b0, a0, a1, minDist); ok {
|
||||
closestVertex = 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
if minDist, ok = UpdateMinDistance(b1, a0, a1, minDist); ok {
|
||||
closestVertex = 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch closestVertex {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return a0, Project(a0, b0, b1)
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
return a1, Project(a1, b0, b1)
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
return Project(b0, a0, a1), b0
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
return Project(b1, a0, a1), b1
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("illegal case reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
237
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/encode.go
generated
vendored
237
vendor/github.com/golang/geo/s2/encode.go
generated
vendored
|
|
@ -1,237 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Copyright 2017 Google Inc. All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
//
|
||||
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
// limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
package s2
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/binary"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// encodingVersion is the current version of the encoding
|
||||
// format that is compatible with C++ and other S2 libraries.
|
||||
encodingVersion = int8(1)
|
||||
|
||||
// encodingCompressedVersion is the current version of the
|
||||
// compressed format.
|
||||
encodingCompressedVersion = int8(4)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// encoder handles the specifics of encoding for S2 types.
|
||||
type encoder struct {
|
||||
w io.Writer // the real writer passed to Encode
|
||||
err error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeUvarint(x uint64) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var buf [binary.MaxVarintLen64]byte
|
||||
n := binary.PutUvarint(buf[:], x)
|
||||
_, e.err = e.w.Write(buf[:n])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeBool(x bool) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var val int8
|
||||
if x {
|
||||
val = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeInt8(x int8) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeInt16(x int16) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeInt32(x int32) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeInt64(x int64) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeUint8(x uint8) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, e.err = e.w.Write([]byte{x})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeUint32(x uint32) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeUint64(x uint64) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeFloat32(x float32) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *encoder) writeFloat64(x float64) {
|
||||
if e.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.err = binary.Write(e.w, binary.LittleEndian, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type byteReader interface {
|
||||
io.Reader
|
||||
io.ByteReader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// byteReaderAdapter embellishes an io.Reader with a ReadByte method,
|
||||
// so that it implements the io.ByteReader interface.
|
||||
type byteReaderAdapter struct {
|
||||
io.Reader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b byteReaderAdapter) ReadByte() (byte, error) {
|
||||
buf := []byte{0}
|
||||
_, err := io.ReadFull(b, buf)
|
||||
return buf[0], err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func asByteReader(r io.Reader) byteReader {
|
||||
if br, ok := r.(byteReader); ok {
|
||||
return br
|
||||
}
|
||||
return byteReaderAdapter{r}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type decoder struct {
|
||||
r byteReader // the real reader passed to Decode
|
||||
err error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readBool() (x bool) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var val int8
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &val)
|
||||
return val == 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readInt8() (x int8) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readInt16() (x int16) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readInt32() (x int32) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readInt64() (x int64) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readUint8() (x uint8) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
x, d.err = d.r.ReadByte()
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readUint32() (x uint32) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readUint64() (x uint64) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readFloat32() (x float32) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readFloat64() (x float64) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
d.err = binary.Read(d.r, binary.LittleEndian, &x)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *decoder) readUvarint() (x uint64) {
|
||||
if d.err != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
x, d.err = binary.ReadUvarint(d.r)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show more
Loading…
Reference in a new issue